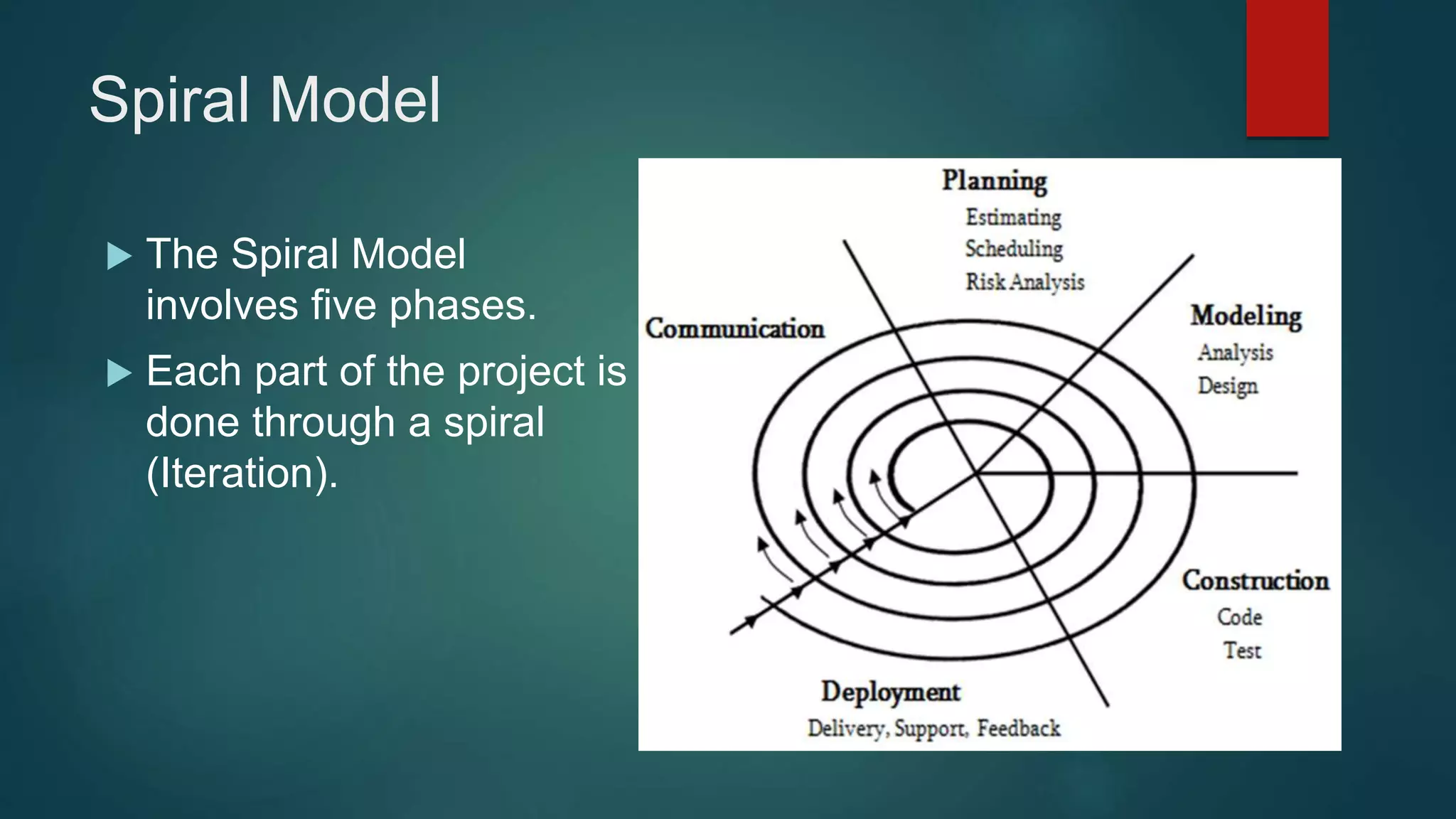
The Spiral Model is a software development lifecycle model that combines elements of prototyping and the waterfall model. It involves iterating through phases for communication, planning, modeling, construction and deployment in spirals to obtain early feedback from customers. Each iteration allows for refinement of deliverables based on customer evaluations and helps manage risks for large, expensive and complex projects.