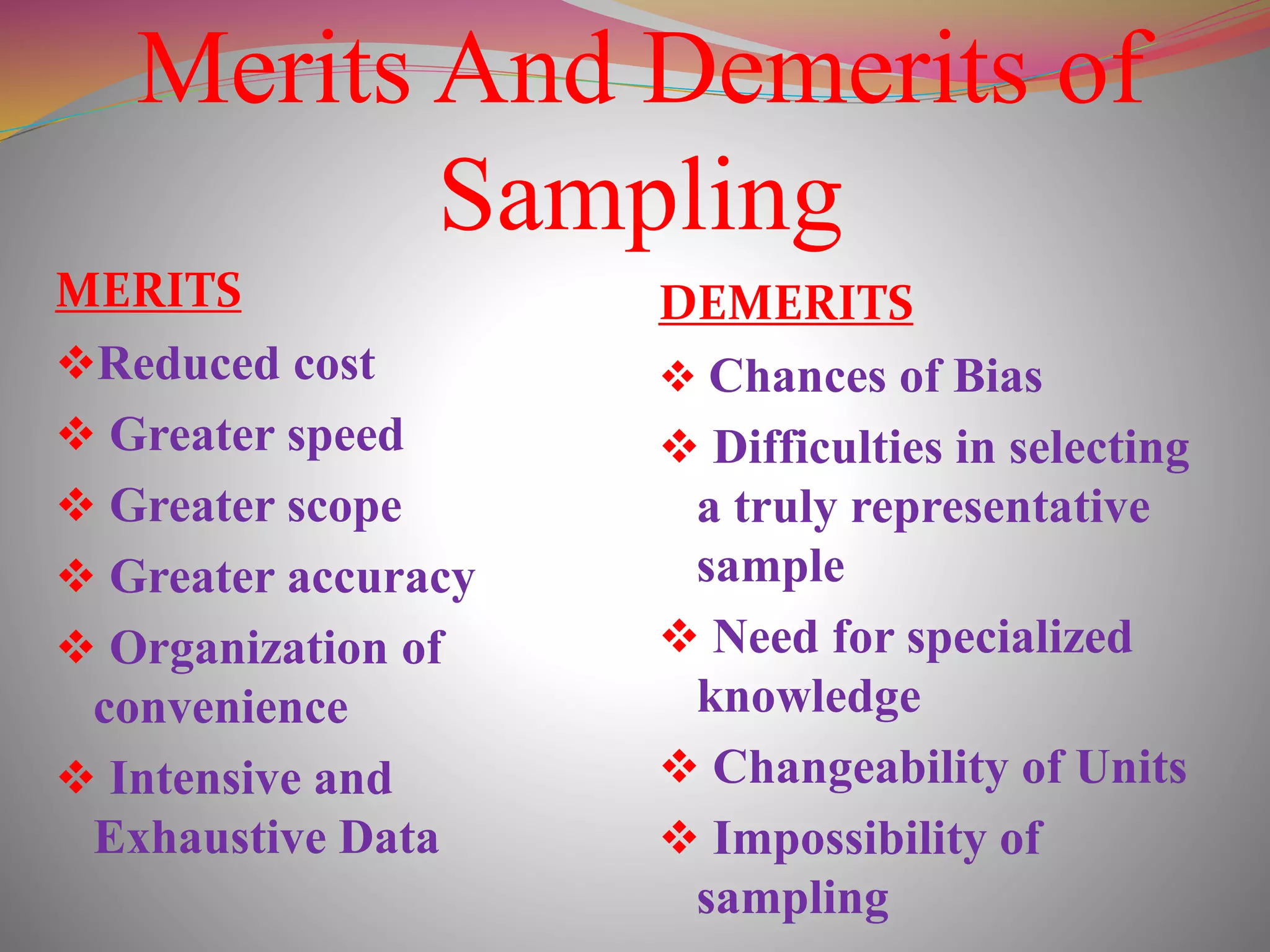
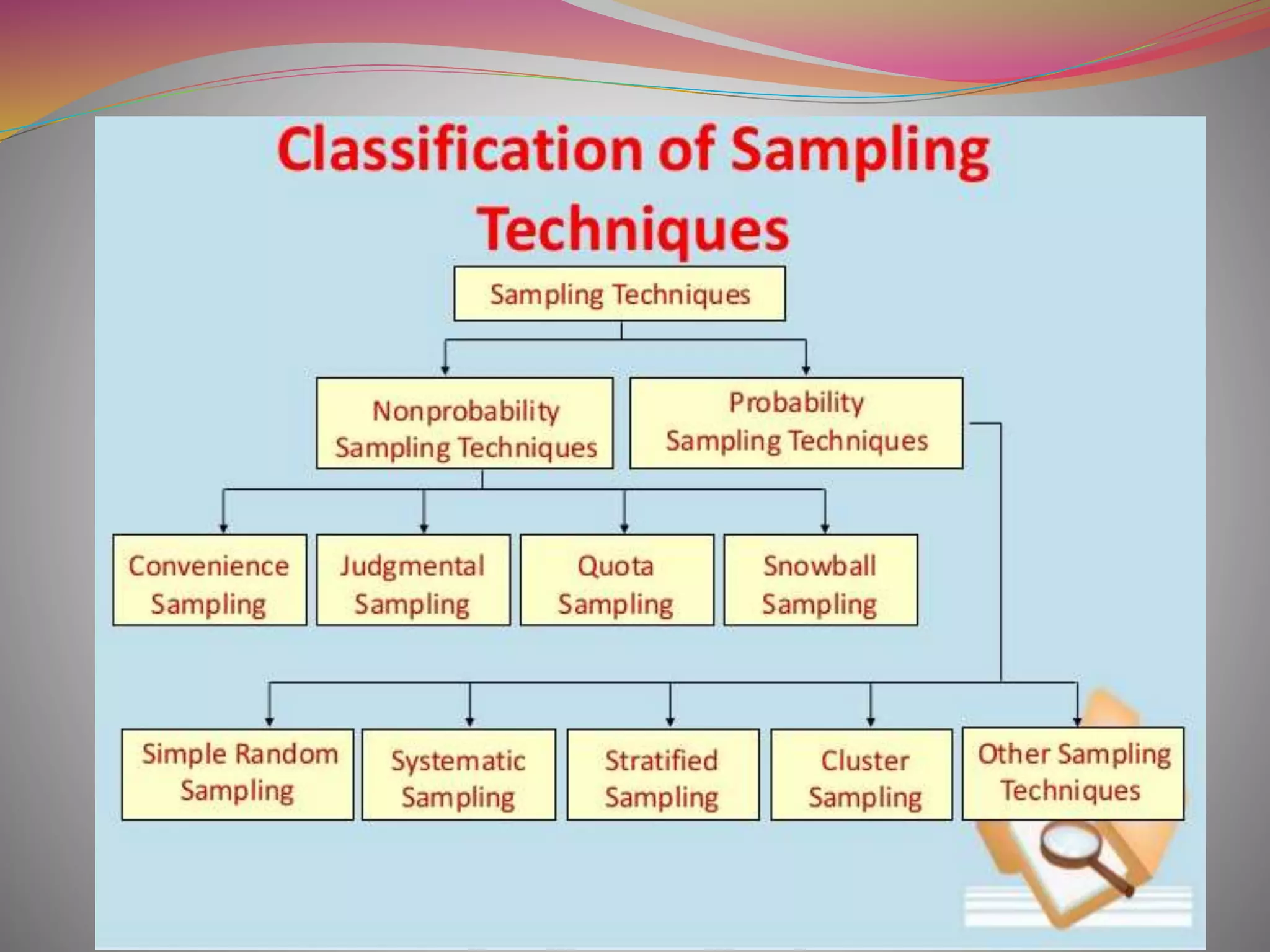
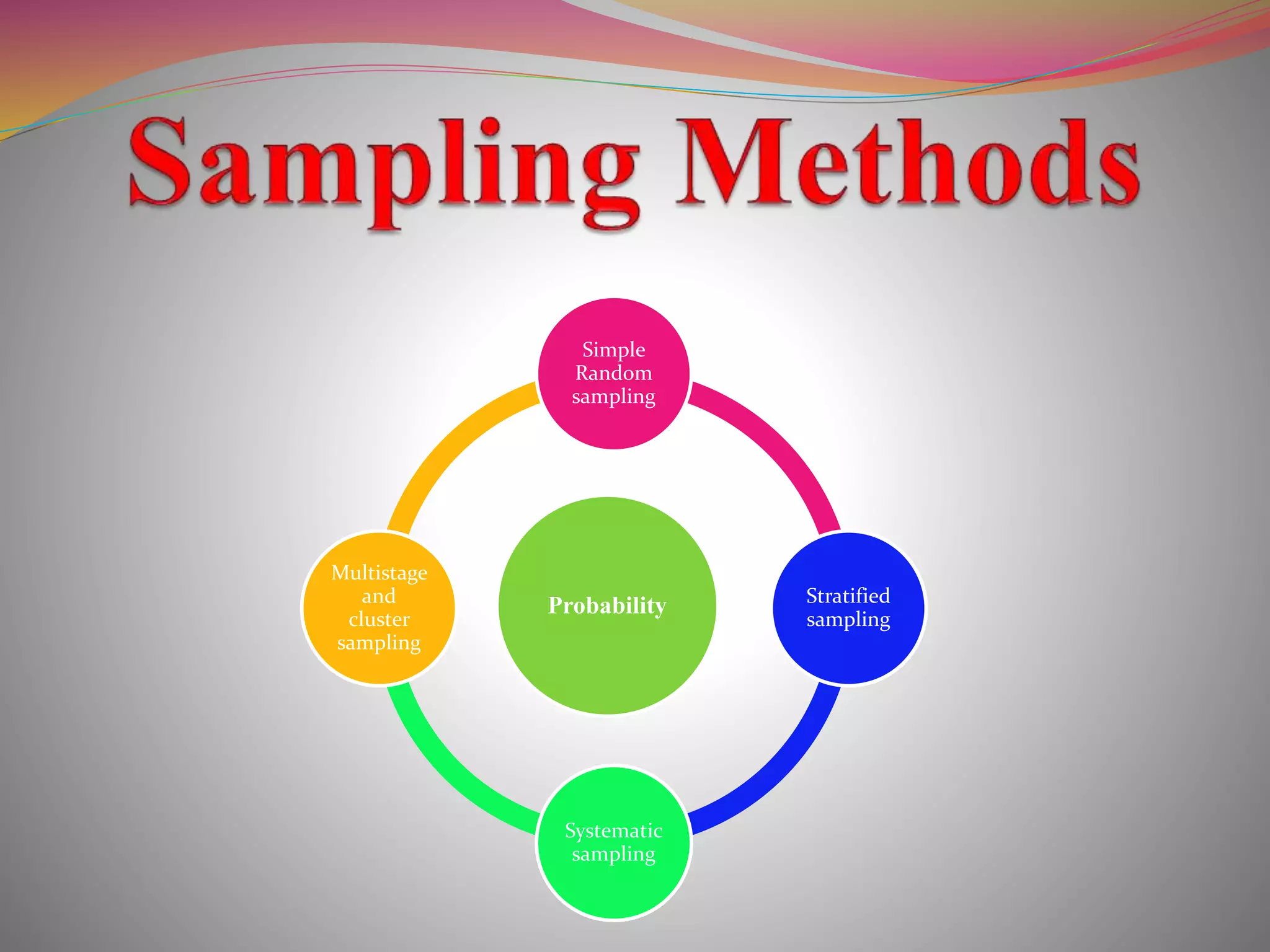
