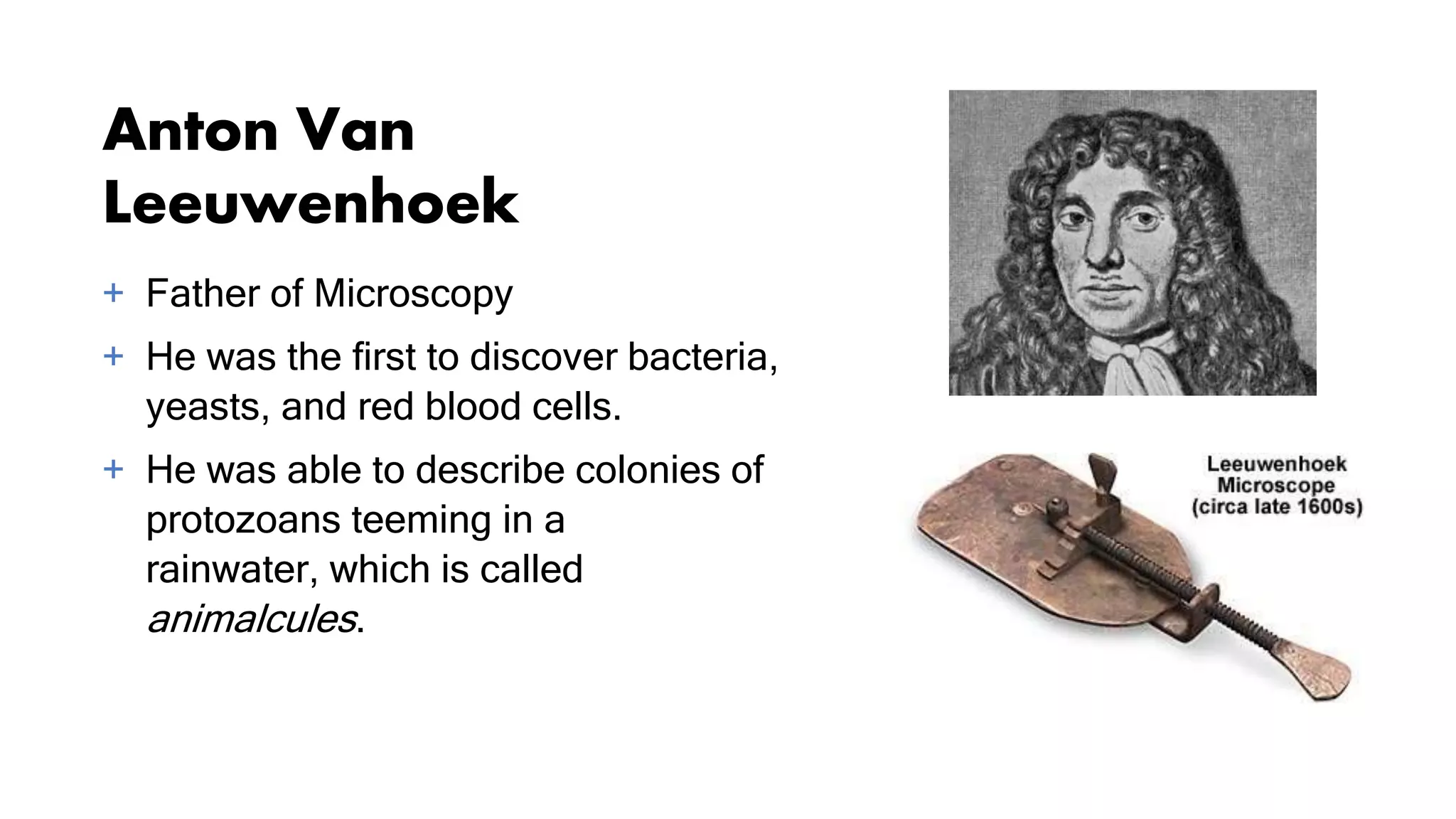
The document discusses the history and development of the microscope from its earliest forms to modern compound microscopes. It describes key figures like Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who was the first to observe and describe microorganisms, and Robert Hooke, who first observed and named plant and animal cells after viewing cork tissue under a microscope. The document also outlines the basic parts and functions of simple microscopes, which use a single lens, and compound microscopes, which use multiple lenses to provide higher magnification. Compound microscopes are described as having illuminating, magnifying, and mechanical parts that work together to provide clear, enlarged views of microscopic specimens.