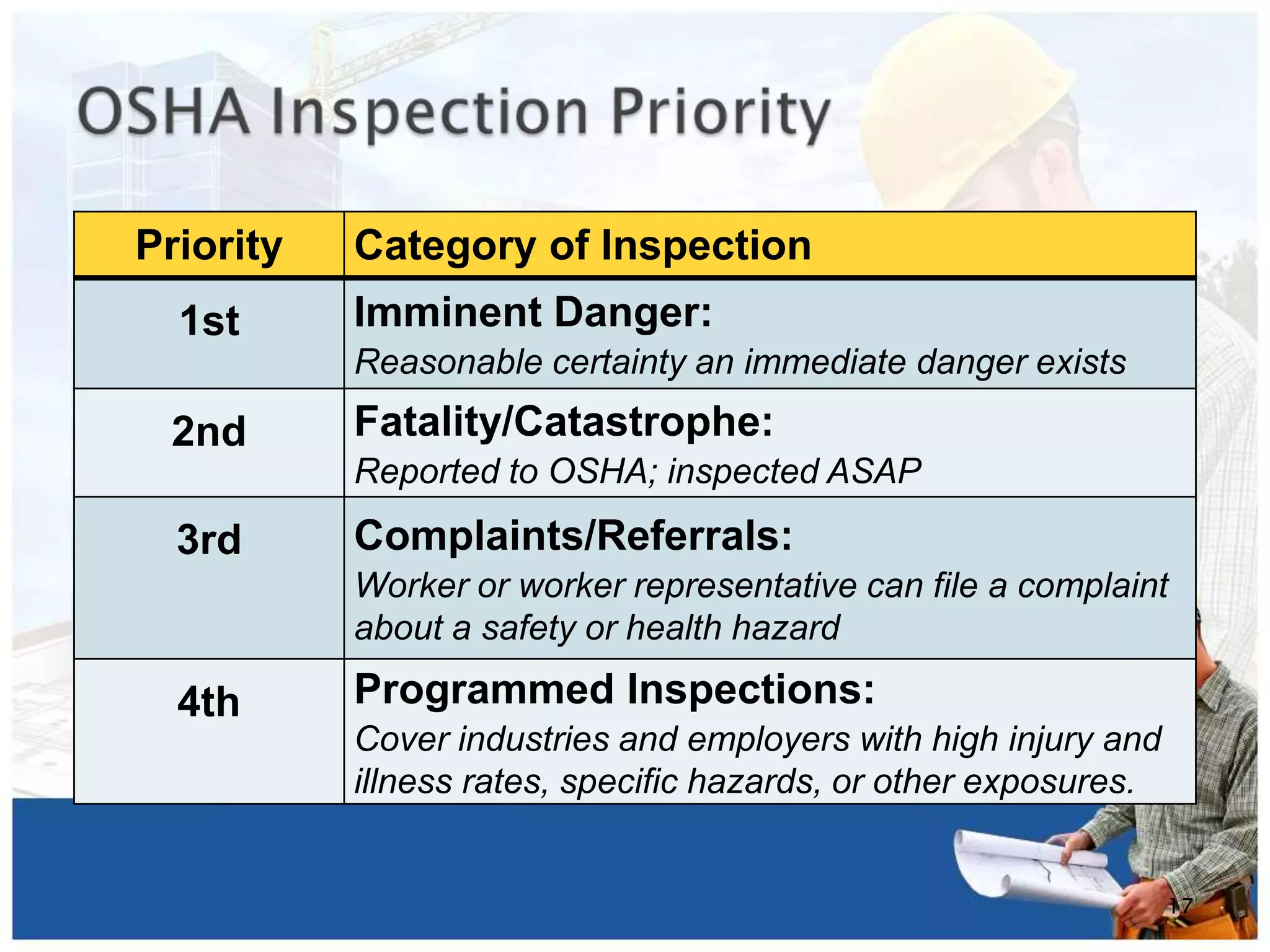
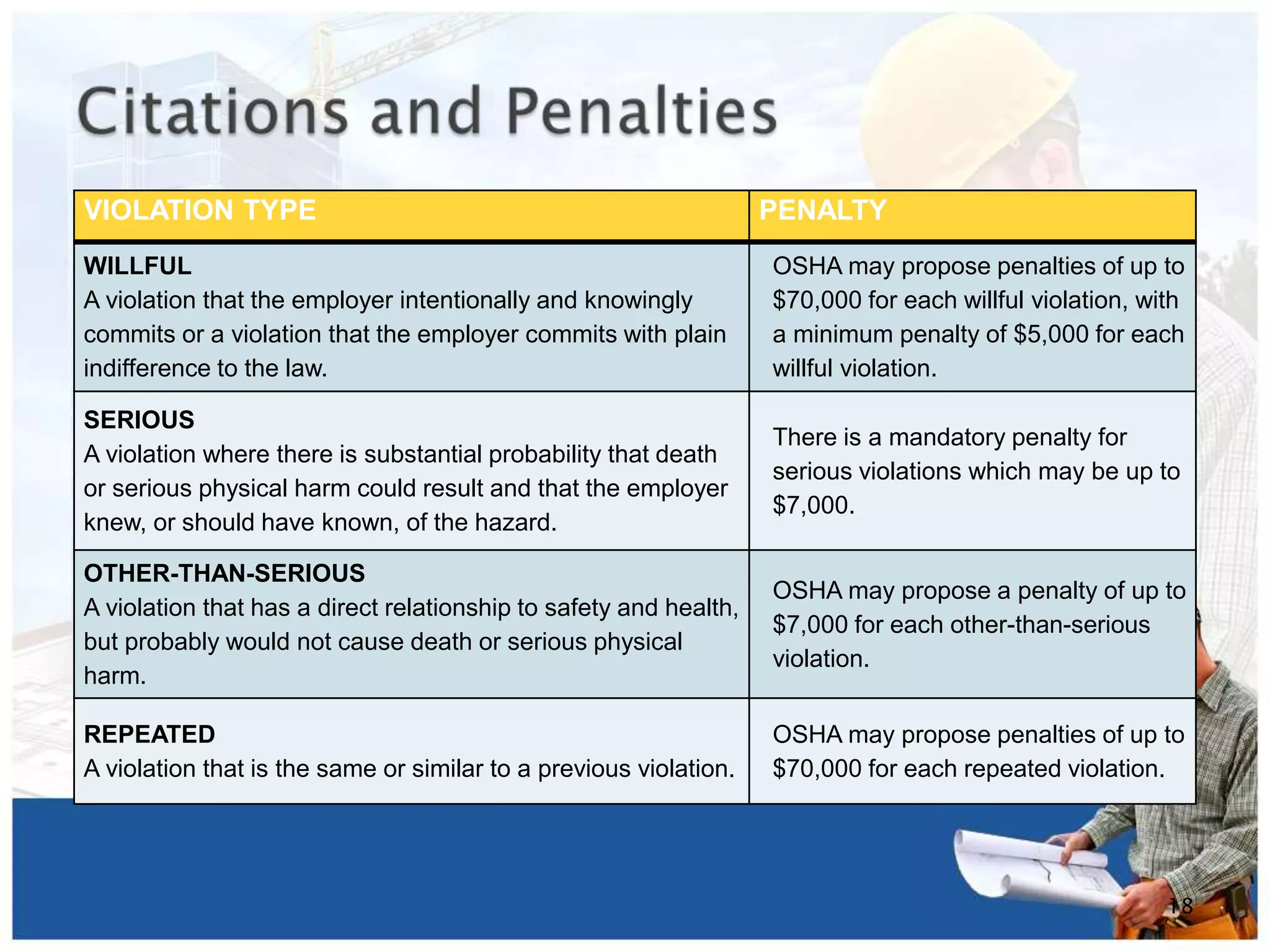
This document provides an overview of OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) in 3 sentences: OSHA is a US government agency tasked with ensuring worker safety and health. It was created in 1971 and gives workers rights like a safe workplace, hazard information and complaint procedures. The document outlines OSHA's mission and topics like employer responsibilities, inspection processes, and where to find help regarding workplace safety and health issues.








![• Workers may bring up safety and health concerns in the workplace to their
employers without fear of discharge or discrimination, as long as the
complaint is made in good faith.
• OSHA regulations [29CFR 1977.9(c)] protect workers who complain to
their employer about unsafe or unhealthful conditions in the workplace.
9
Your Right to…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lectur2-150708072406-lva1-app6892/75/Introduction-to-OSHA-9-2048.jpg)