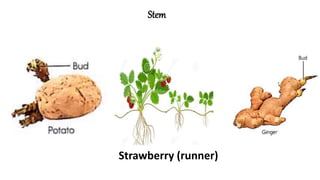
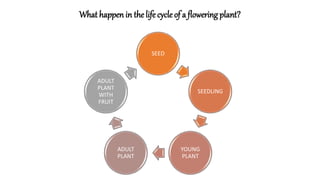
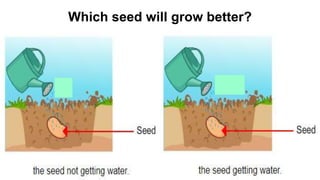
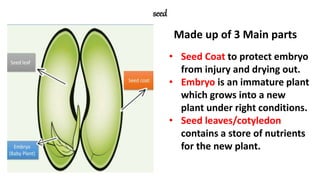
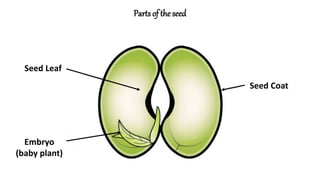
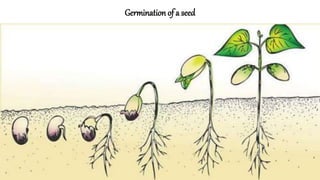
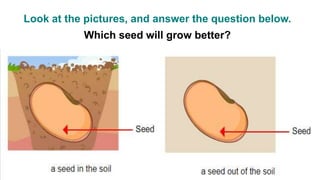
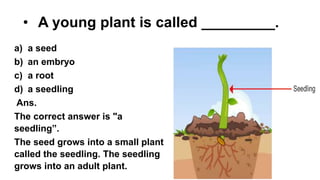
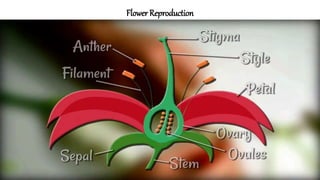
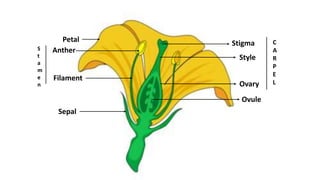
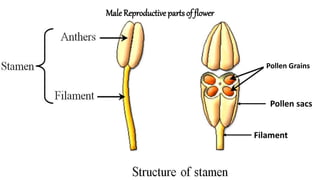
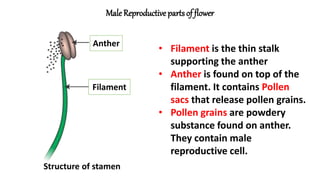
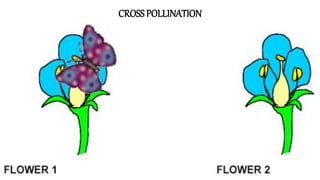
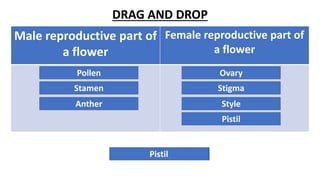
The document discusses the reproduction and life cycle of flowering plants, emphasizing the importance of seeds, pollination, and the various methods of plant reproduction including through seeds, stems, leaves, and spores. It explains the anatomy of flowers and the functions of different flower parts in reproduction. Additionally, it outlines specific plant examples for various reproductive methods and summarizes the germination process and factors necessary for seed growth.