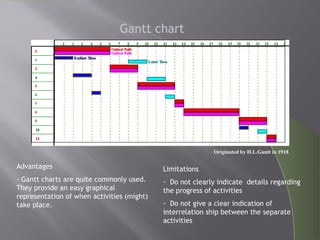
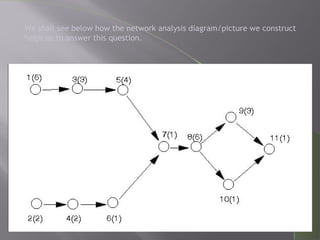
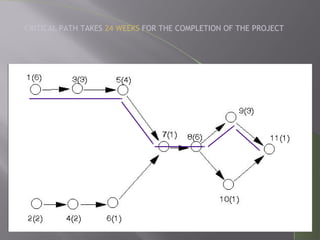
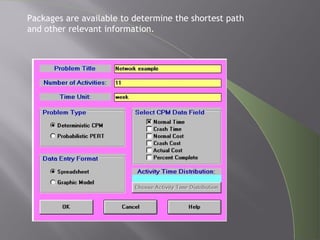
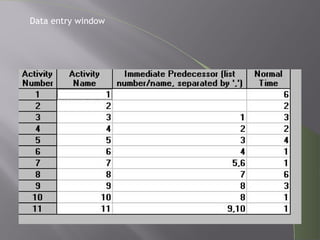
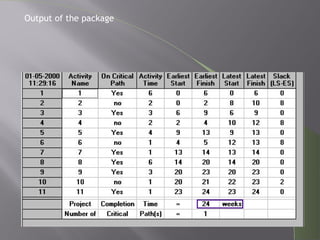
CPM and PERT are network analysis techniques developed in the 1950s to schedule complex projects. CPM was developed by DuPont for chemical plants and focuses on cost/time tradeoffs. PERT was developed by the US Navy for the Polaris missile program to minimize time. Both use networks of activities and precedence relationships but PERT uses probabilistic time estimates to handle uncertainty while CPM uses deterministic estimates. They are now combined techniques useful for project scheduling.