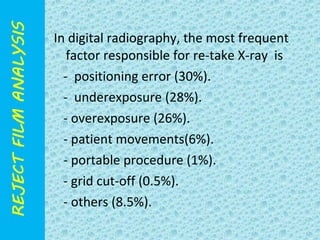
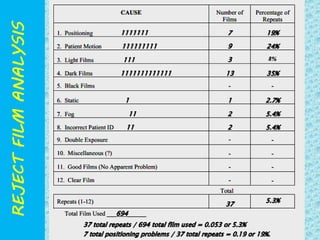
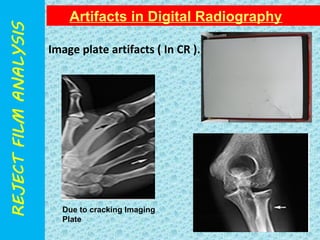
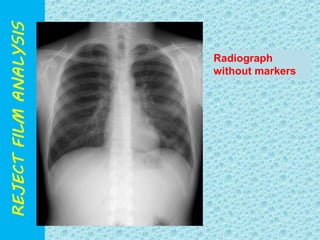
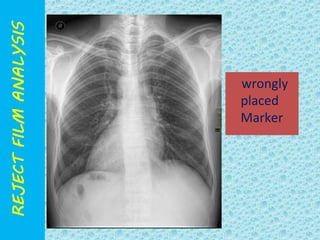
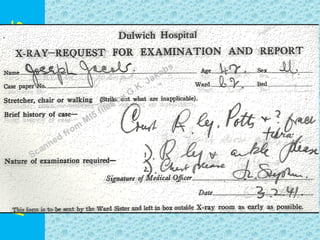
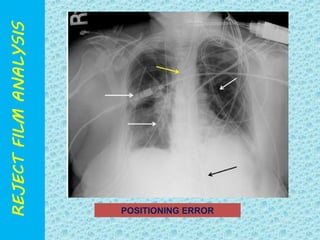
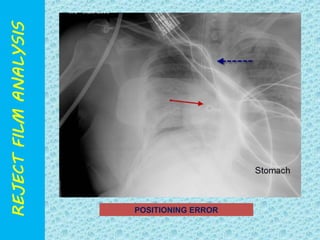
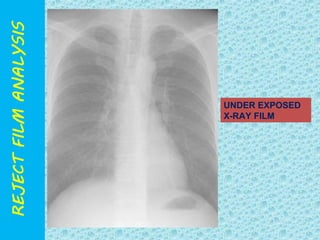
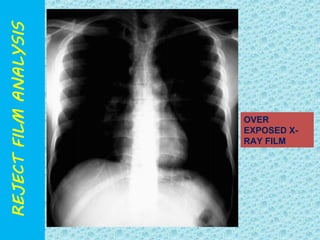
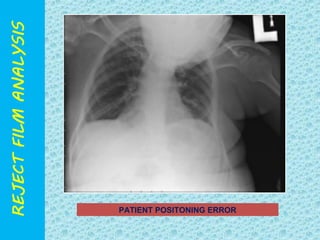
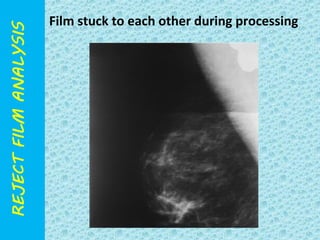
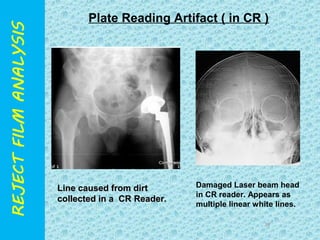
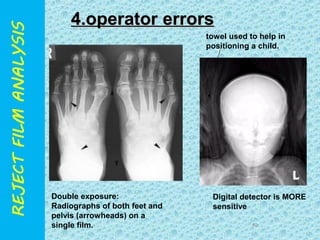
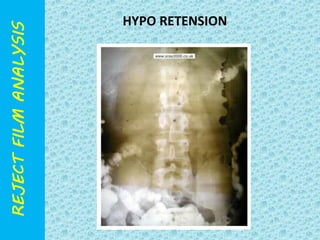
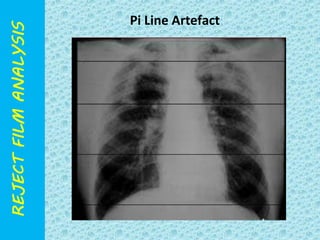
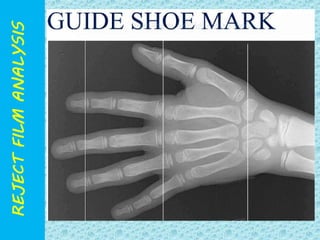
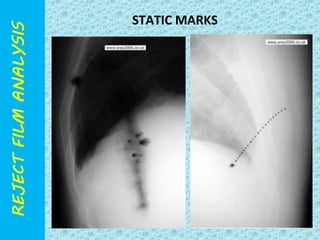
