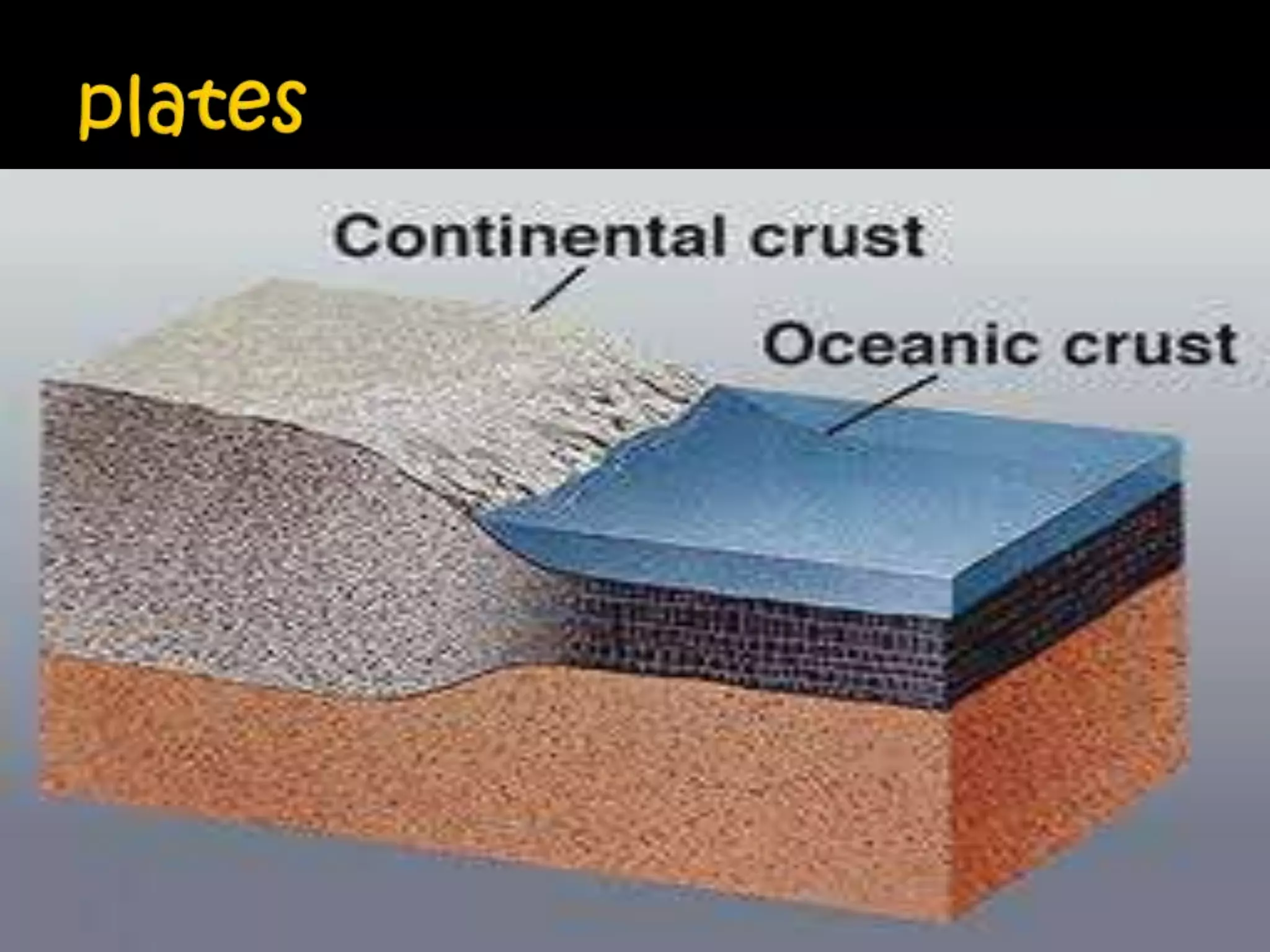
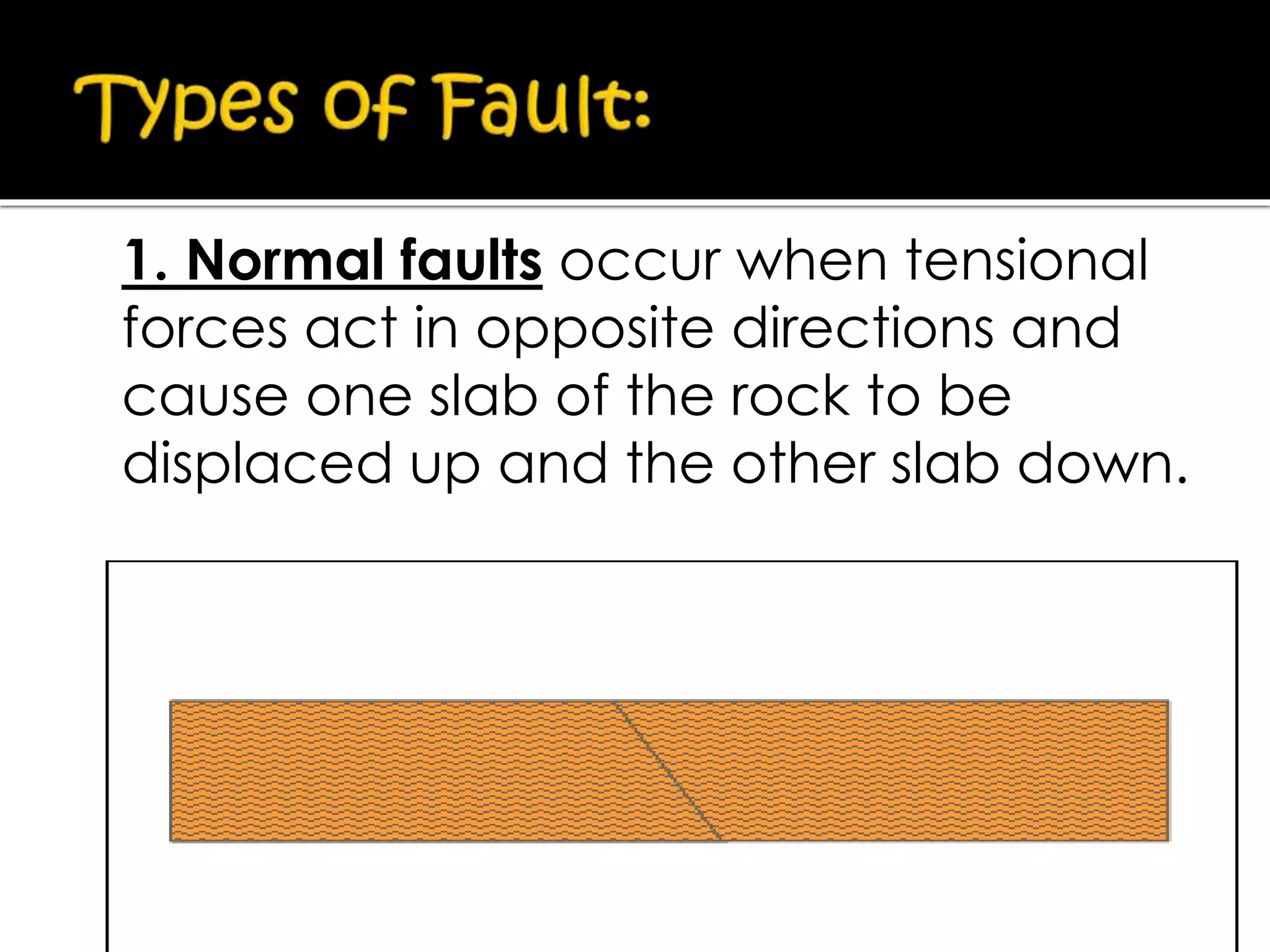
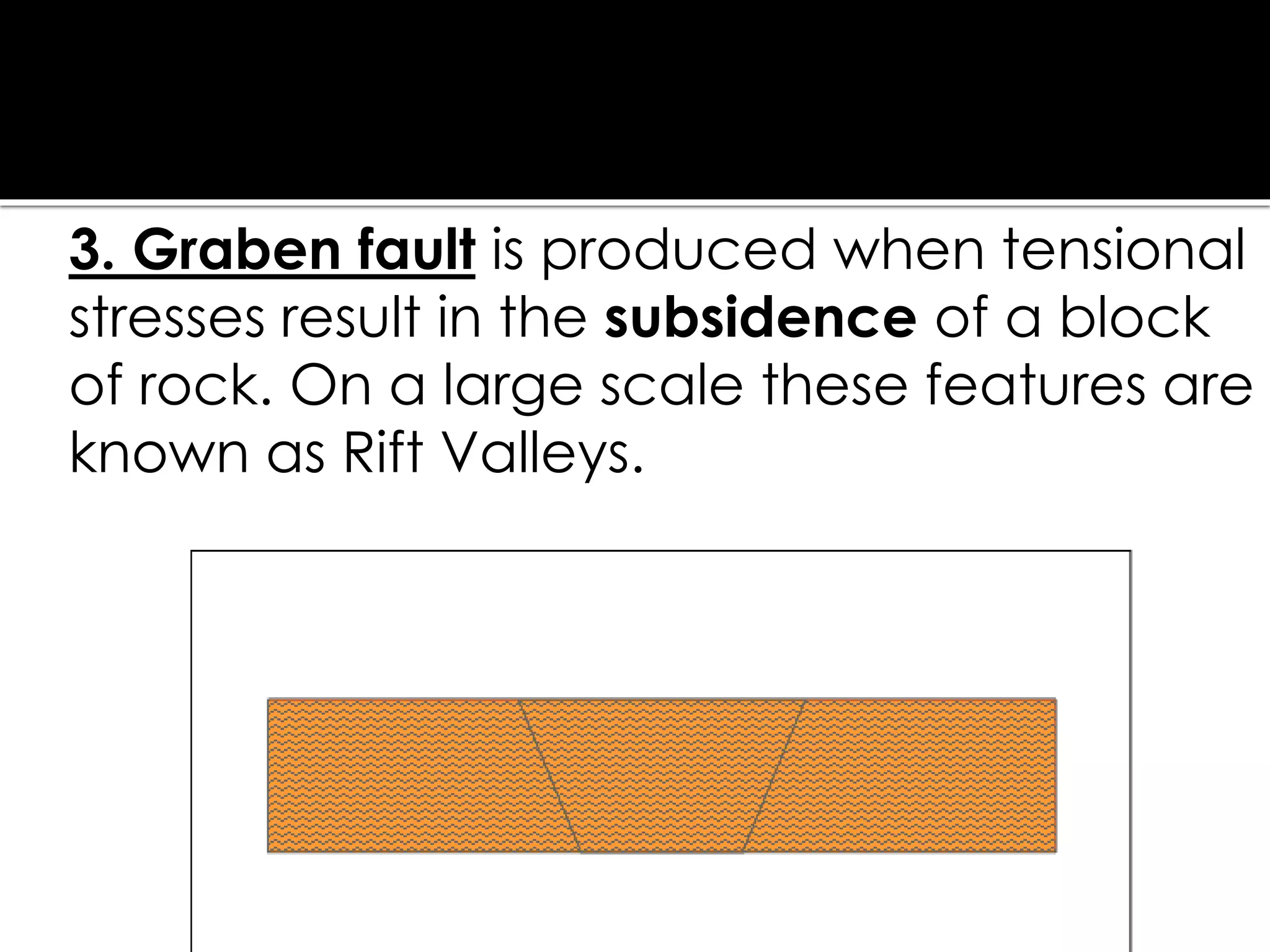
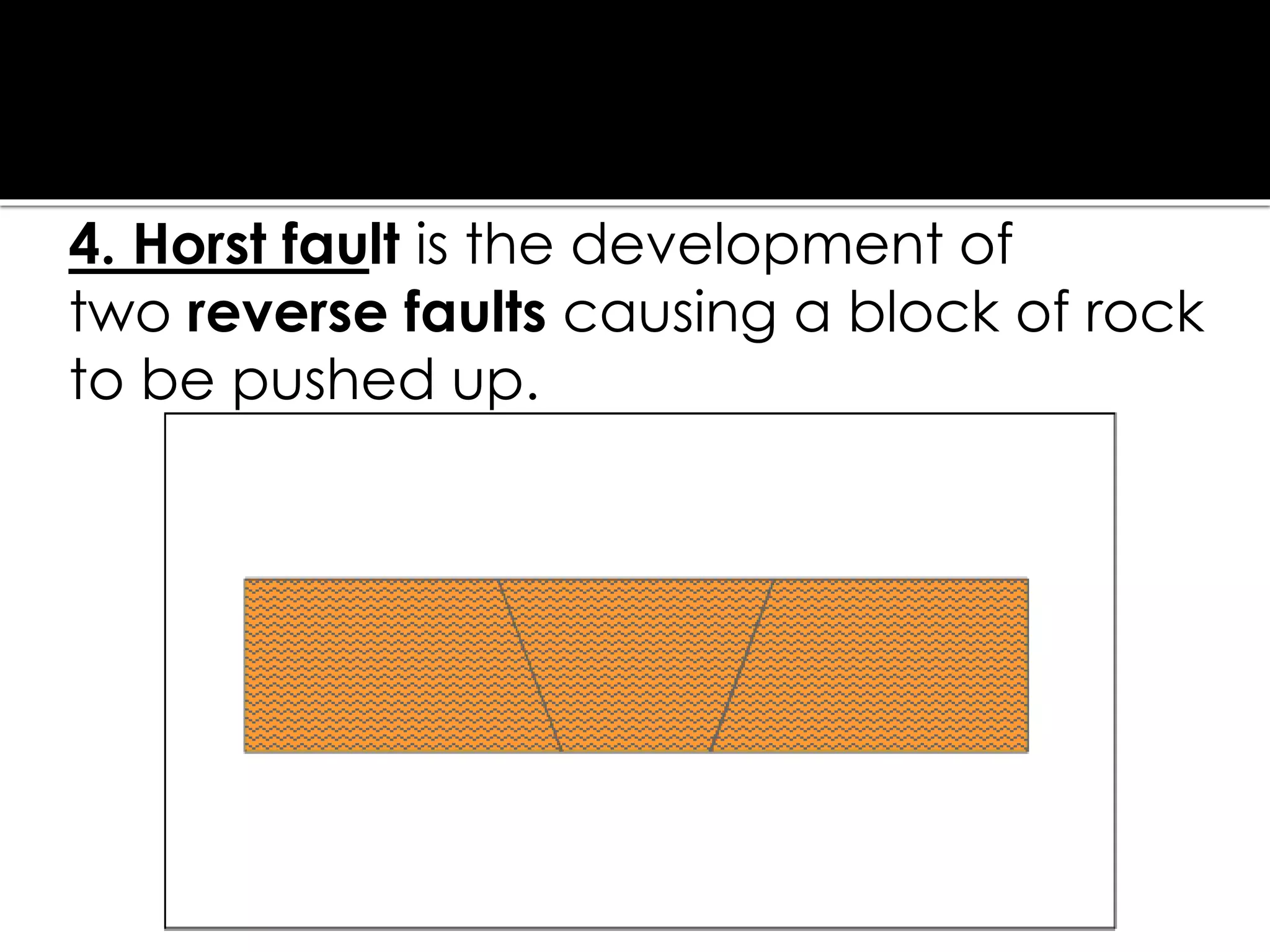
