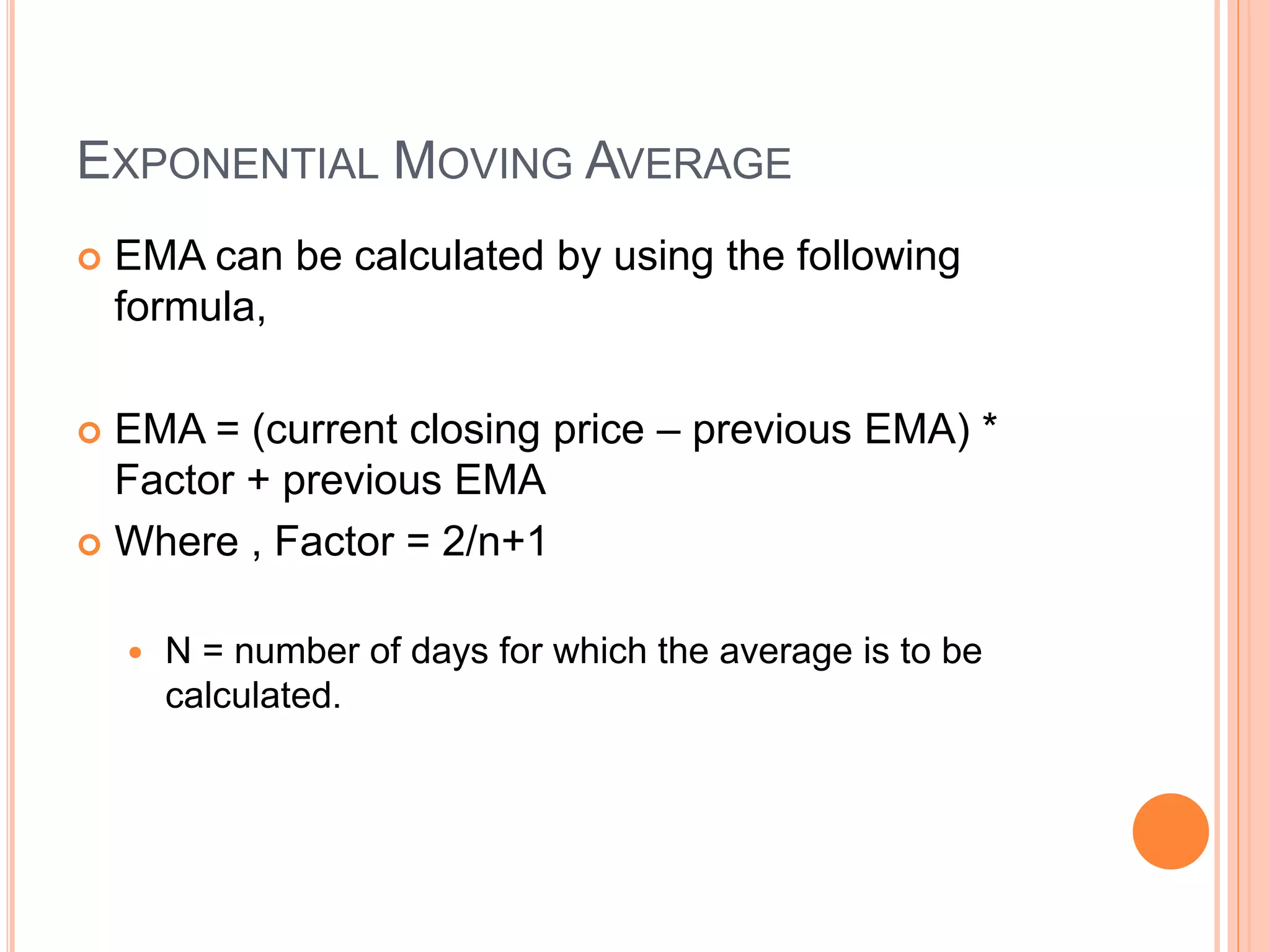
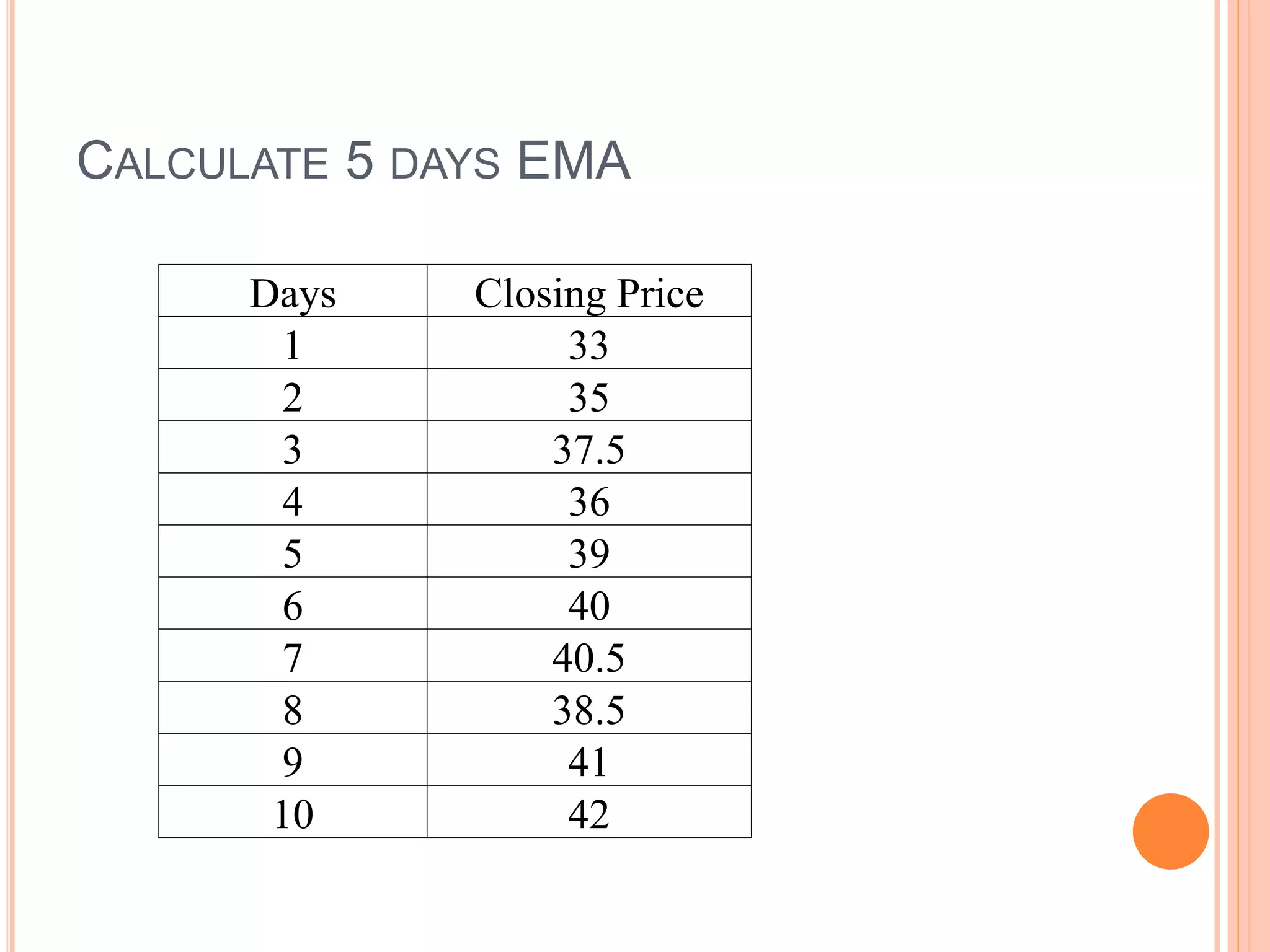
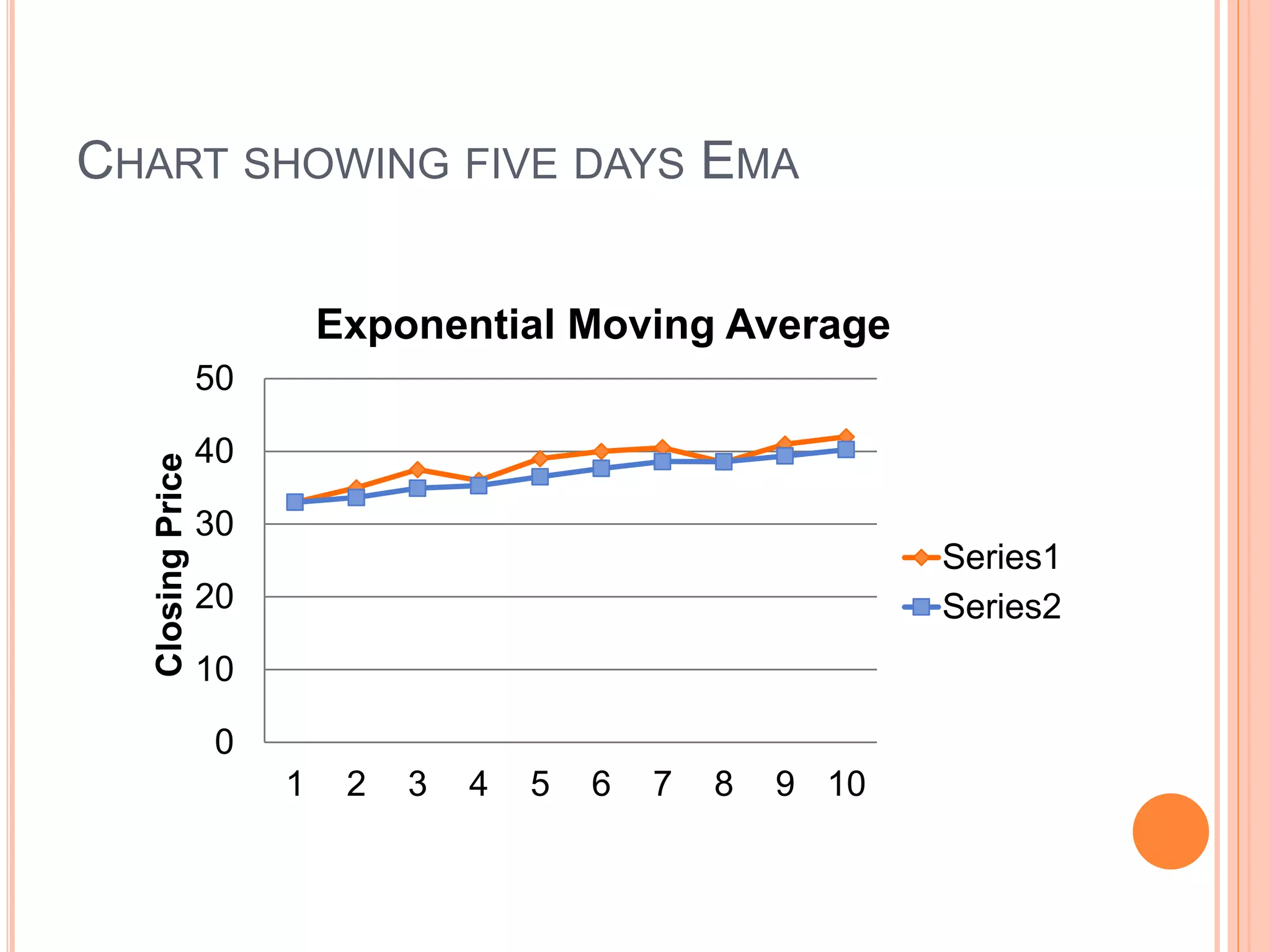
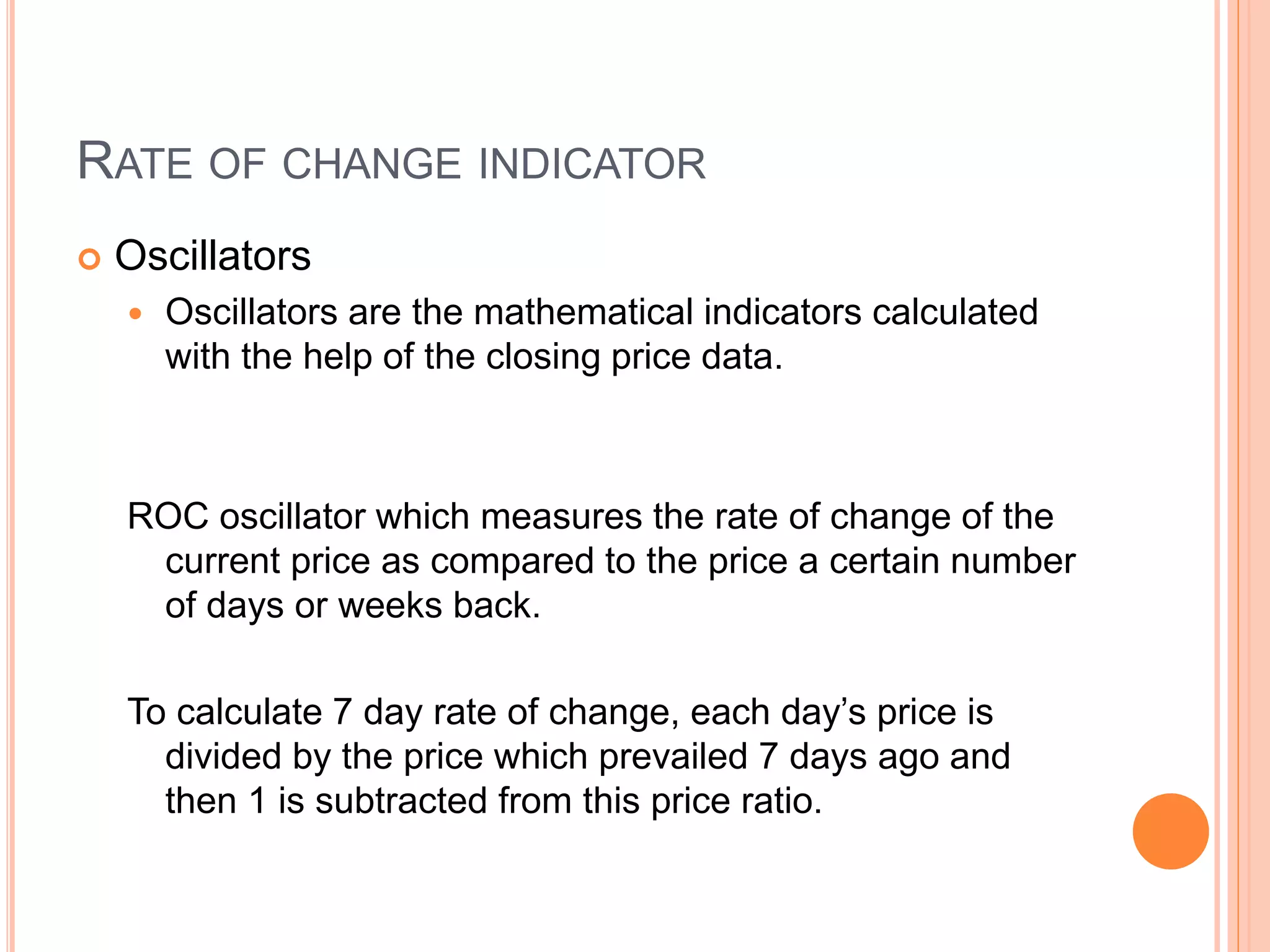