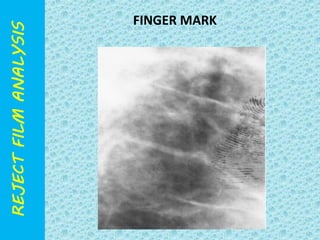
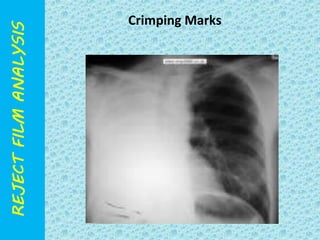
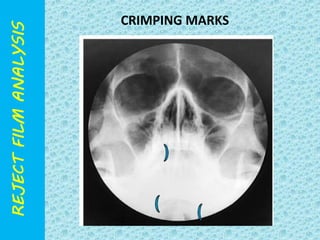
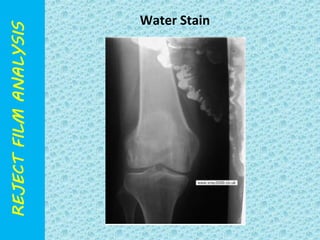
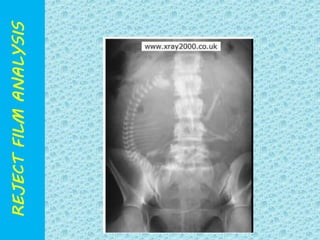
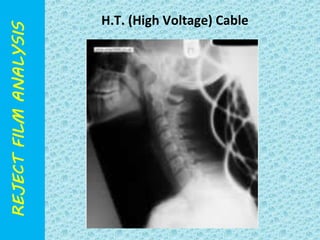
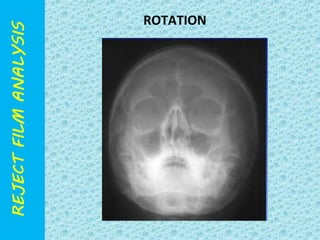
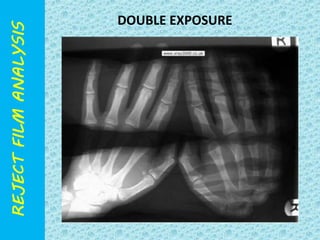
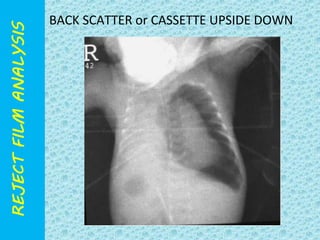
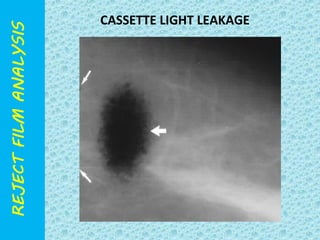
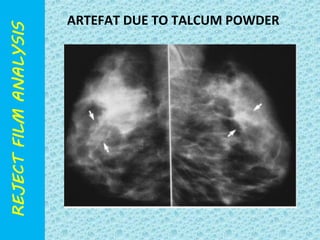
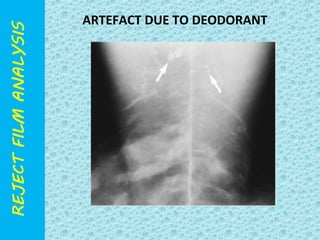
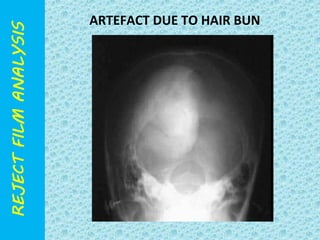
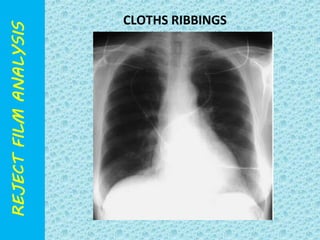
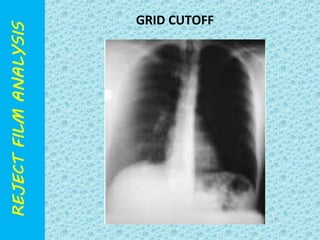
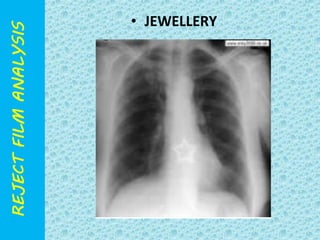
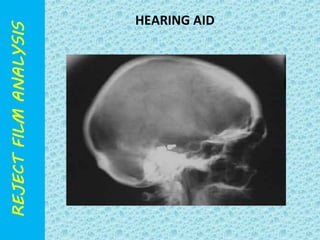
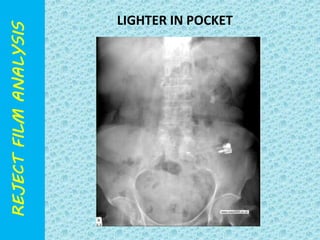
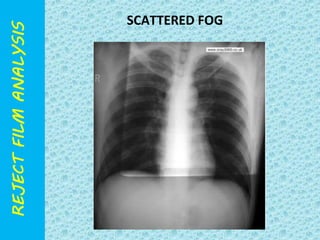
