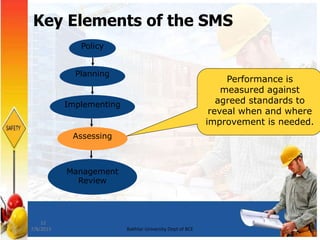
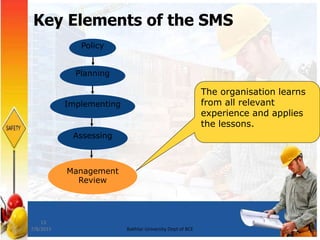
An SMS is a comprehensive, integrated system that ensures all work at a facility is conducted safely. It comprises work practices and procedures for monitoring and improving safety. Key elements include a safety policy, planning, implementing controls, assessing performance, and management review. The SMS should define roles, maintain hazard awareness, plan controls, set improvement targets, manage change, and review itself. Performance is measured against standards to identify areas for improvement.