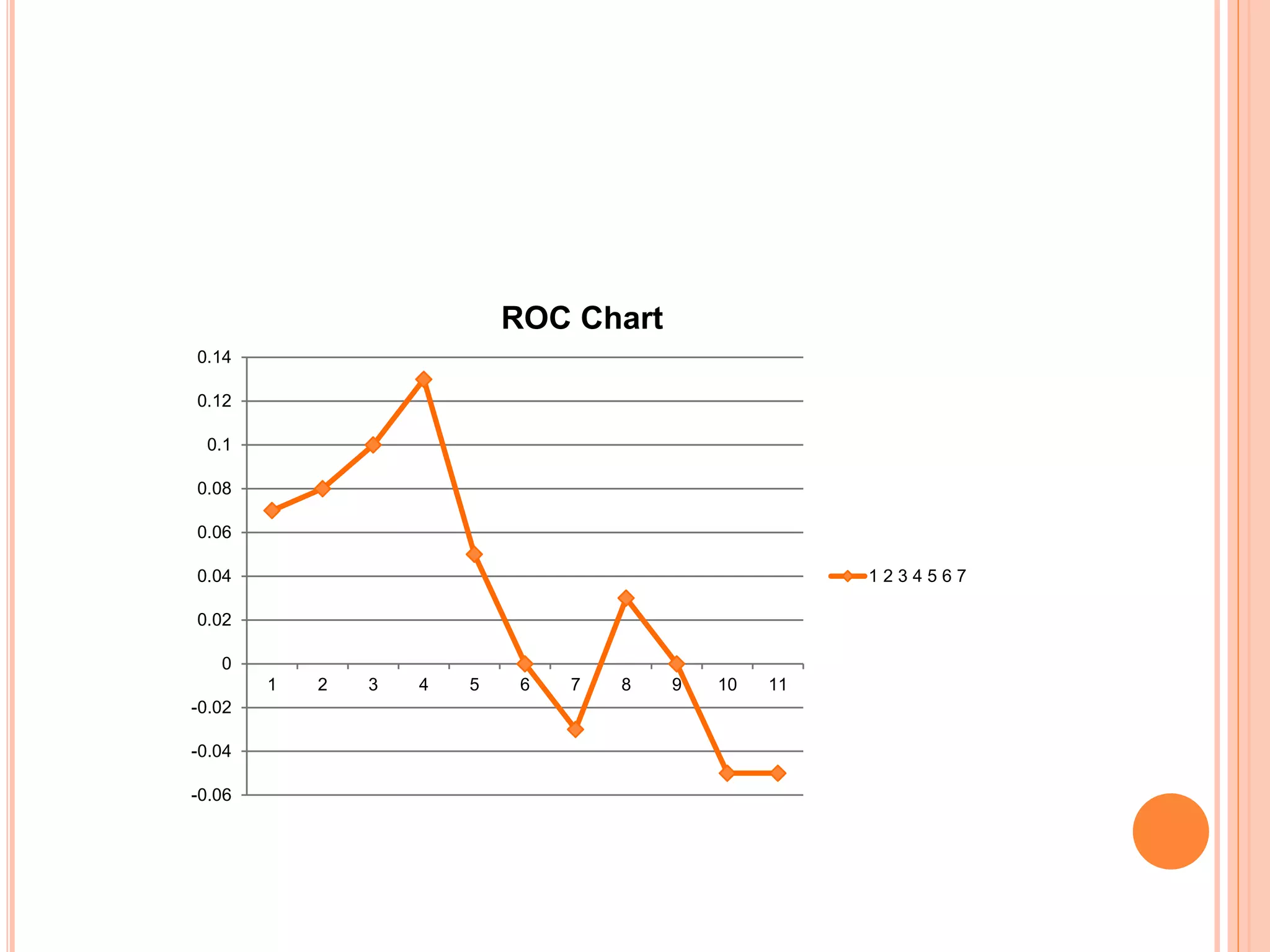
The document discusses various mathematical indicators used in technical analysis for stocks including moving averages, exponential moving averages, rate of change indicator, and relative strength index. It provides formulas to calculate exponential moving averages and the relative strength index. Sample calculations and charts are shown to illustrate how to calculate a 5-day exponential moving average and 7-day rate of change indicator. Moving averages are used to represent short, medium, and long term trends in stock prices.






