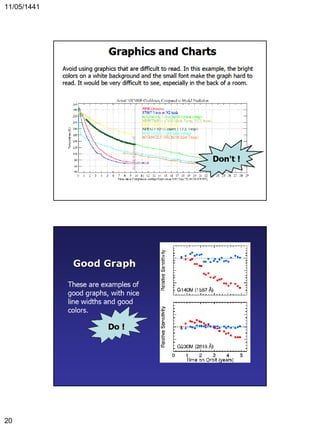
This document provides guidance on preparing an effective scientific presentation. It discusses identifying the key message and desired outcome, organizing the presentation into a logical flow with the main points first, and using visuals like slides to reinforce the main topics. The document also covers tips for delivery, such as practicing aloud, speaking clearly, maintaining eye contact, and managing time limits. The overall message is that preparation, structure, visual aids, and delivery techniques are essential for an effective presentation.