The document discusses the evolution of the universe from the Big Bang theory to present day. It covers:
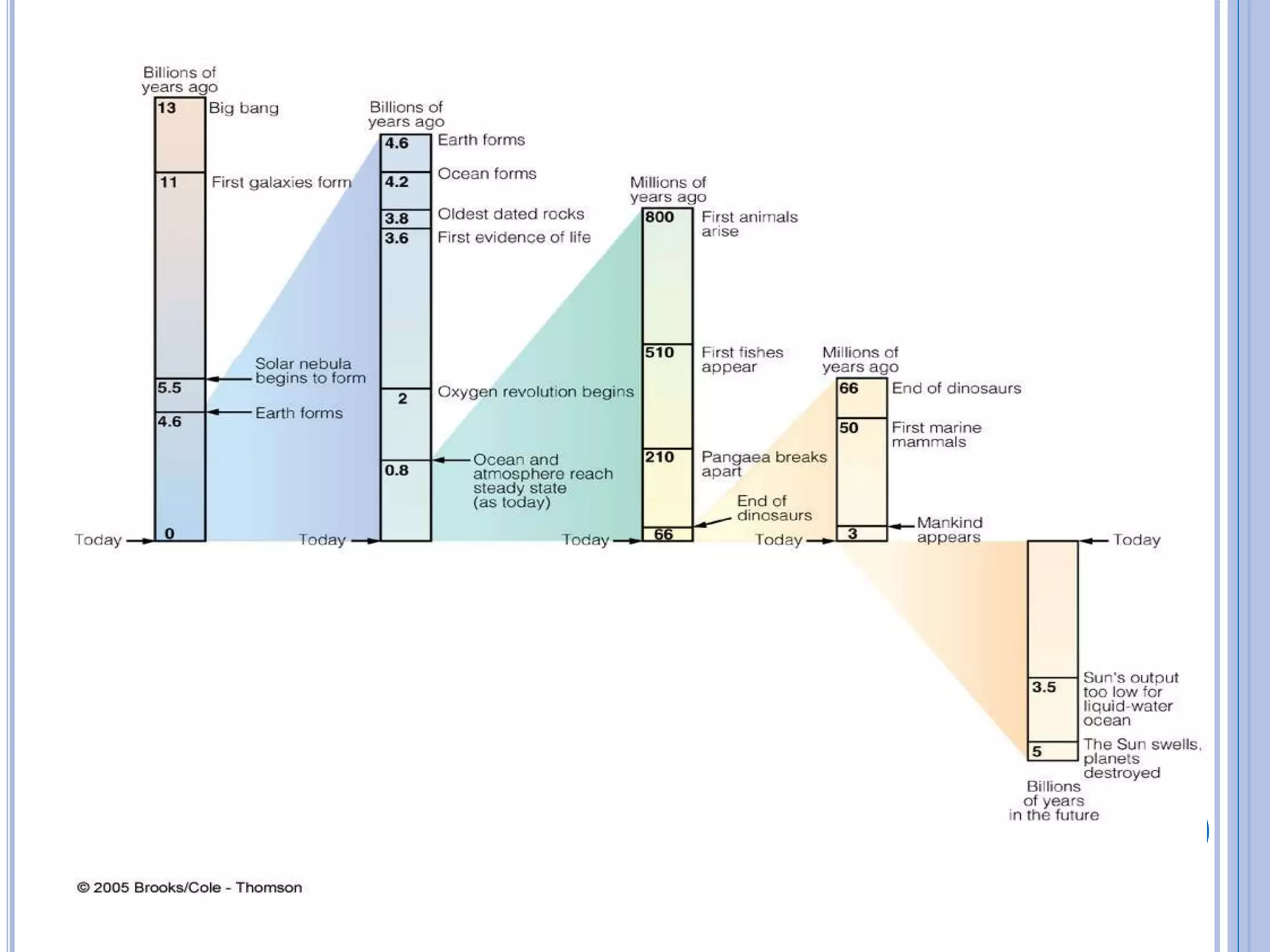
1) The Big Bang theory which proposes the universe began as a hot, dense point around 14 billion years ago and has been expanding and cooling ever since.
