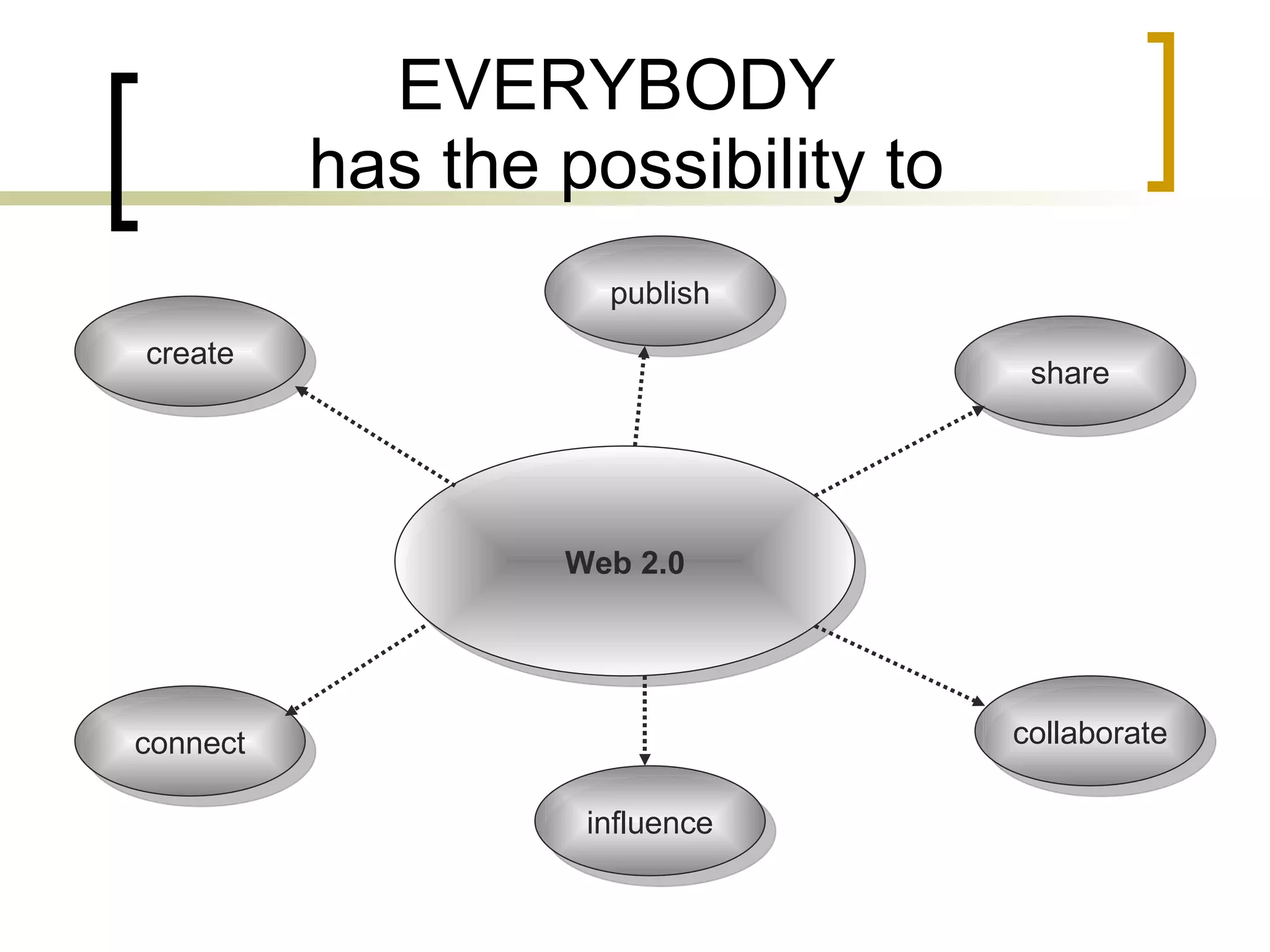
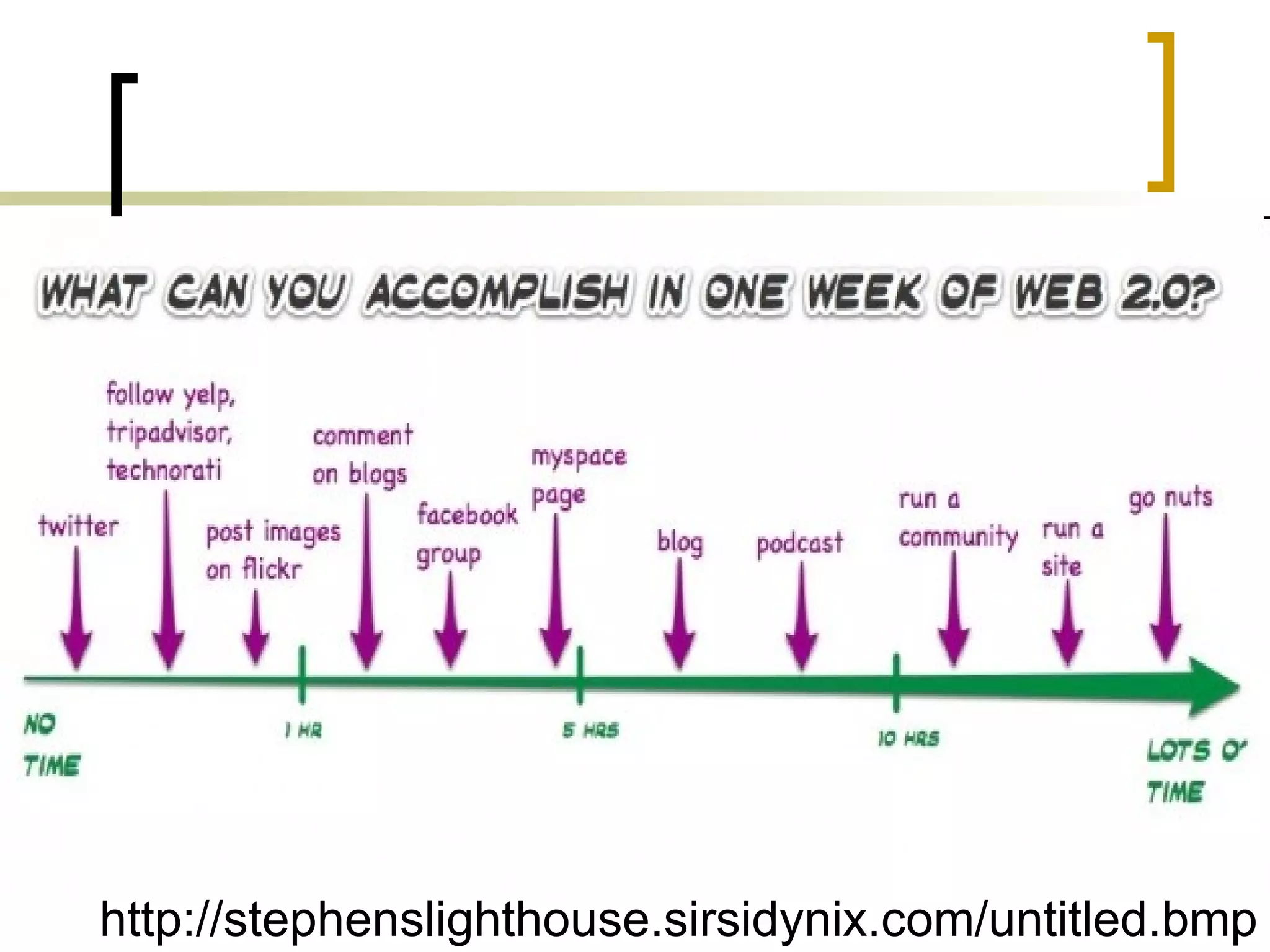
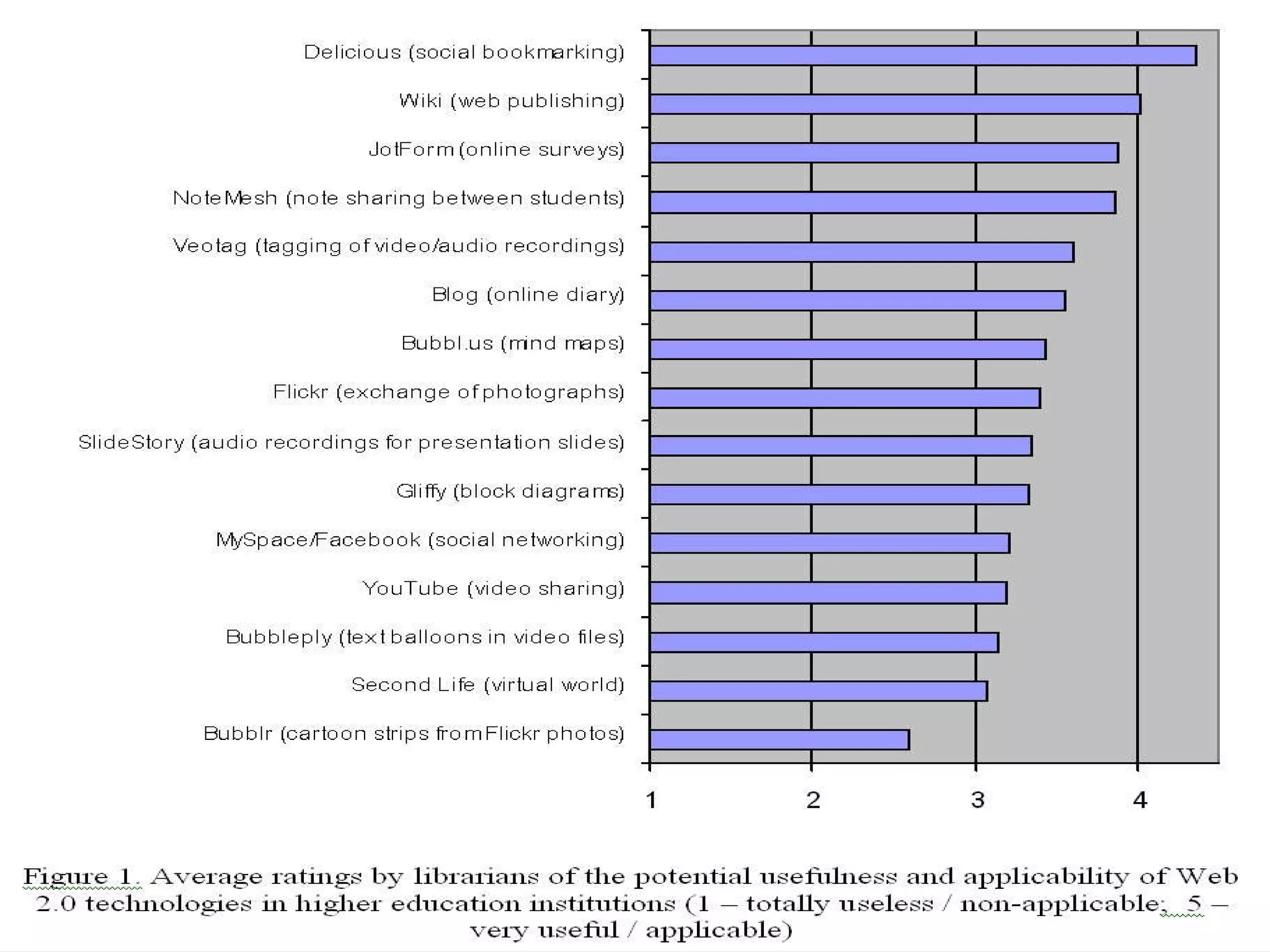
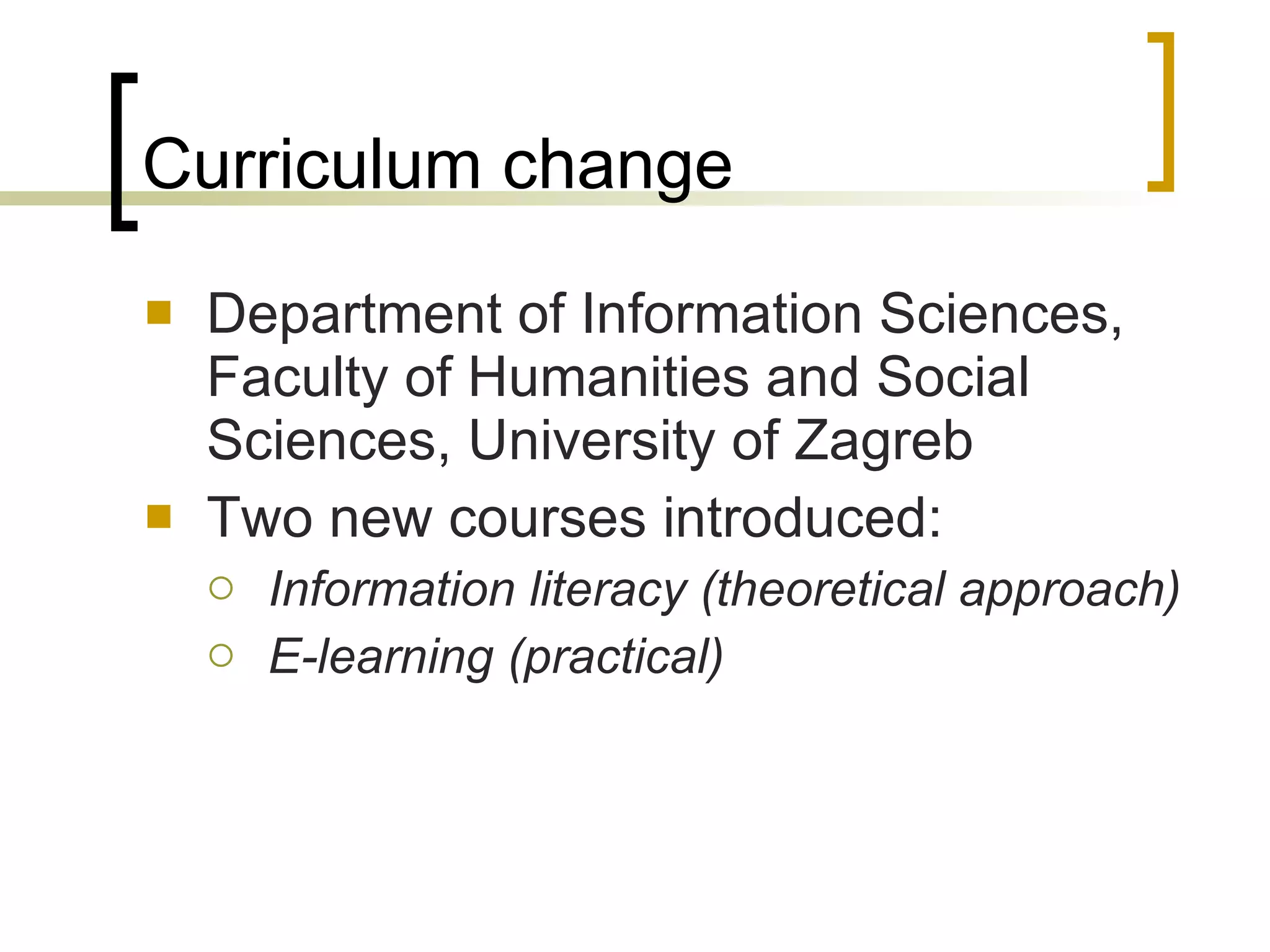
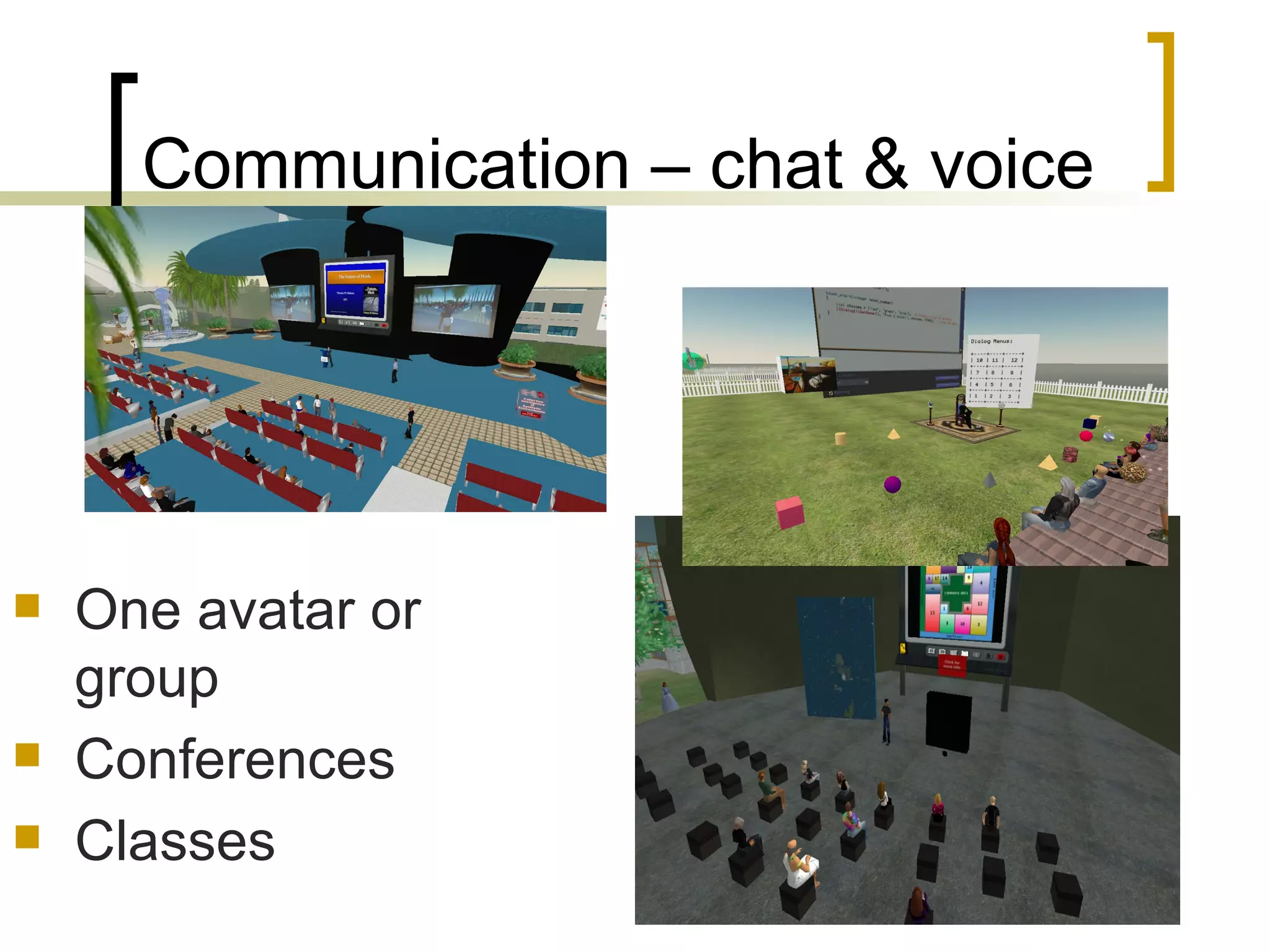
