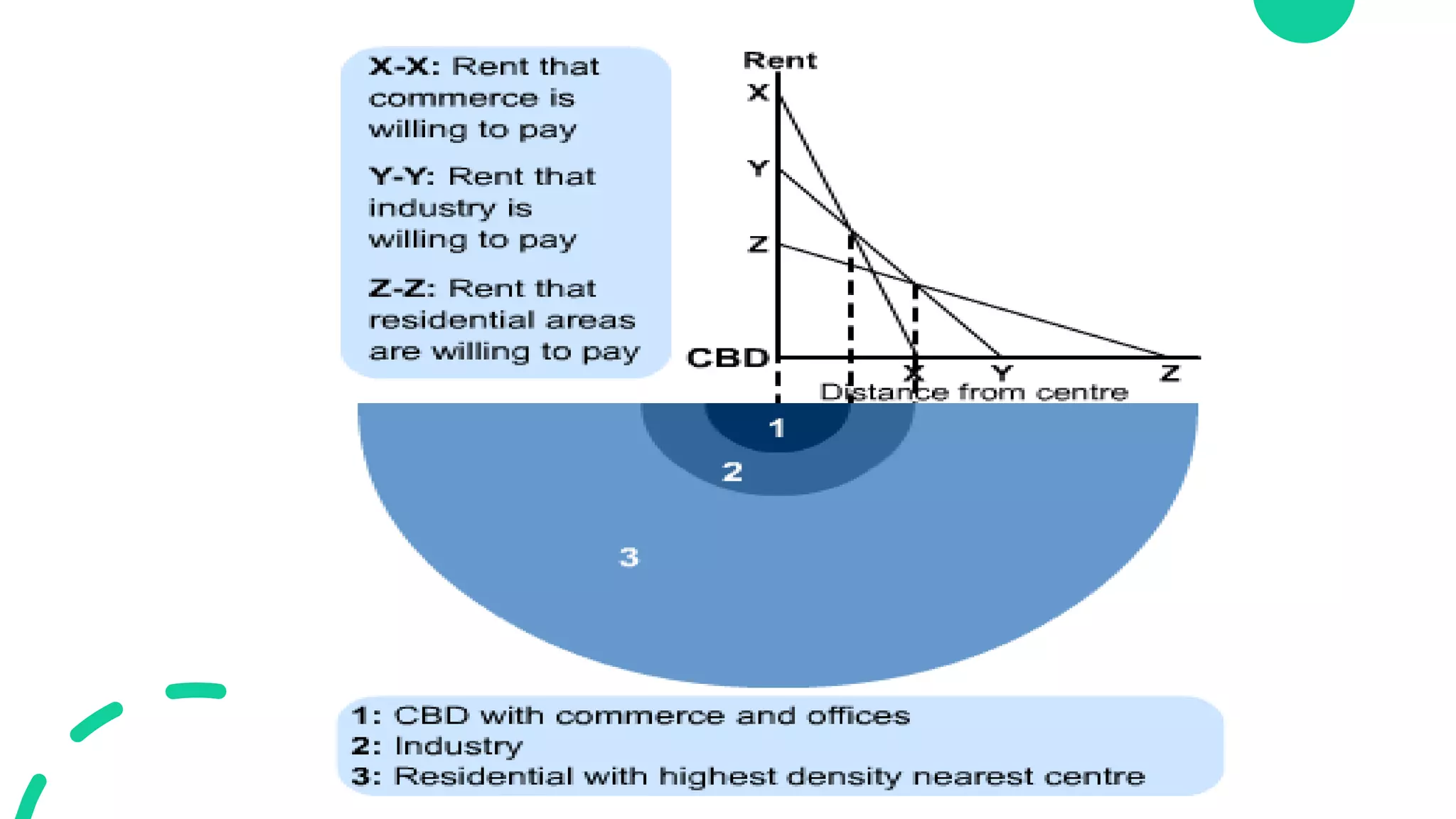
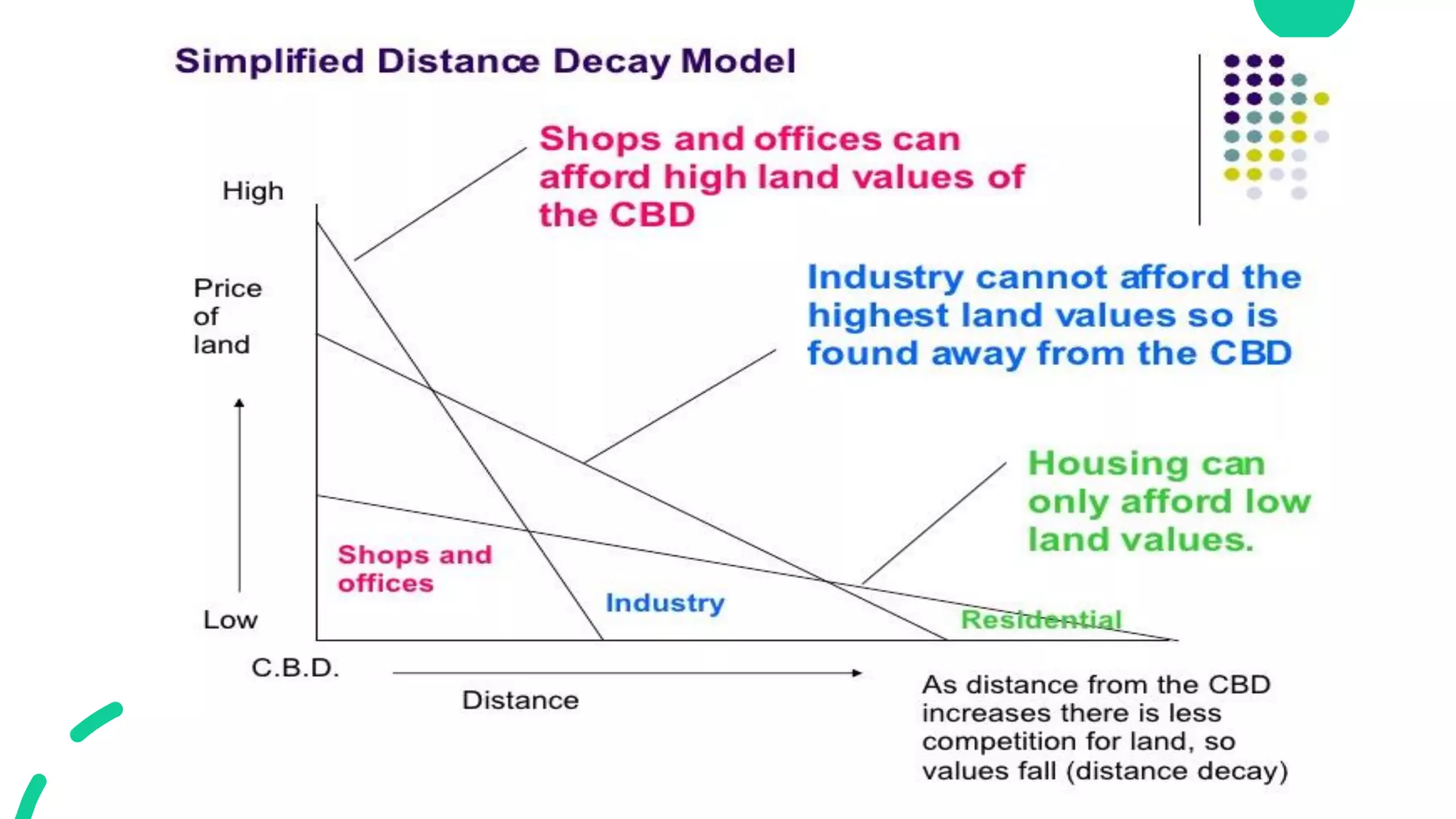
The bid rent theory proposes that the price of land decreases as distance from the central business district (CBD) increases. This is because retail establishments are willing to pay more to locate closer to the CBD to maximize profits from higher customer concentration. The commercial sector bids highest for CBD land, while the industrial sector requires more space and bids less. Residential bidding is also lower farther from the CBD as residents are less willing to pay high land costs far from the center. However, the theory does not account for all urban planning and transportation factors.