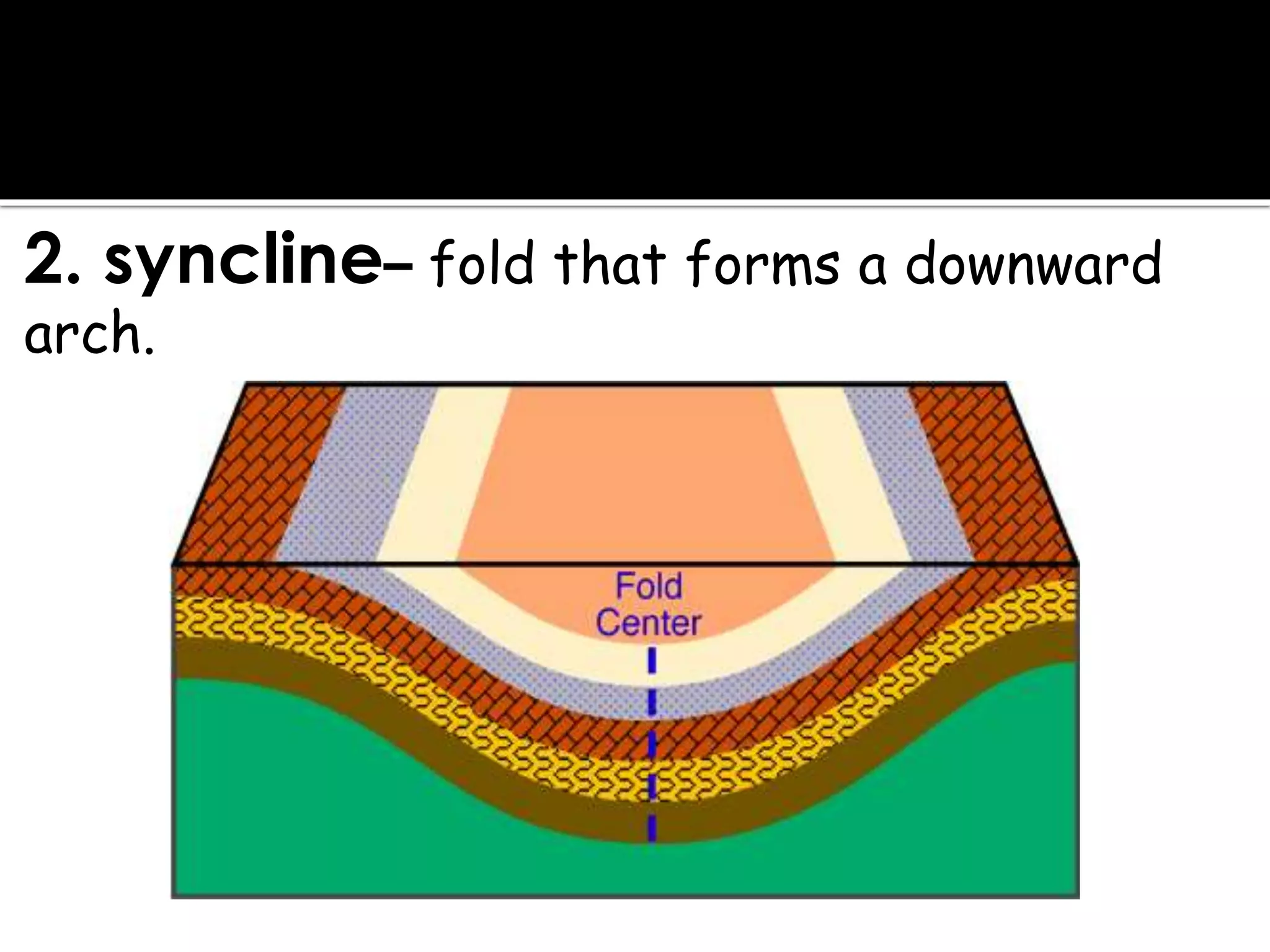
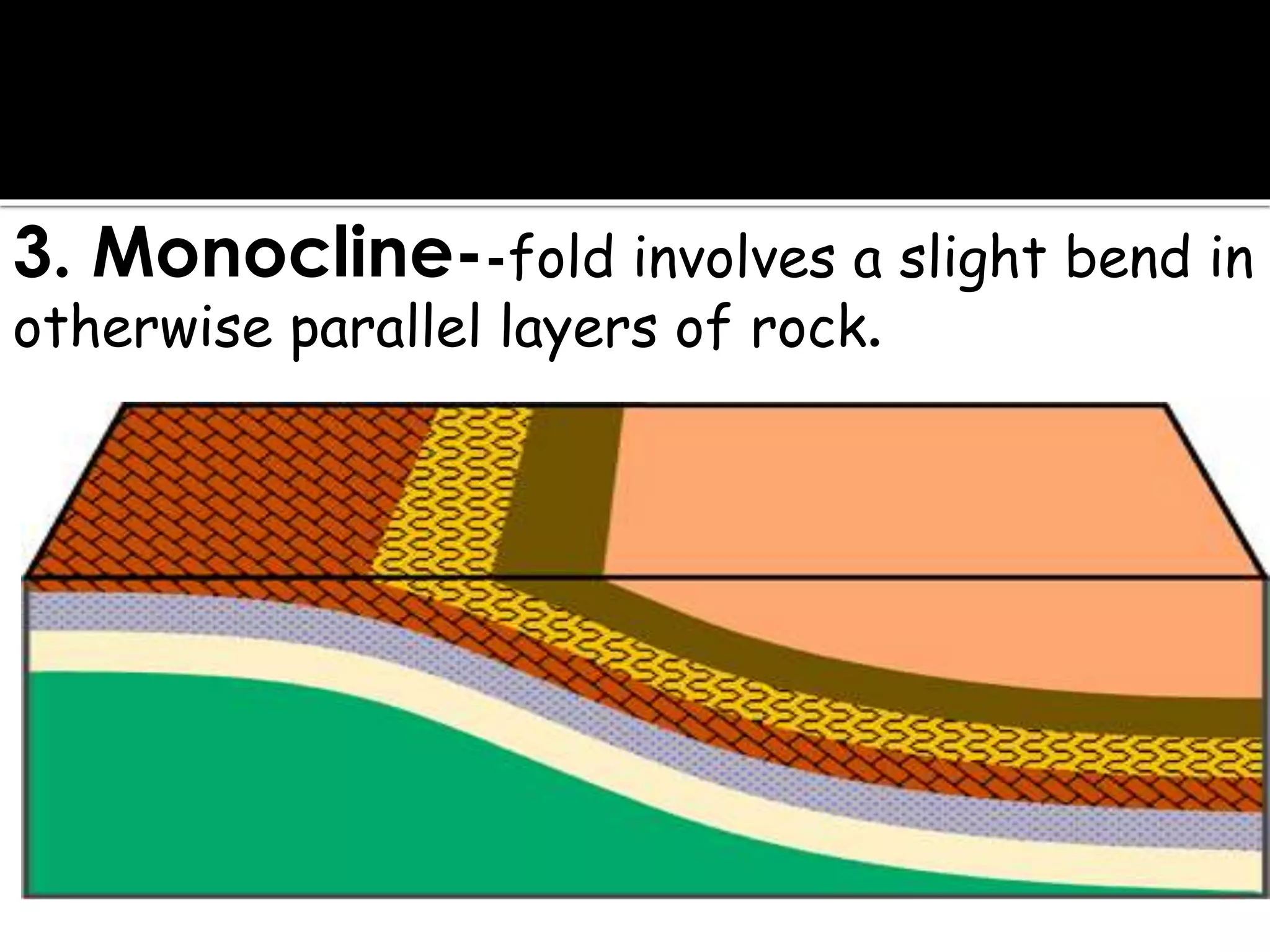
This document summarizes key concepts related to geology and landscape formation. It discusses two major processes that change landscapes: endogenous processes that occur underground like plate tectonics, and exogenous processes above ground like weathering and erosion. Plate tectonics involves the movement of tectonic plates composed of continental and oceanic crust. Stresses from plate interactions cause deformation through tension, compression, and shearing, resulting in faulting and folding of the Earth's crust. Volcanism is another underground process where magma is forced to the surface. Weathering breaks rocks into fragments through physical and chemical processes, while erosion transports weathered material, and deposition accumulates eroded sediments.