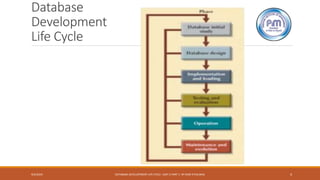
The document discusses the database development life cycle (DDLC), which is a six-phase process for designing, implementing, and maintaining a database system to meet an organization's information needs. The six phases are: 1) database initial study, 2) database design, 3) implementation and loading, 4) testing and evaluation, 5) operation, and 6) maintenance and evolution. Each phase is described in detail, from analyzing requirements in the initial study to ongoing maintenance activities once the database is operational.