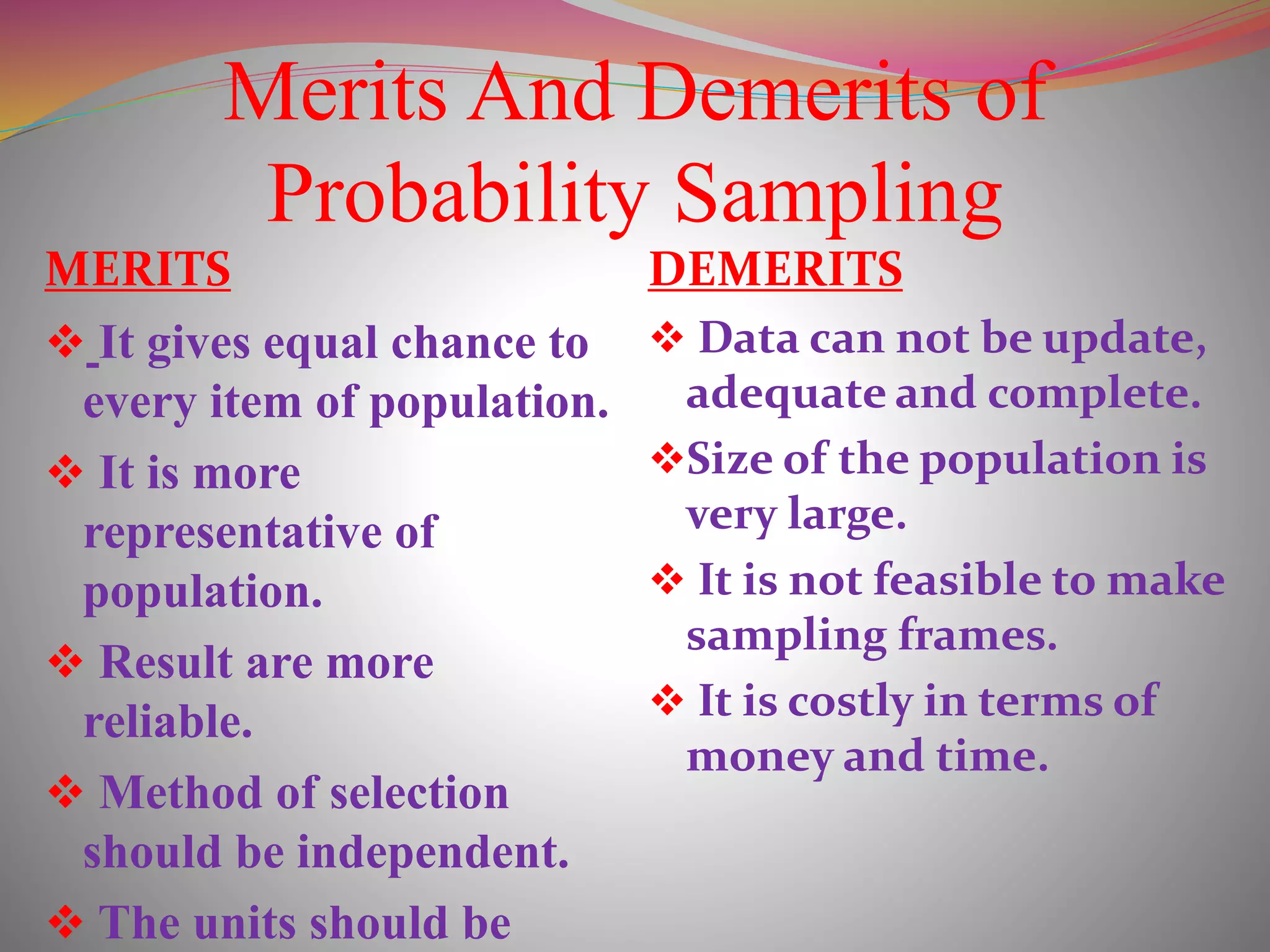
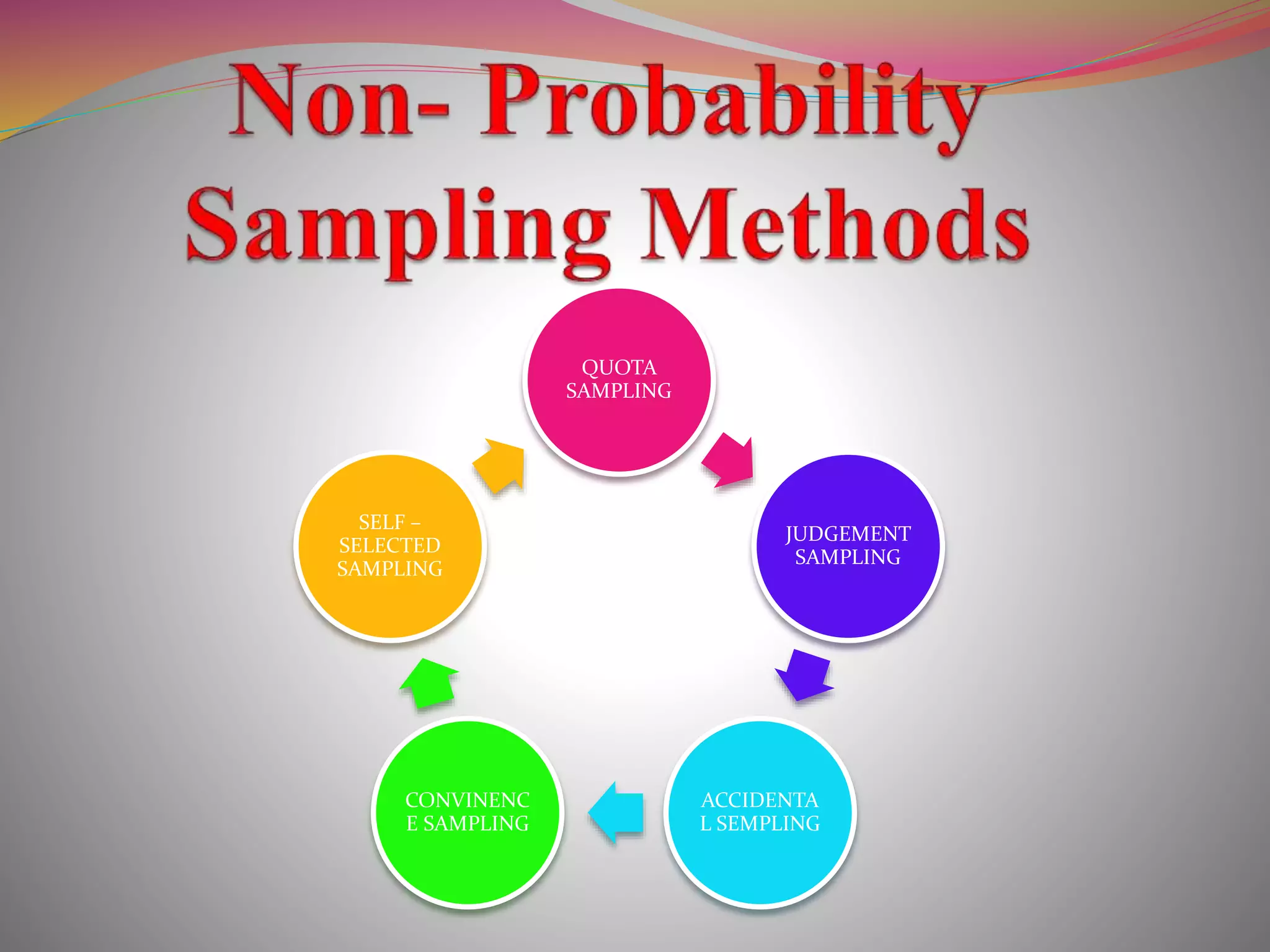
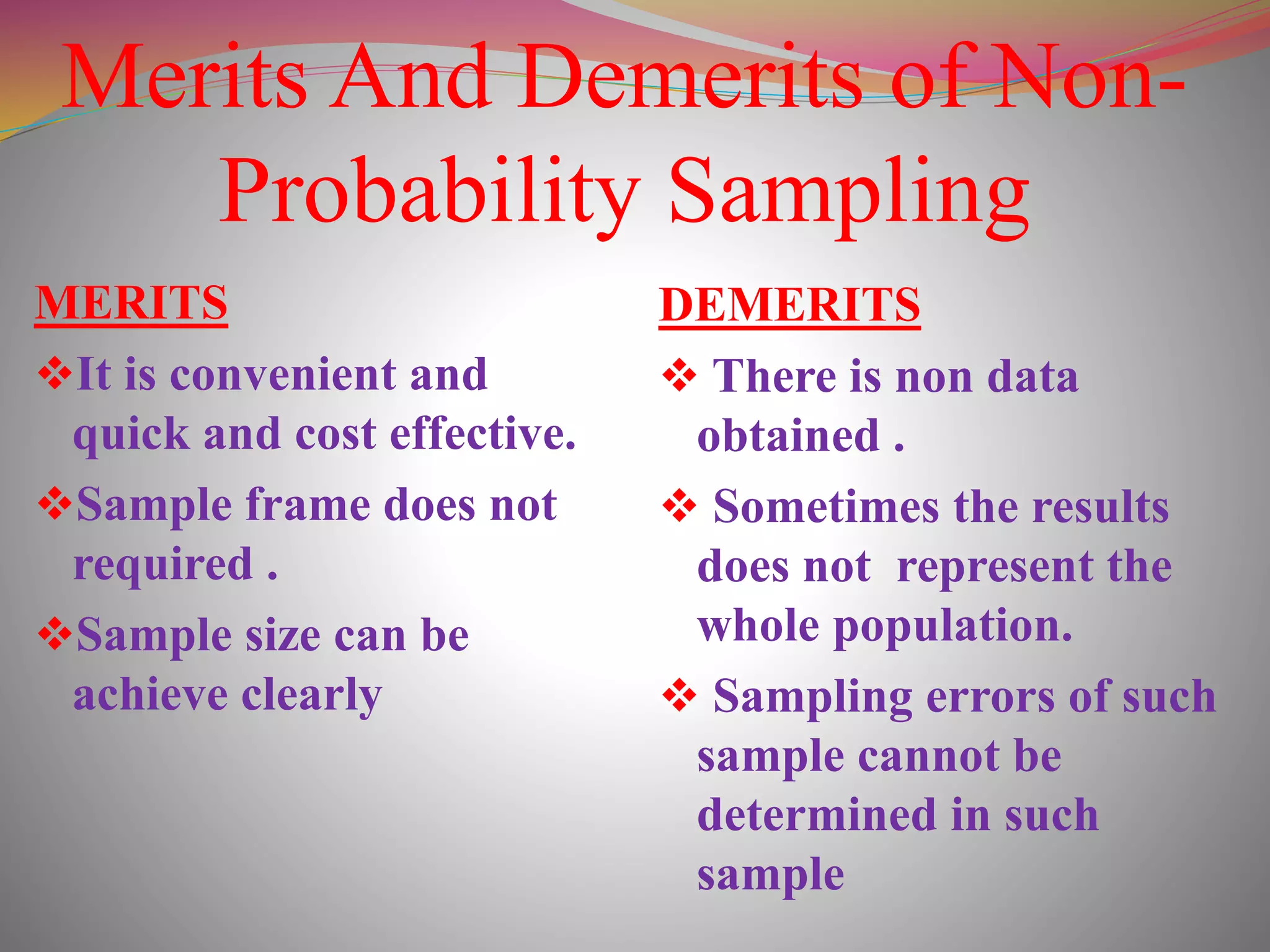
