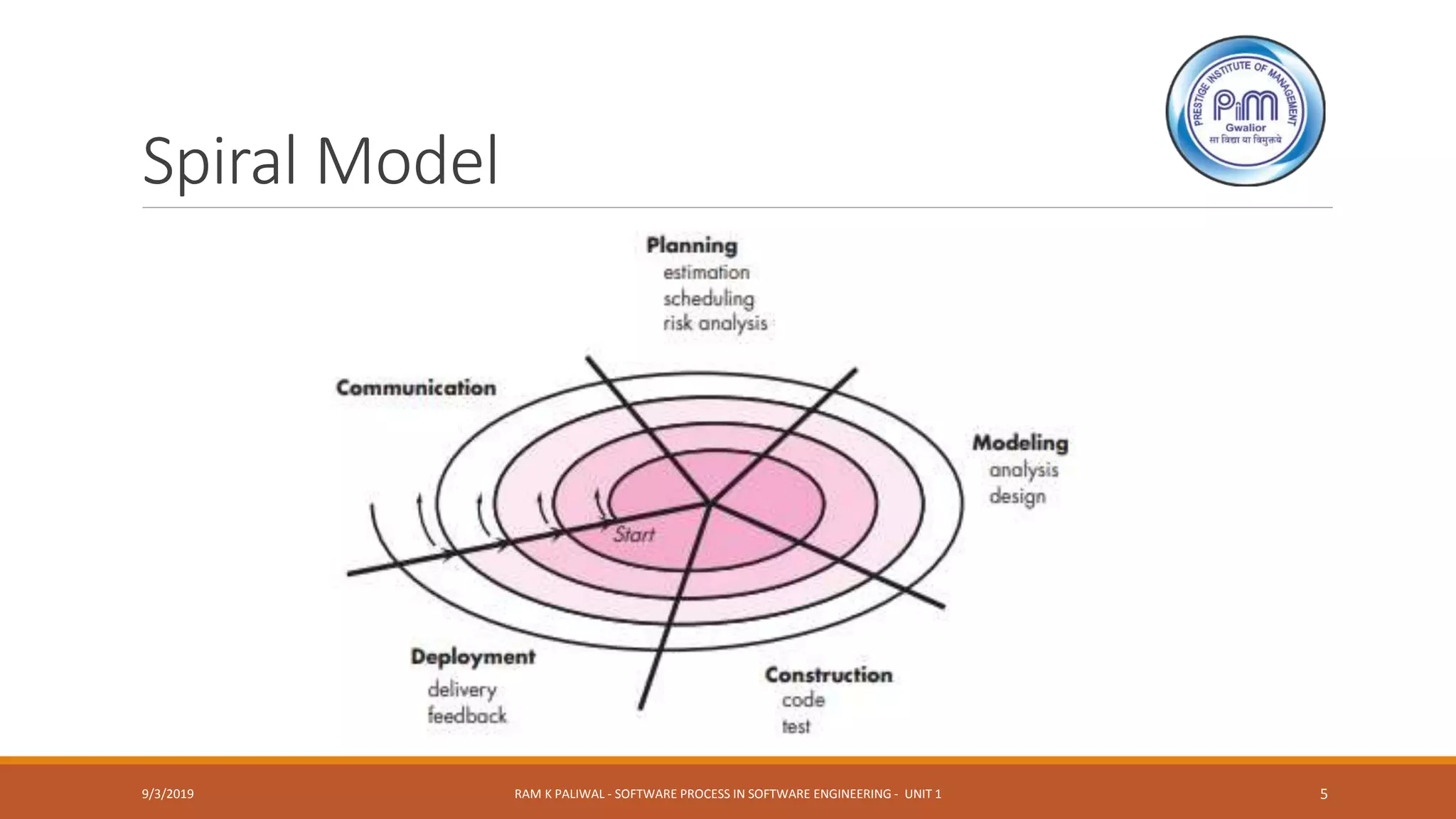
The document discusses software process models and the spiral model in particular. It notes that prescriptive process models brought order to software development but work remains complex. The spiral model is an evolutionary model that combines iterative prototyping with controlled aspects of waterfall. With spiral, software is developed through a series of evolutionary releases from initial prototypes to more complete versions. Each pass through the planning phase allows for adjustments to the project plan based on customer feedback.