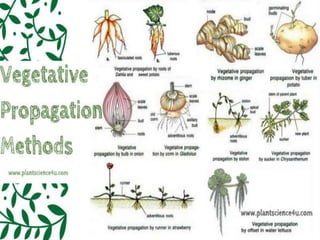
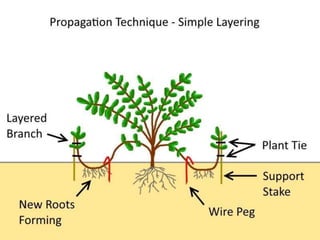
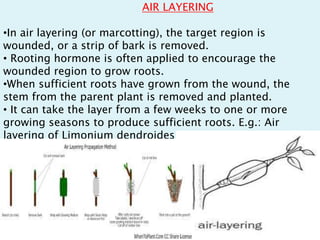
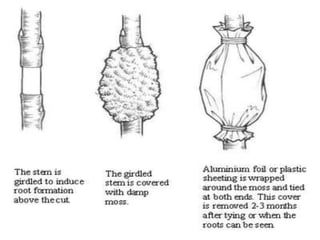
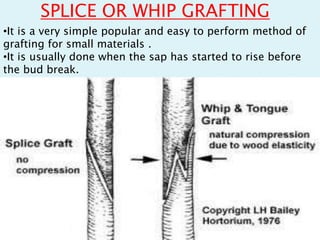
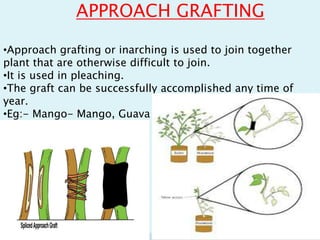
Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual plant reproduction that involves using plant parts like stems, leaves, and roots to produce new plants with identical genetics to the parent plant. It allows for mass production of plants and preservation of desirable traits without using seeds. Common vegetative propagation techniques include stem and root cuttings, layering, and grafting. Layering involves roots developing on a stem still attached to the parent plant, while grafting joins tissue from two plants together. Vegetative propagation is widely used in horticulture to reproduce desired varieties of crops.