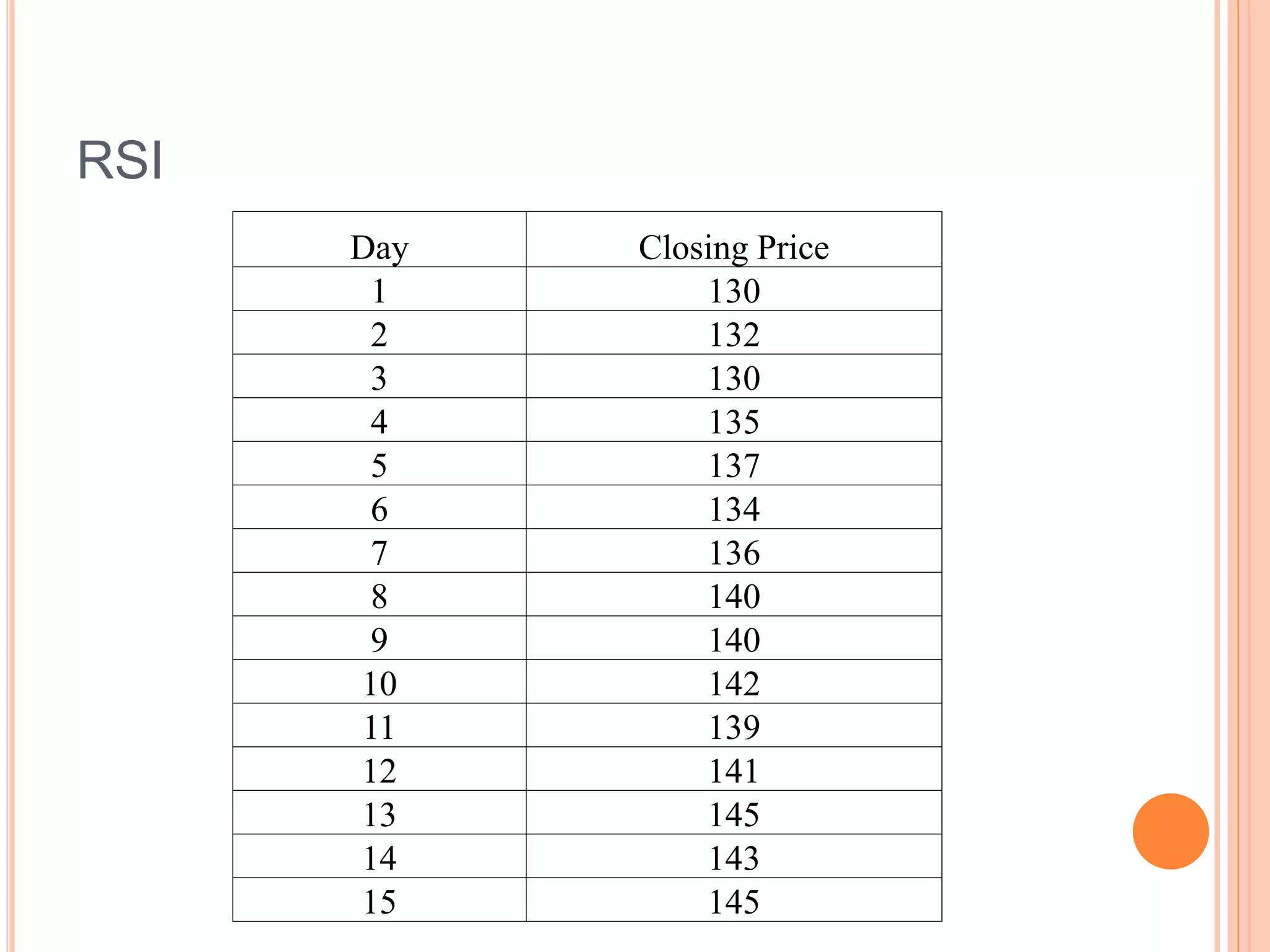
![RELATIVE STRENGTH INDEX
A powerful indicator that signal buying and selling
opportunities ahead of the market.
RSI for a share is calculated by using the following
formula
RSI = 100- [100/(1+RS)]
Where,
RS = Average Gain per day/ Average loss per day](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wgu8ew3wqnwymzgjdswk-signature-a45d406a0728c13fd02db1cd16855327a029e68ed9f27e646d890187533de483-poli-150420025834-conversion-gate02/75/Mathematical-indicators-13-2048.jpg)