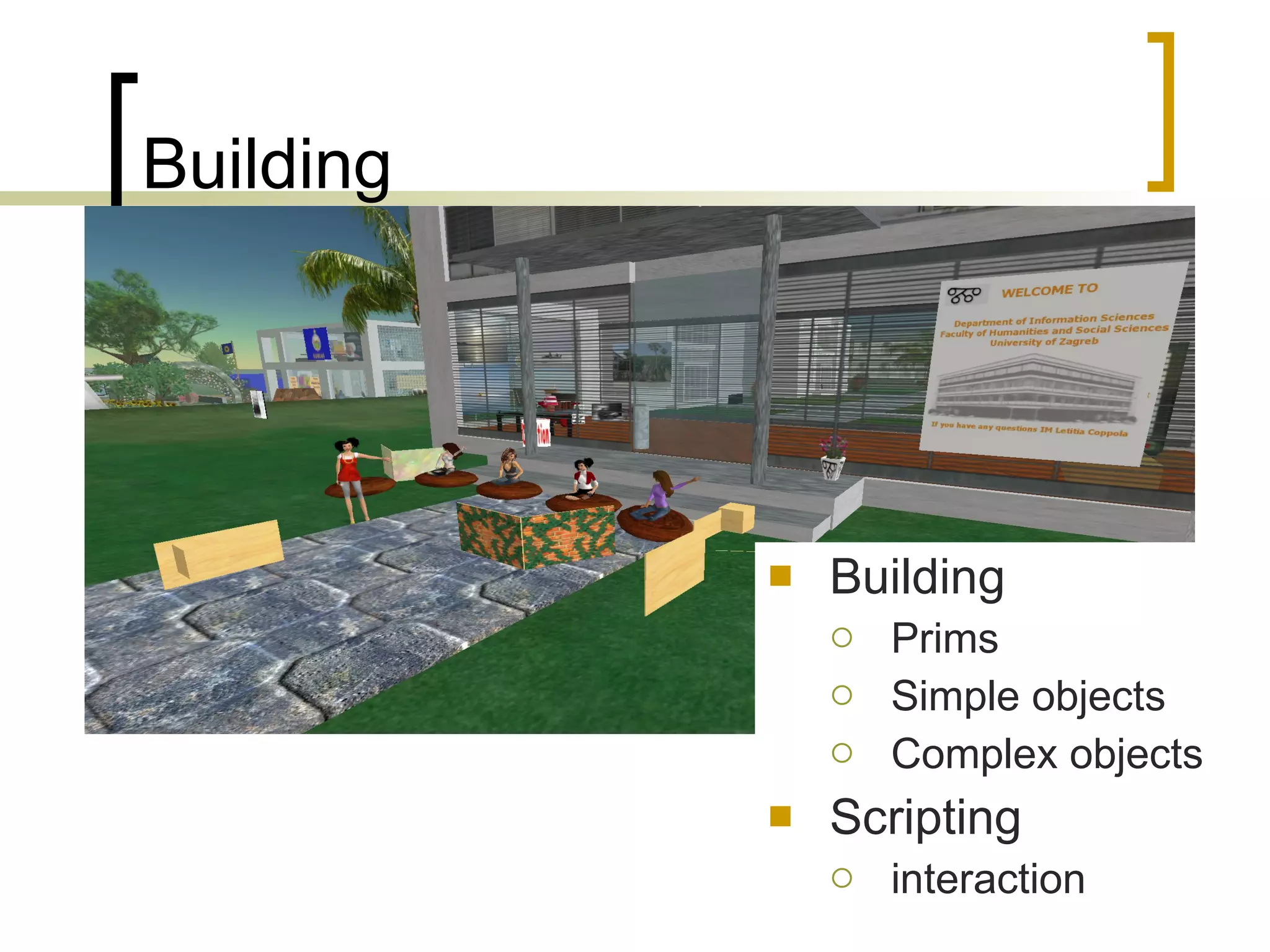
The document discusses the evolution of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 and the concept of Library 2.0 as a reaction to developments in information and communication technologies. It notes that most students are familiar with popular Web 2.0 tools like wikis, blogs, YouTube and social media, but less than half have knowledge of tools like Flickr, Delicious or Second Life. The document also discusses how the Department of Information Sciences at the University of Zagreb introduced new courses on information literacy and e-learning and how libraries and educational institutions are using virtual worlds like Second Life for teaching and learning.
![Jadranka Lasic-Lazic jlazic @ ffzg.hr Mihaela Banek Zorica mbanek @ ffzg.hr Sonja Spiranec [email_address] Department of Information sciences, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Universtiy of Zagreb, Croatia School librarians coping with electronic environment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/library2-090916150704-phpapp02/75/School-librarians-coping-with-electronic-environment-1-2048.jpg)