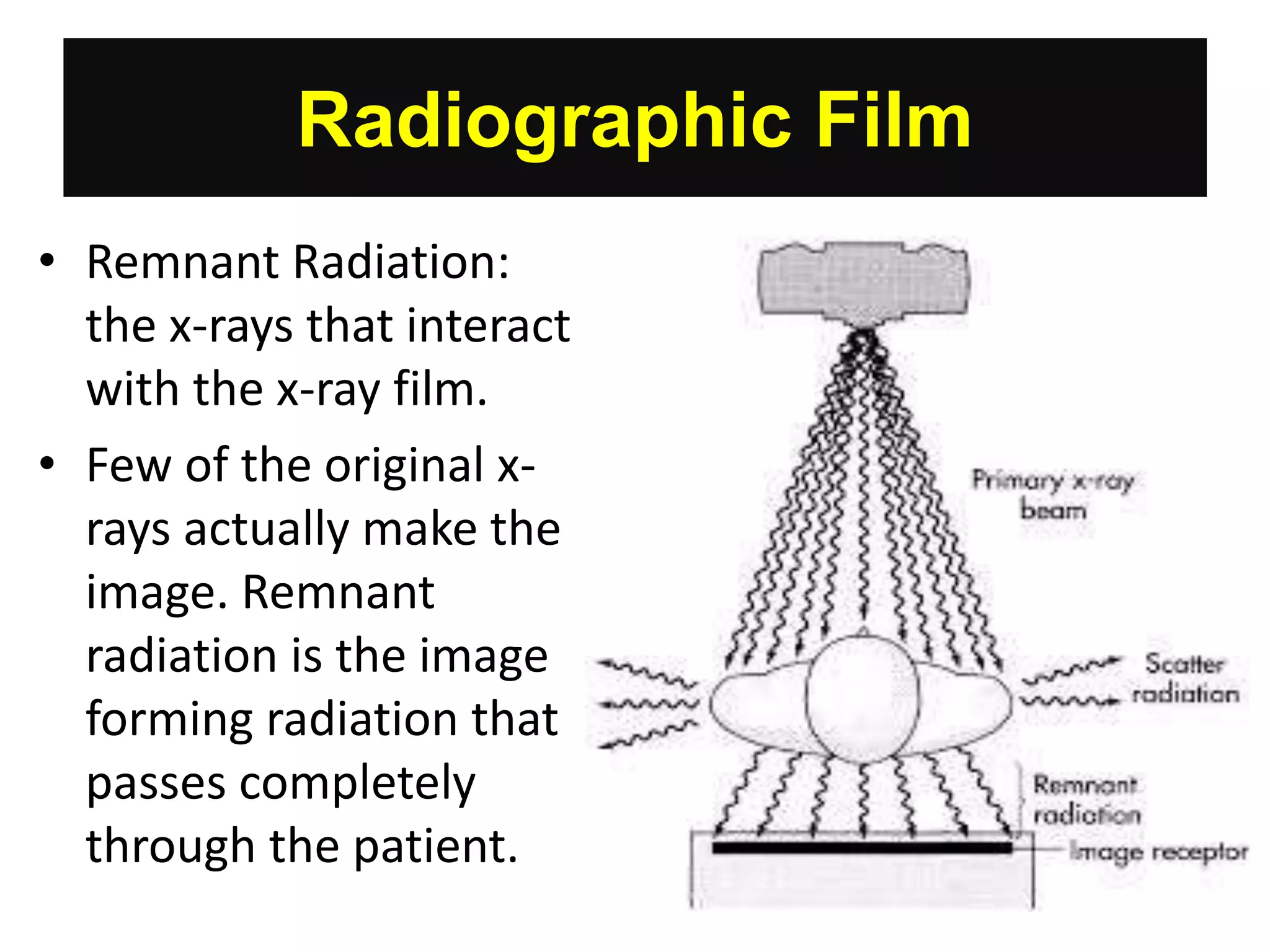
Radiographic film has evolved from glass plates to cellulose nitrate and now polyester bases. It consists of a gelatin emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide crystals. When exposed to x-rays, a latent invisible image is formed via interactions at silver halide crystal sensitivity centers. Proper handling and storage of film requires control of heat, humidity, light and static to prevent artifacts and loss of image quality or speed. Film expiration dates must be followed and older film used first.