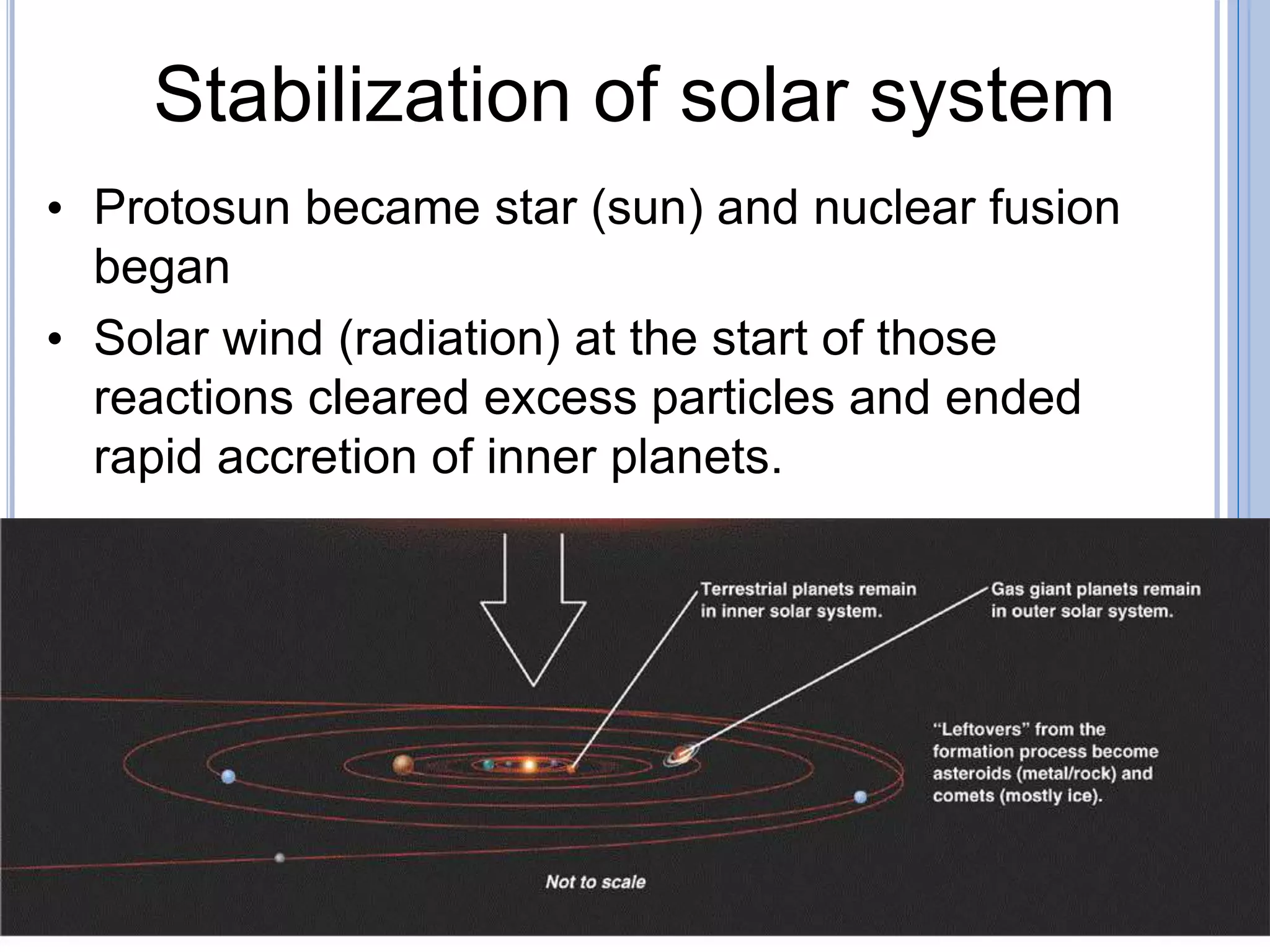
2) The formation of stars, galaxies, and planets as the universe evolved, with our solar system forming around 5 billion years ago.
3) Two other theories - the Steady State theory which proposes the universe has always existed in a constant state, and the Pulsating universe theory.