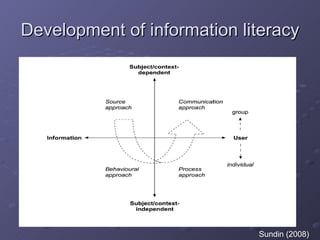
Information literacy is defined as the ability to locate, evaluate, and use information effectively in the modern knowledge society, evolving from basic tool-based skills to teaching competencies essential for lifelong learning. The shift from web 1.0 to web 2.0 has transformed information access and authority, emphasizing user-generated content and collaborative knowledge production. To adapt, educational institutions and librarians must integrate new literacies related to social networking and the evaluation of information authenticity into their programs.
![Information literacy 2.0 Mihaela Banek Zorica [email_address] Sonja Špiranec [email_address] University of Zagreb, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences Department of Information Sciences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/informationliteracy2mbz1slideshare-090916082651-phpapp01/85/Information-Literacy-2-0-1-320.jpg)