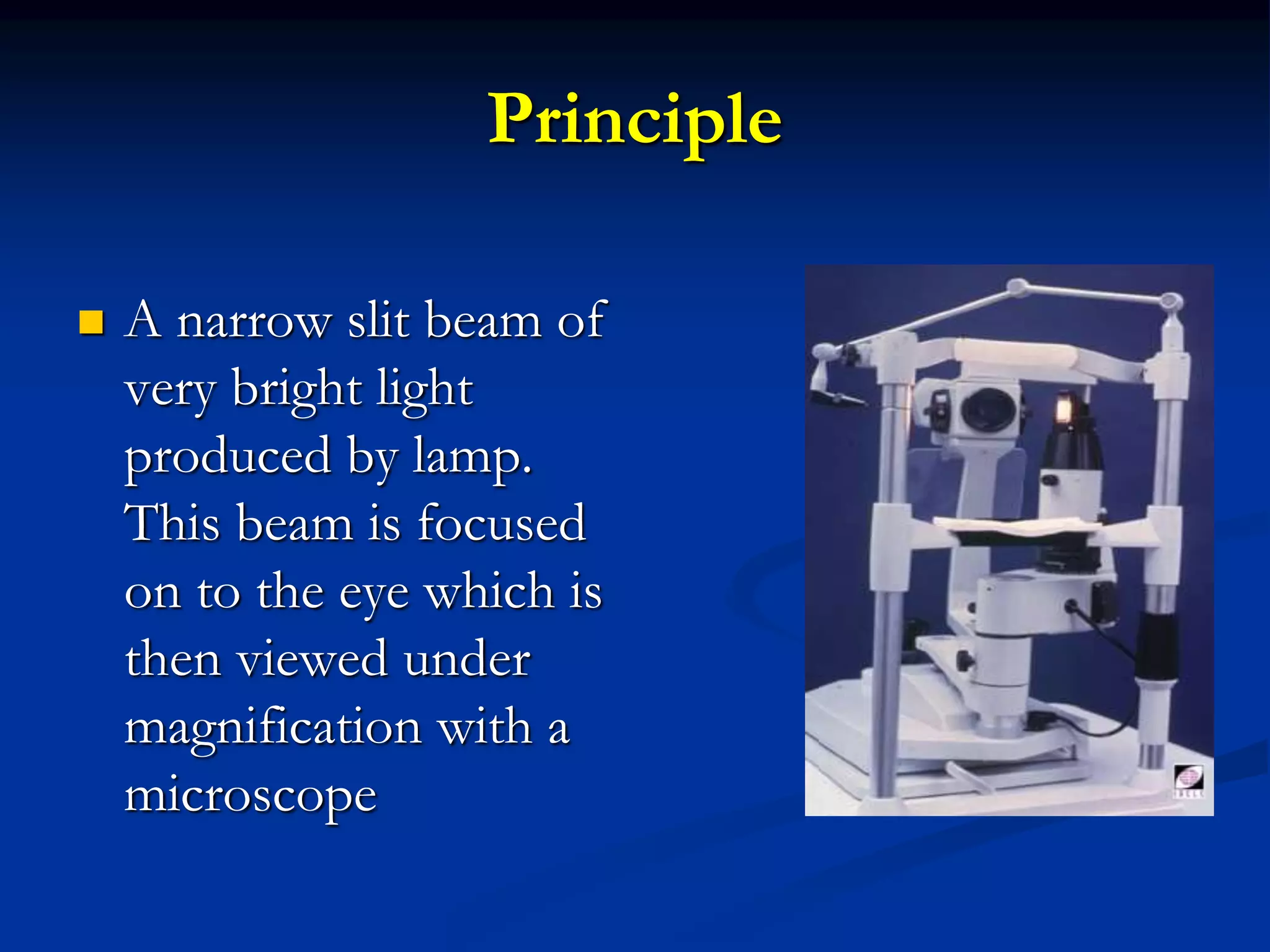
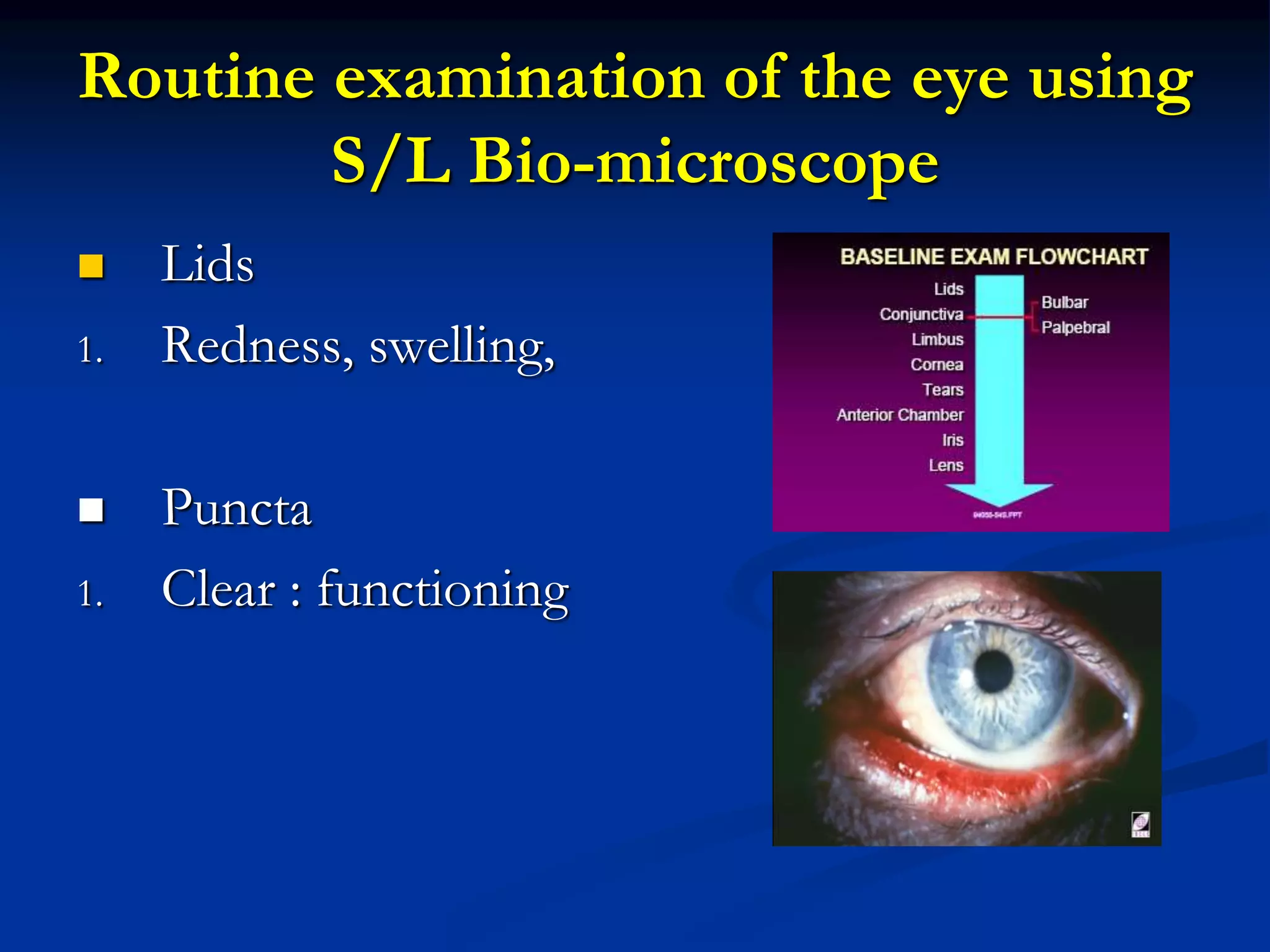
The document describes the slit lamp examination used in optometry. It discusses the history, principles, parts, magnification ranges, and illumination techniques of the slit lamp. The slit lamp uses a bright light source to illuminate the eye structures and allow examination at different magnifications. Various illumination techniques like diffuse, direct, and retro illumination can be used to examine different parts of the eye. The slit lamp allows for a detailed examination of the lids, conjunctiva, cornea, anterior chamber, iris, and lens.