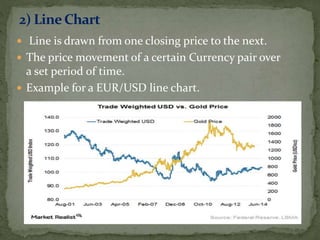
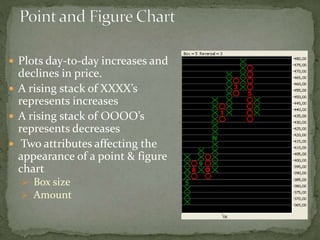
The document discusses two primary types of stock analysis: fundamental and technical. Fundamental analysis focuses on various financial metrics and economic factors affecting a company's stock value, while technical analysis examines historical price movements and patterns to predict future price trends. It also highlights challenges and limitations in both methods, such as the dependency on market behavior and the potential for false signals in technical analysis.