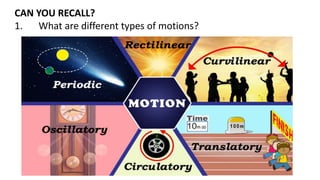
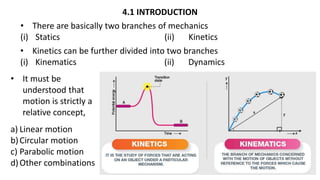
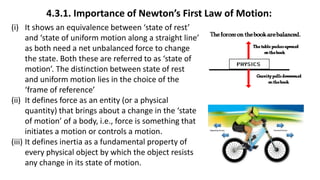
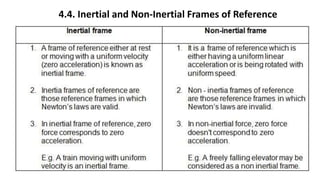
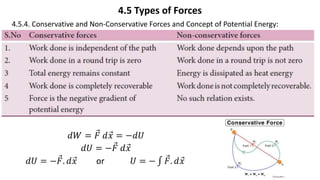
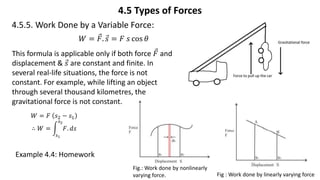
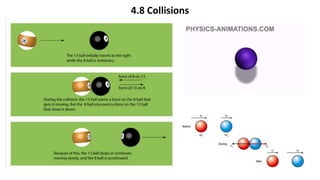
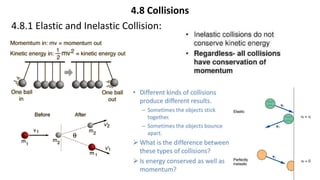
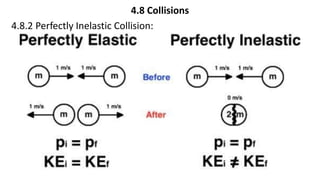
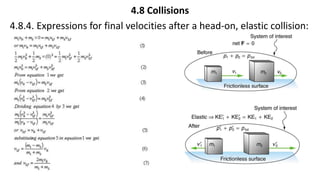
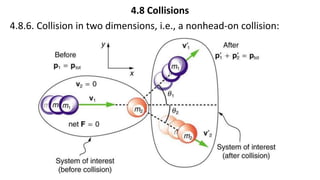
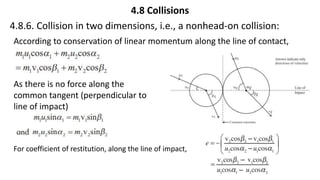
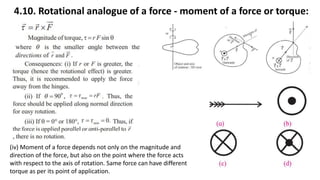
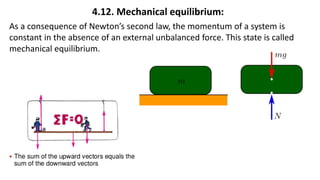
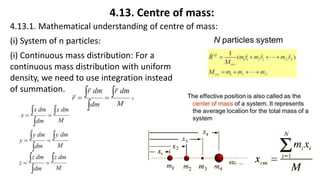
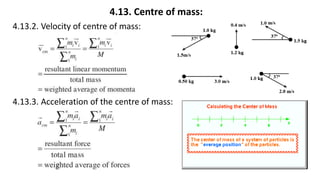
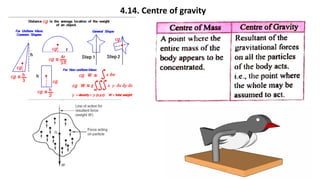
This document provides a summary of key concepts from a Physics chapter on the laws of motion. It begins with an introduction to kinematics and dynamics. It then discusses Newton's three laws of motion and their importance. The document outlines different types of forces, including fundamental forces, real/pseudo forces, and conservative/non-conservative forces. It also covers work, energy, impulse, torque, equilibrium, center of mass, and center of gravity. Examples and simulations are provided to help explain various concepts related to motion and forces.