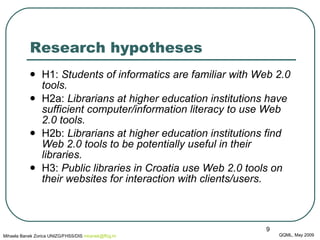
The document discusses the potential applications of Web 2.0 tools in improving communication and engagement between libraries and their clients. It presents research findings on the familiarity and utilization of Web 2.0 tools among students and librarians in Croatia, ultimately suggesting that libraries should adapt to these technologies to enhance user experience and interaction. The authors also propose curriculum changes in library and information science to better prepare future librarians for these developments.
![Potential Uses of Web 2.0 Tools for Library Client Communication and Relationship Development Jadranka Lasic-Lazic [email_address] Mihaela Banek Zorica [email_address] Goran Bubas [email_address] University of Zagreb, Croatia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qqmlmbz-090916081800-phpapp01/85/QQML-conference-presentation-1-320.jpg)