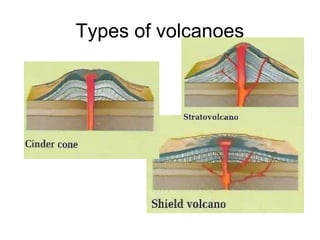
Volcanoes form over thousands of years as magma is forced onto the Earth's surface from underground magma chambers, dries, and hardens. Most volcanoes share features like vents where lava is released and lava tubes through which lava travels. Volcanoes occur at boundaries where tectonic plates meet or move apart, and at hot spots deep in the Earth. There are three main types of volcanoes - shield volcanoes which form wide, gentle slopes from non-explosive eruptions, cinder cone volcanoes which are steep and form from explosive eruptions, and composite volcanoes which can erupt explosively or gently.