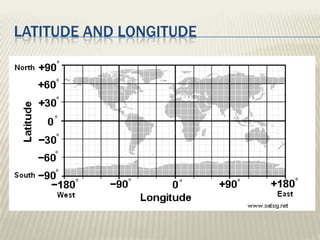
Austen Layard dug up statues in Iraq from the Assyrian civilization that were 3,000 years old, showing how geography studies people and their environments. There are five themes of geography: location, place, movement, region, and human-environment interaction. Location describes where a place is, using latitude and longitude. Place examines physical features like landforms and human characteristics like economic activities. People have interacted with their environment throughout history by using resources. Movement of people has occurred as they followed animals, migrated to cities, and traded between places as settlers. Regions can be defined by location or shared political, economic, or cultural characteristics.