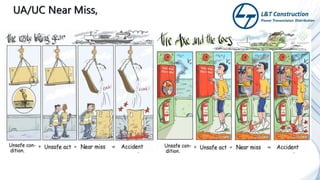
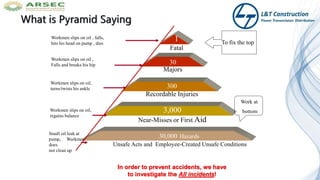
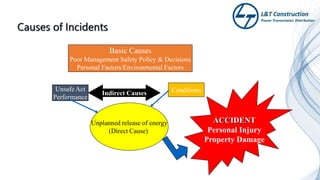
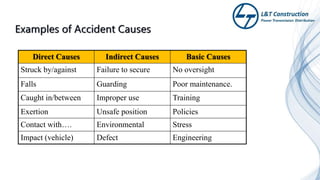
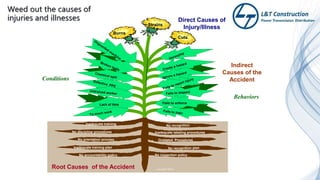
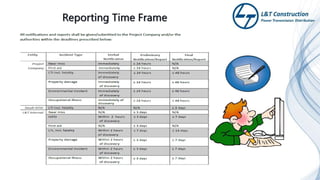
The document outlines the objectives and procedures for accident investigation and reporting in L&T Construction's power transmission and distribution projects in Saudi Arabia. It emphasizes the importance of investigating incidents to determine root causes and implement preventive measures to enhance health and safety. The training covers definitions of accidents and incidents, their consequences, investigation procedures, and the analysis needed to prevent future occurrences.