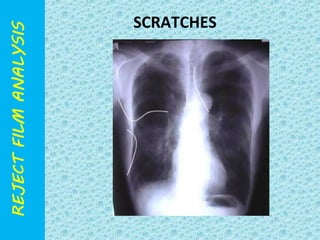
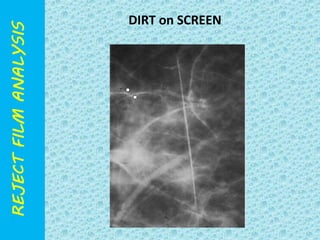
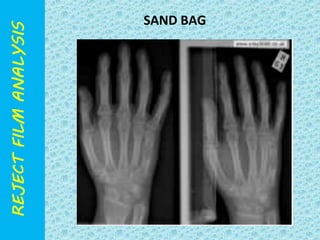
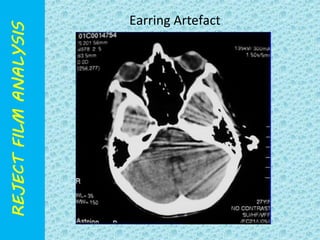
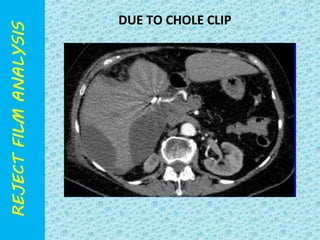
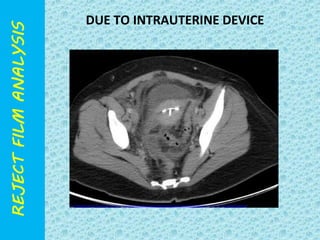
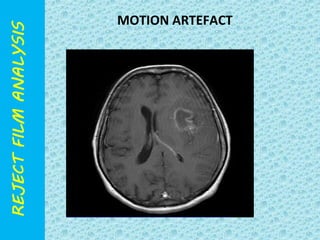
The document discusses reject film analysis in radiology. Reject film analysis measures actual quality against standards and identifies necessary corrective actions. It aims to minimize patient exposure, reduce costs, improve throughput and image quality. Common reasons for rejected films include positioning errors, under/over exposure, and patient movement. Analyzing reject films helps address equipment issues and identifies areas for improved training.