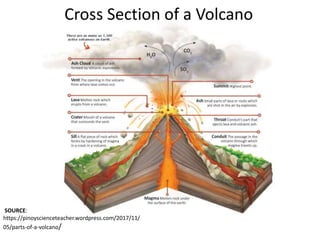
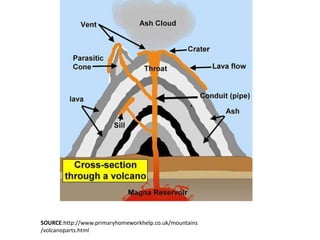
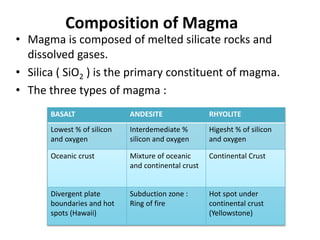
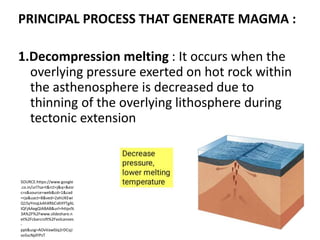
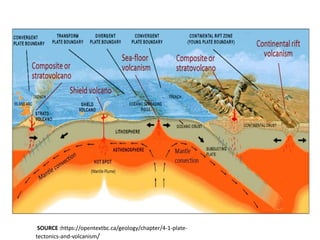
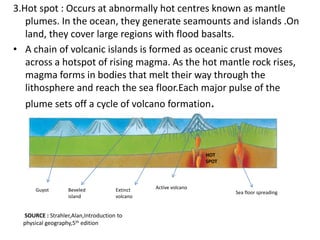
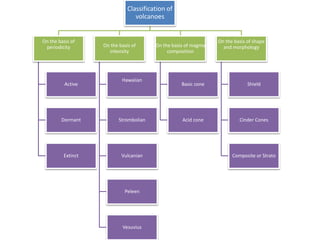
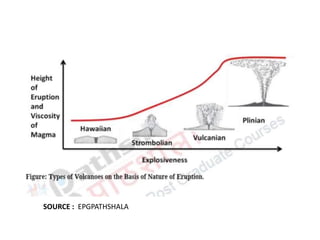
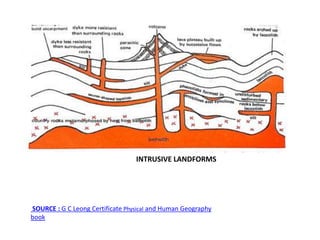
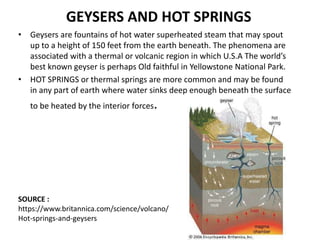
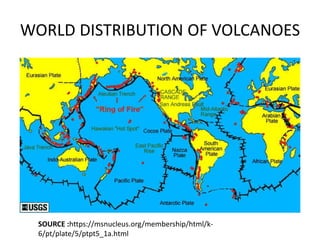
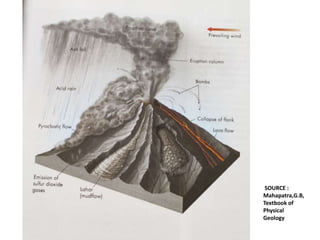
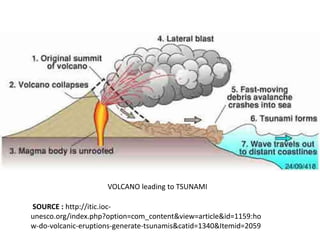
This document provides an overview of volcanoes. It begins by defining a volcano as a vent in the Earth's surface through which molten rock and gases erupt. It then discusses the internal structure of volcanoes including magma, which is molten rock below the surface. The causes of volcanism are explained in relation to plate tectonics. Different types of volcanoes are classified based on factors like eruption intensity, magma composition, and shape. Volcanic landforms that form from intrusive and extrusive volcanic activity are also outlined. In summary, the document covers the key components and processes involved in volcanism.