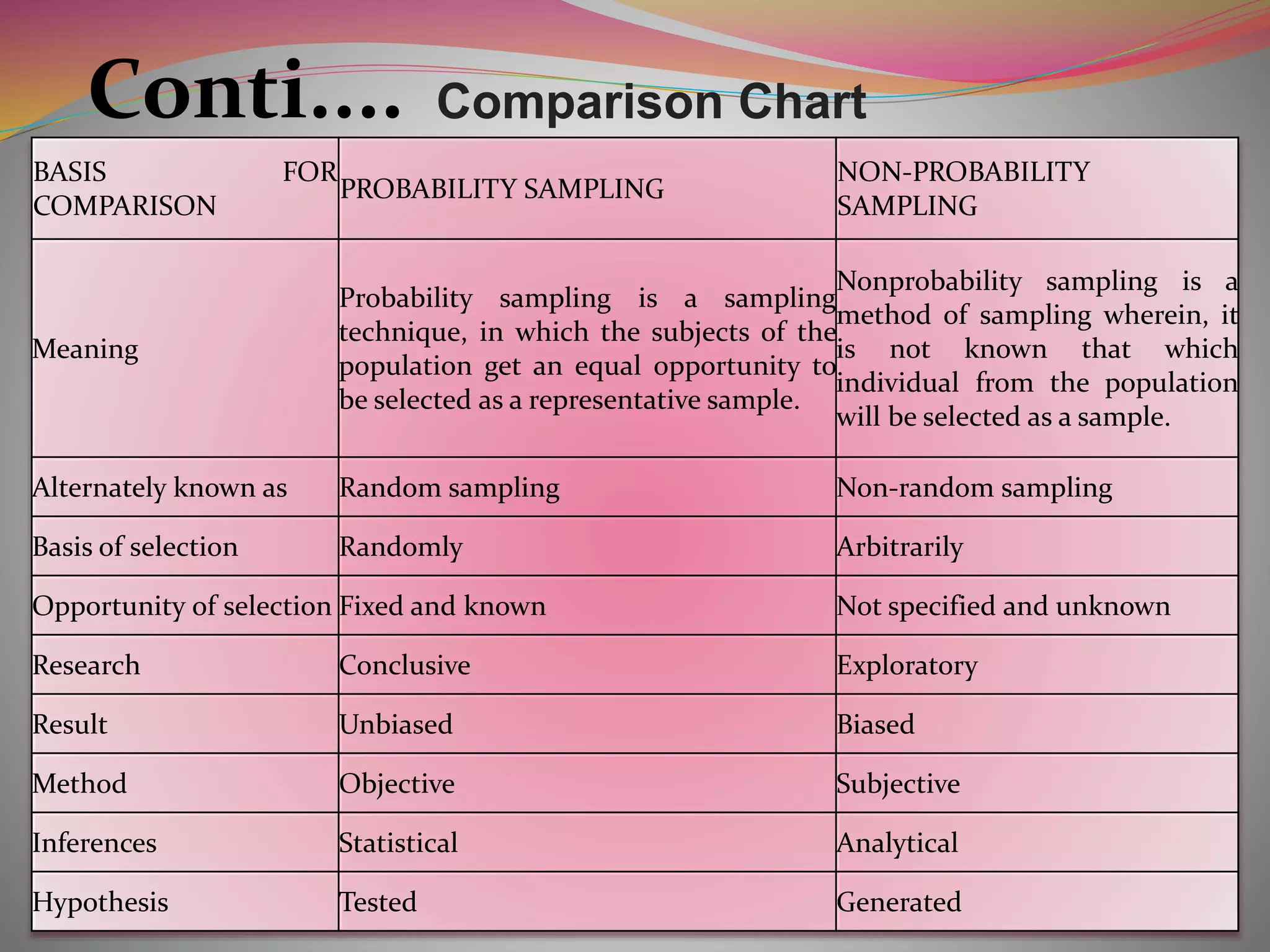
The document discusses the concepts of population and sampling, outlining various methods of sampling such as simple random, stratified, and cluster sampling, along with their merits and demerits. It contrasts probability sampling, which provides equal chances for every item in the population, with non-probability sampling, which lacks a systematic selection process and is often more subjective. Additionally, the document describes the steps in the sampling process and the importance of achieving representative and unbiased samples.