The spiral model is a risk-driven process model for software development that combines elements of both iterative and sequential development. It consists of four phases - planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation - that are repeated in iterations or spirals until the project is complete. Each spiral phase addresses a segment of the product and refines requirements and solutions developed in previous spirals. This allows for incremental refinement and development that takes into account customer feedback at each stage.
![ This model was first described by Barry Boehm in his 1986 paper and published
in 1988 [BOE88] in his similar article.
it was the first model to explain why the iteration matters were typically 6 months
to 2 years long.
It is a systems development method (SDM) used in information technology.
Spiral model is a risk-driven model with a combination of iterative development
process model and sequential linear development model combines the features
of the prototyping model and the waterfall model.
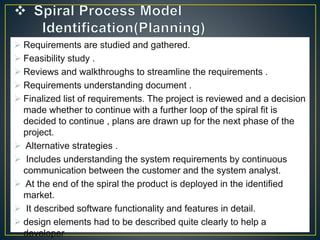
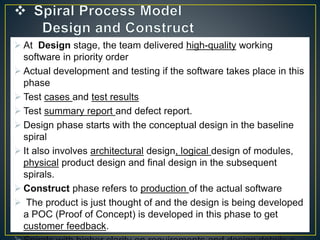
The spiral model has four phases(Identification , Design ,Construct , Evaluation
and Risk)
Each phase starts with a design goal and ends with the client (who may be
internal) reviewing the progress thus far.
Analysis and engineering efforts are applied at each phase of the project, with an
eye toward the end goal of the project.
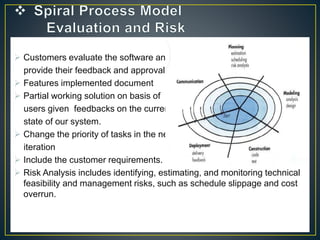
Based on the customer evaluation, software development process enters into the
next iteration and subsequently follows the linear approach to implement the
feedback suggested by the customer. The process of iterations along the spiral
continues throughout the life of the software.
Spiral model is also called meta mode because it comprises with other models of](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignmentofse-170402125205/85/software-engineering-spiral-process-model-2-320.jpg)

![ FCS [Future Combat System] and games are example of spiral model
The US military had adopted the spiral model for its Future Combat Systems pr
ogram. The FCS project was cancelled after six yeas (2003_2009), it had a tw
o year iteration (spiral)
In 2010 with the collaboration of Microsoft Research ,Bangalore, India and Uni
versity of Toronto Canada made a project with spiral.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignmentofse-170402125205/85/software-engineering-spiral-process-model-7-320.jpg)