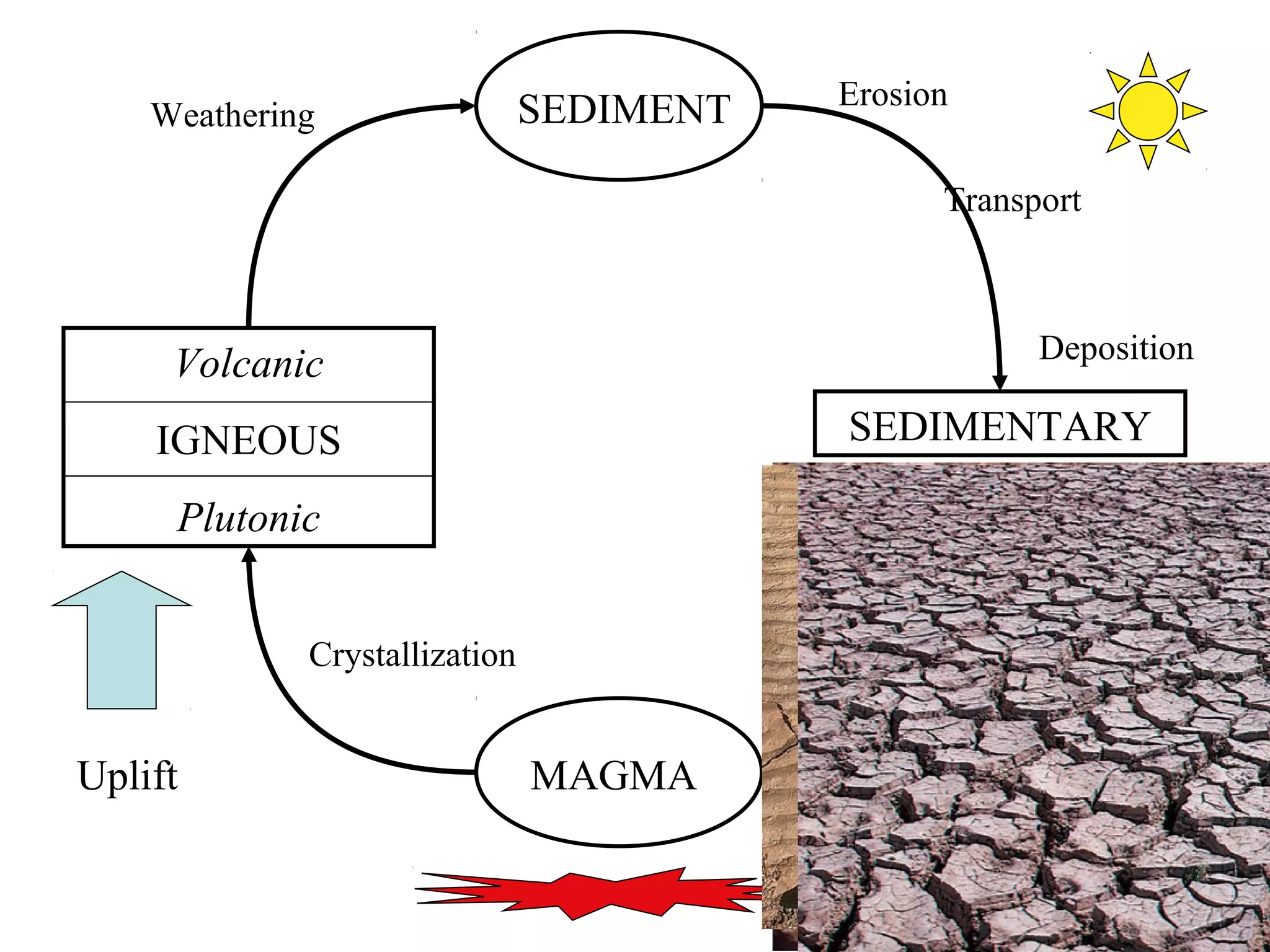
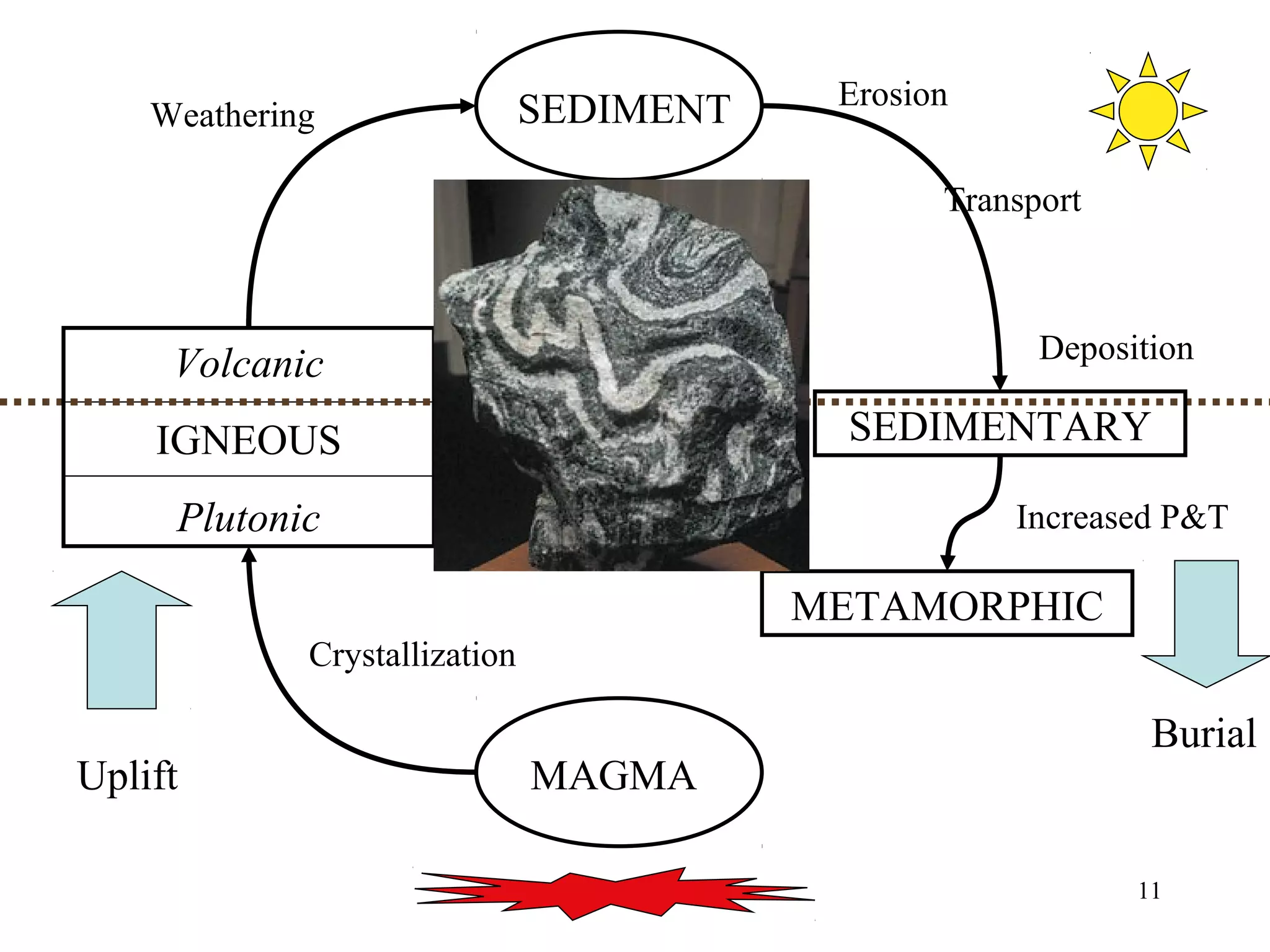
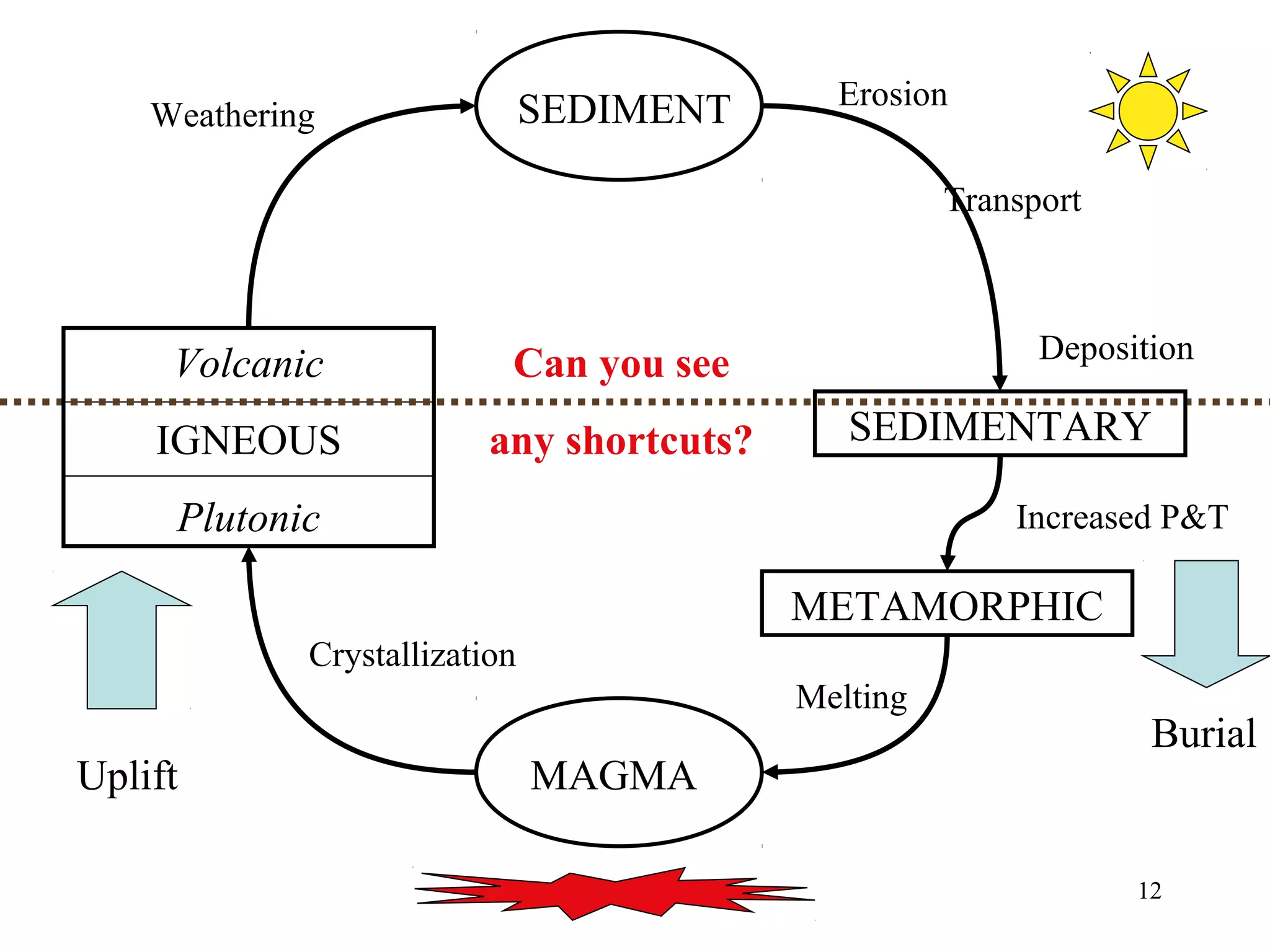
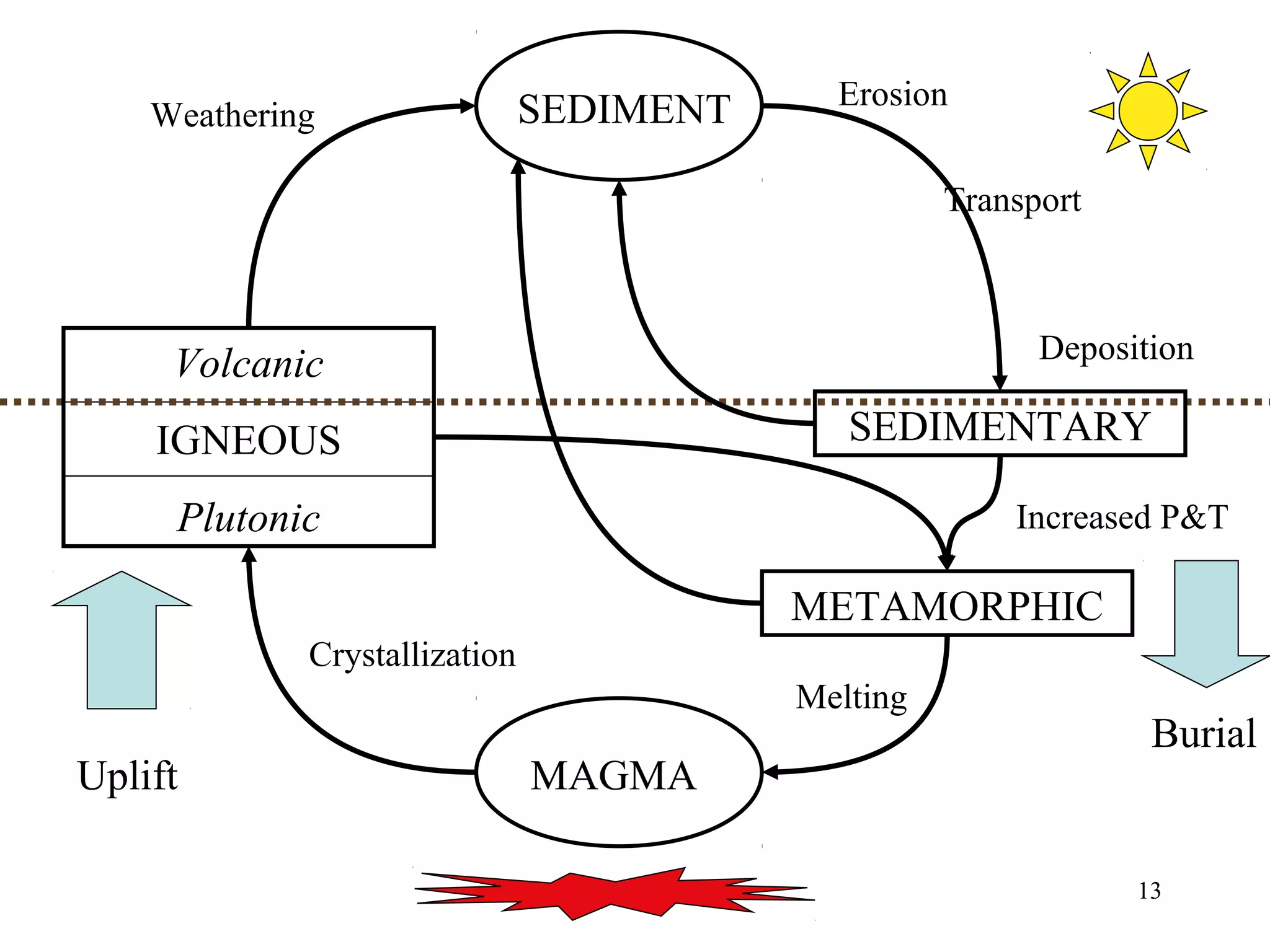
