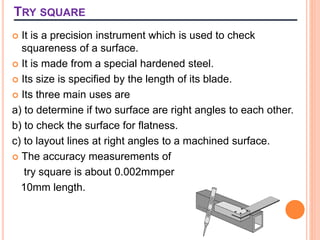
The document outlines various marking tools and techniques used in a workshop, detailing the purpose of marking, types of marking media, and methods for effective marking. It describes specific marking tools such as surface gauges, scribers, dividers, punches, v-blocks, angle plates, and try squares, highlighting their materials, characteristics, and uses in precision work. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of preparing surfaces and cleaning tools after marking tasks.