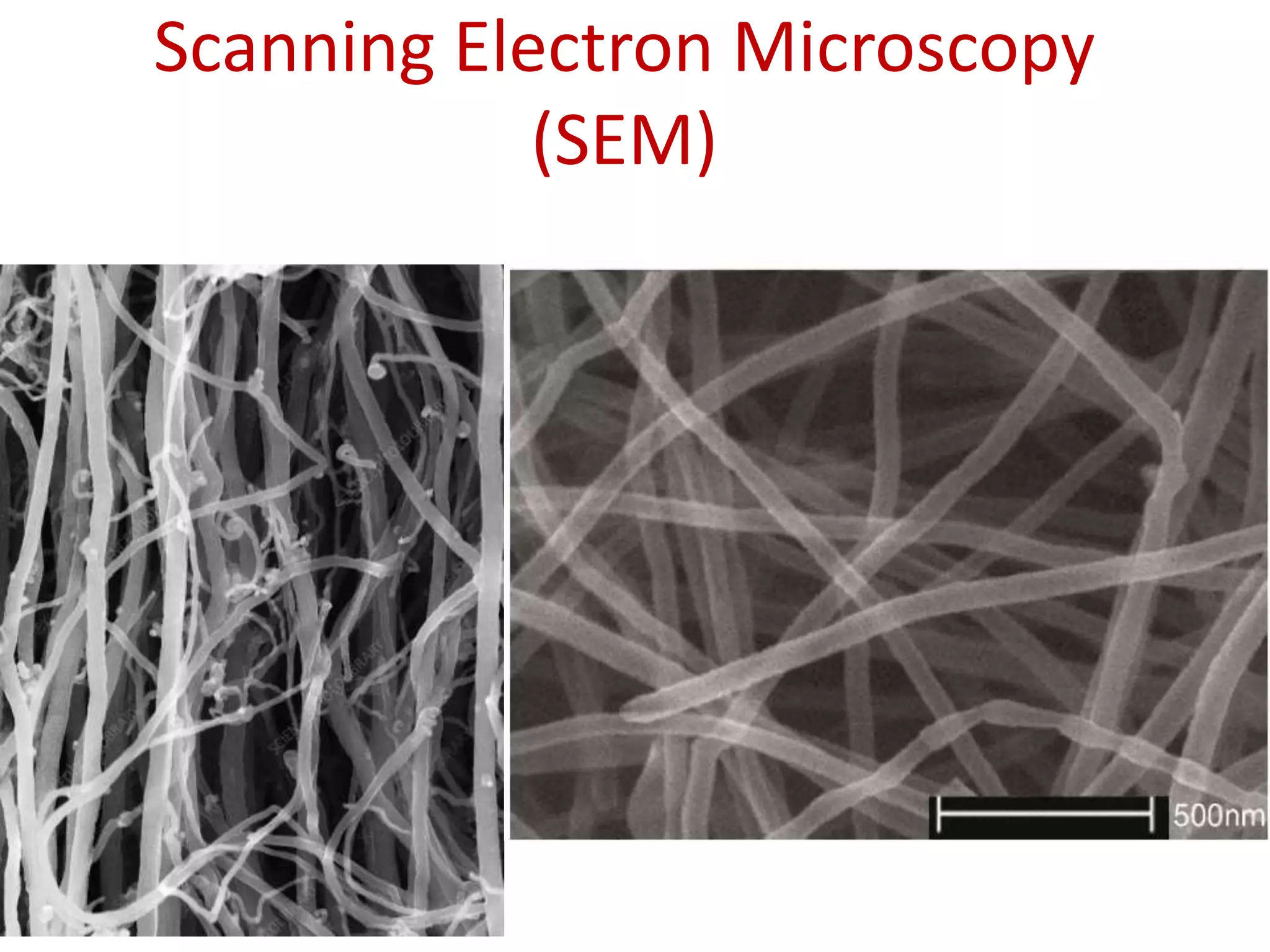
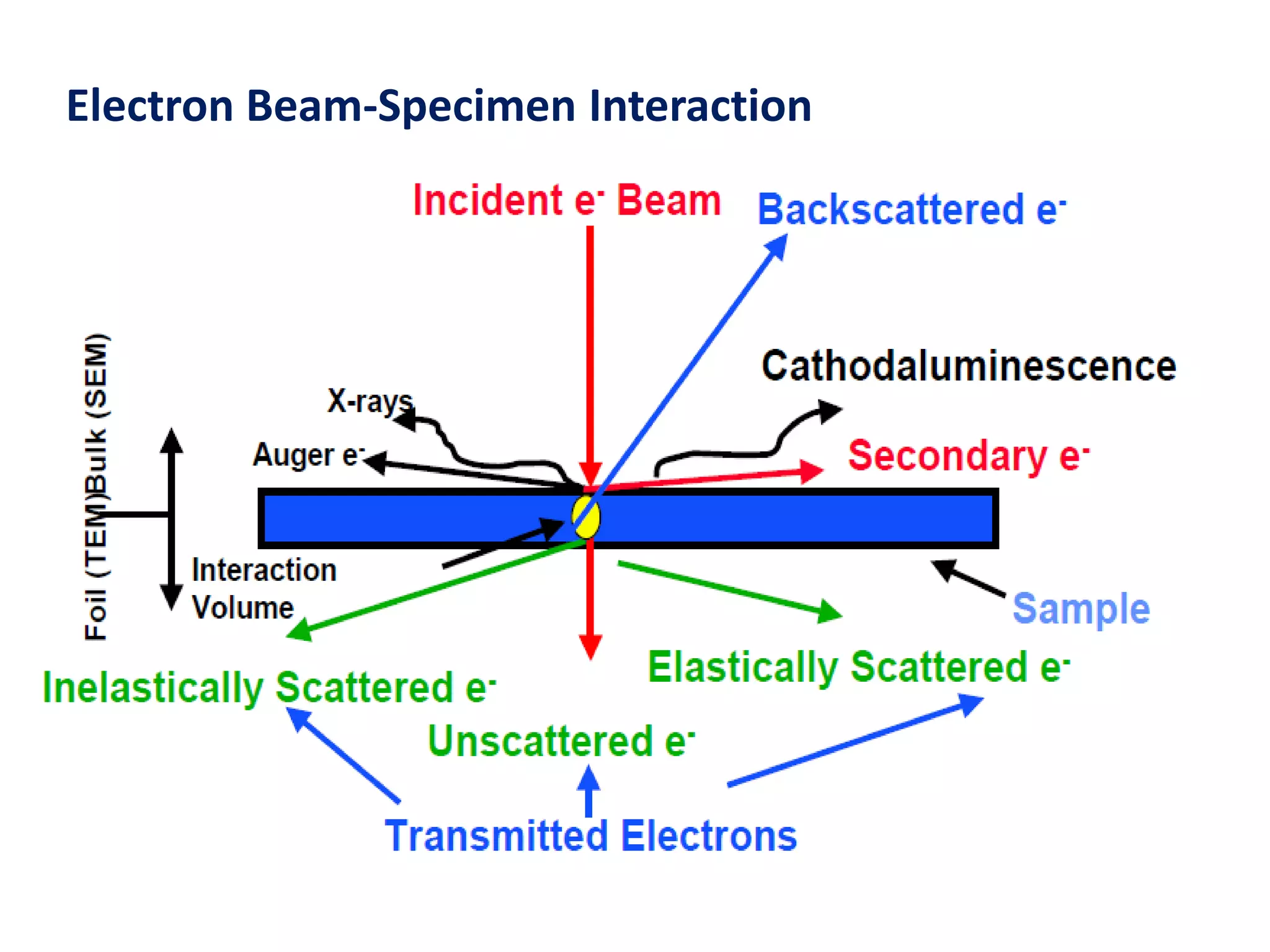
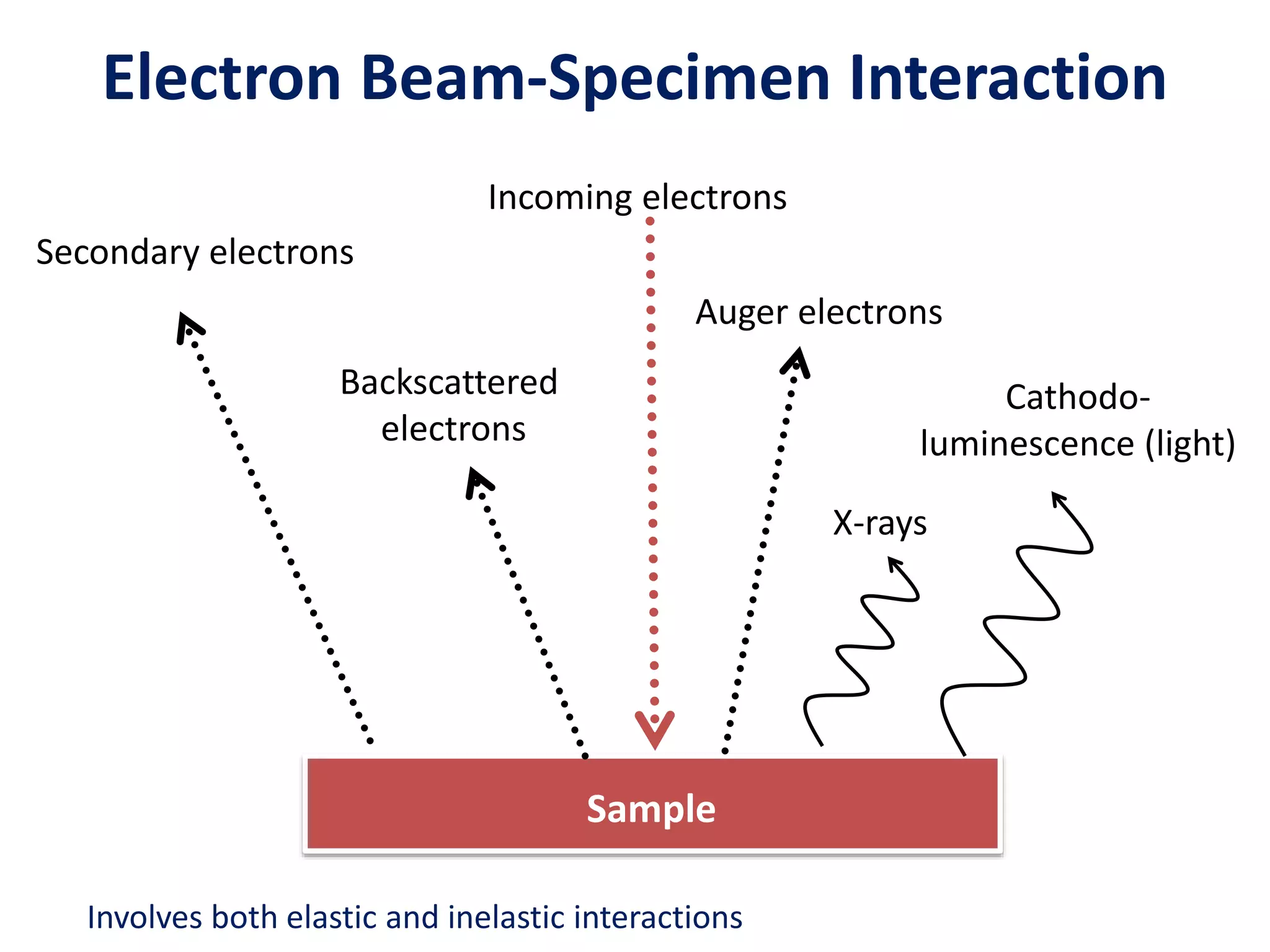
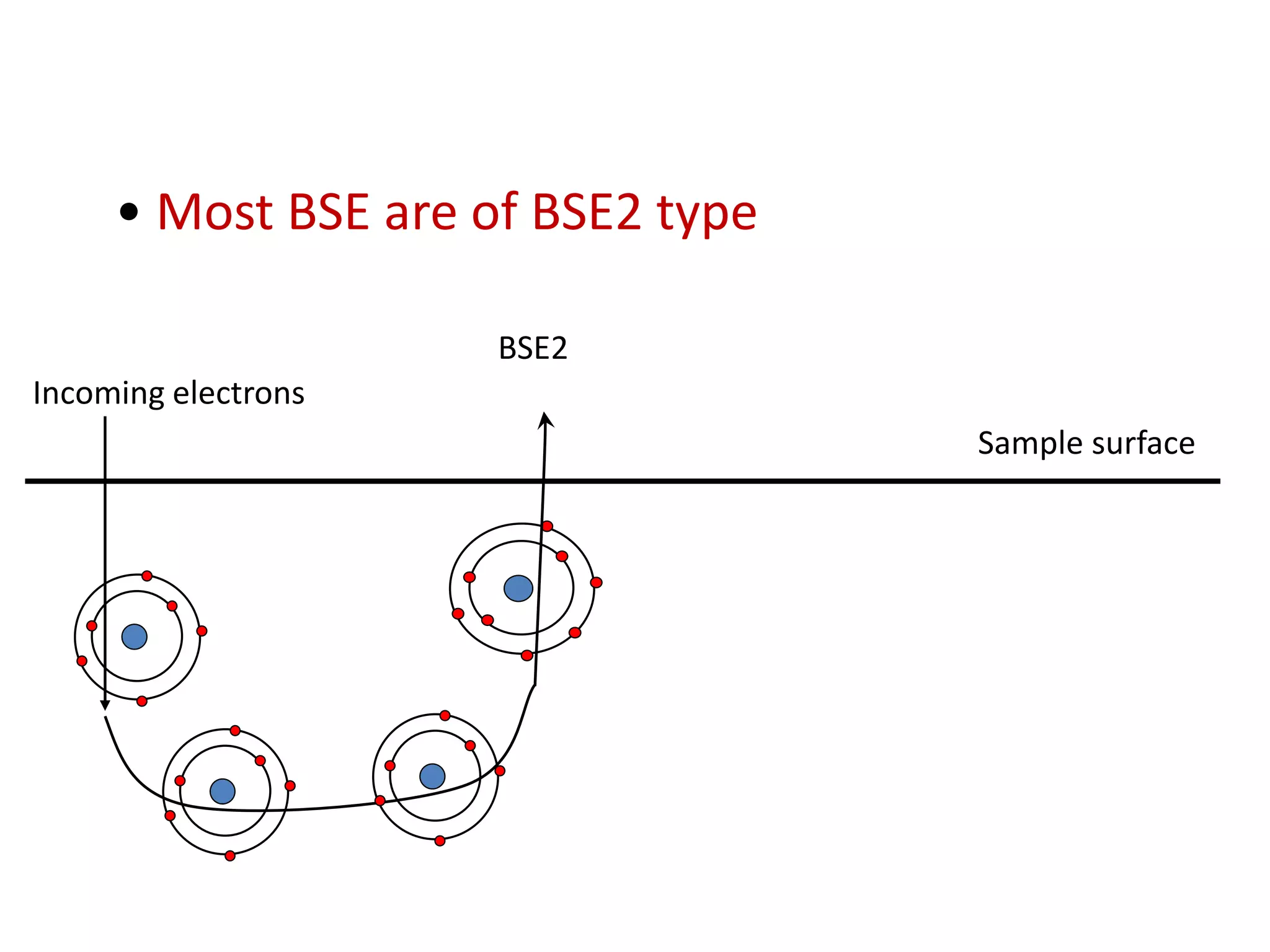
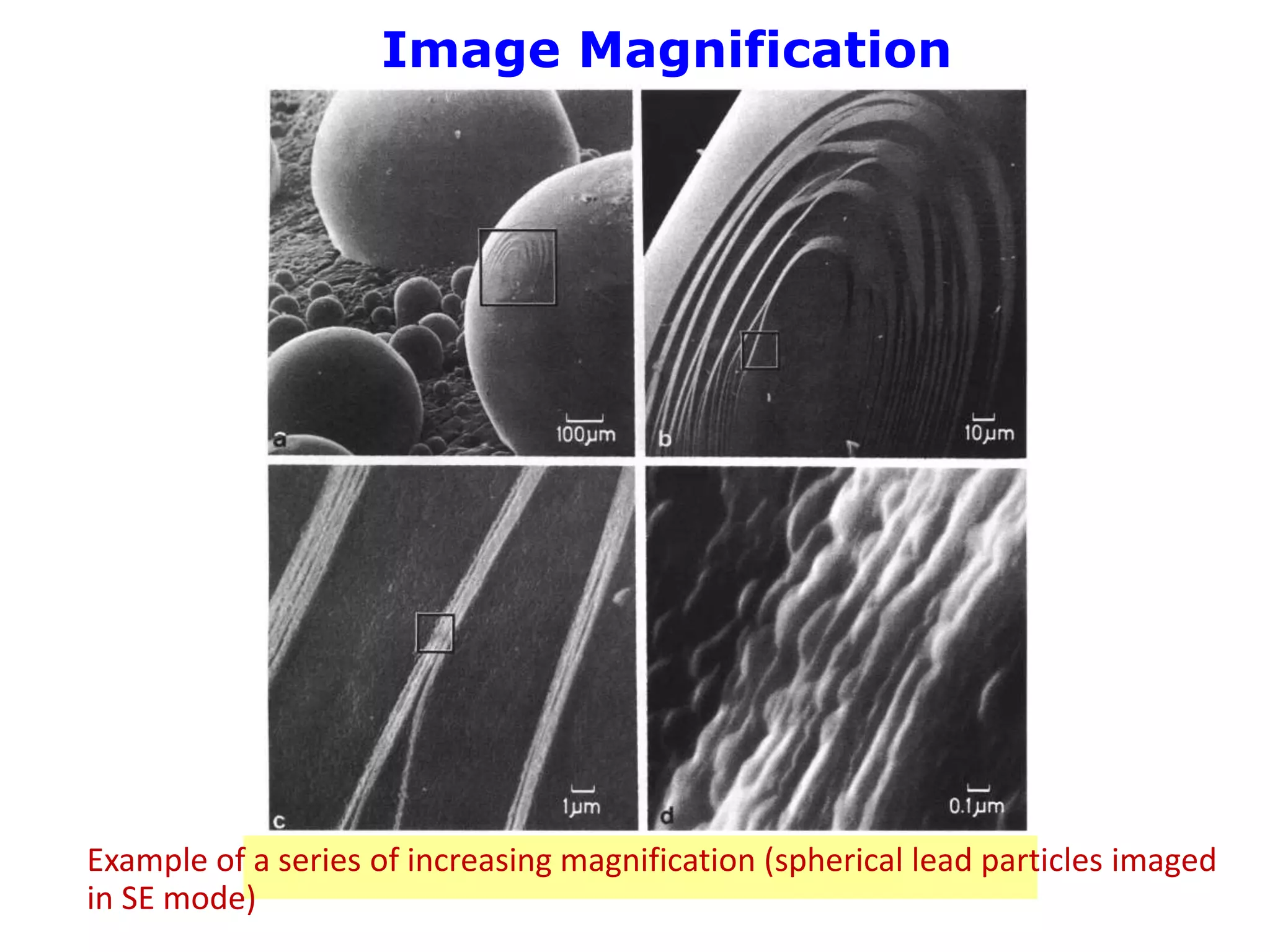
The document provides an overview of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It discusses the history and development of SEM, describing how early SEMs from the 1940s had lower resolution (~50 nm) and only provided morphological information, while modern SEMs can achieve ~10 nm resolution and also provide analytical capabilities. The document explains how SEM works, including how the electron beam interacts with and penetrates the sample, generating various signals like secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, and X-rays from within the interaction volume. It describes the components of an SEM, such as the electron gun, magnetic lenses for beam focusing, detectors for signals, and how changing microscope parameters can affect resolution and depth of field.