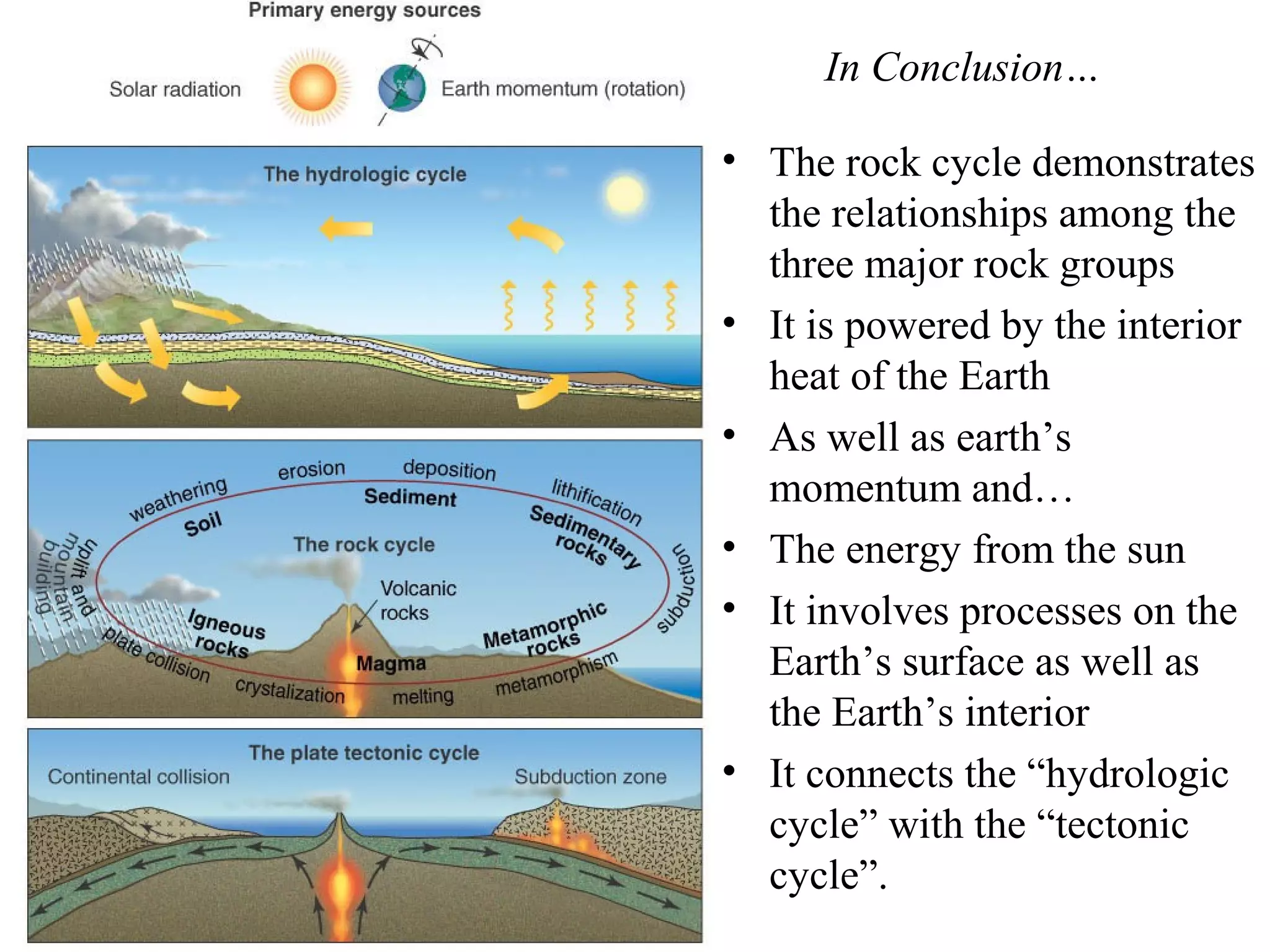
The document discusses the rock cycle and the three main types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, either slowly underground as plutonic rocks or quickly on the surface as volcanic rocks. Sedimentary rocks form from the lithification of sediments at the earth's surface. Metamorphic rocks form by changes to other rock types through heat, pressure, and fluids in the earth's crust. The rock cycle demonstrates how rocks continuously transform between these three types through geological processes over long periods of time.