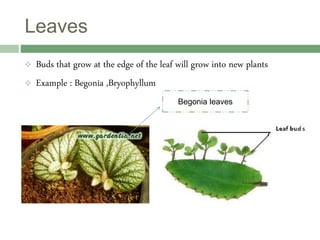
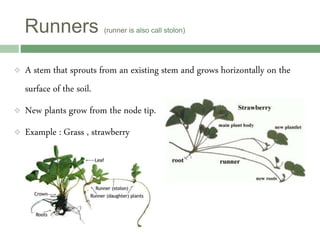
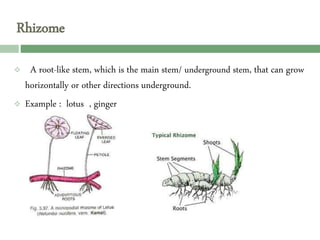
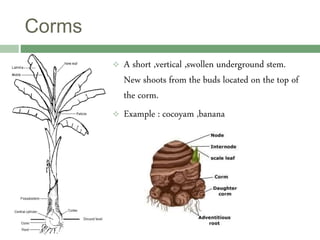
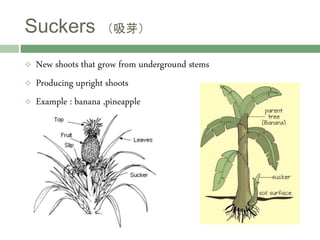
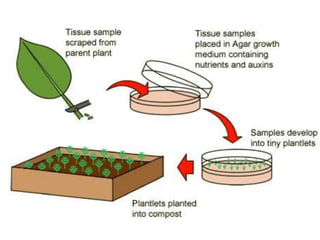
Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction used by plants to produce new individuals without the use of seeds or spores. There are several types of vegetative reproduction including reproduction through leaves, stems, roots, and bulbs. Common methods used are stem cuttings, marcotting, and tissue culture. Vegetative reproduction allows plants to grow faster than from seeds and produce fruits more quickly, but it can lead to overcrowding and lack of genetic variation. It has many agricultural applications for clonal propagation of crops.