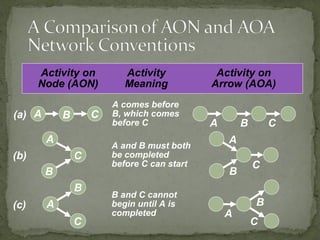
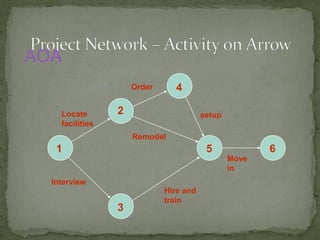
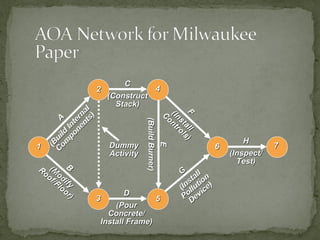
This document discusses project management techniques like PERT and CPM. It explains that PERT and CPM use network diagrams to analyze the sequence and duration of project activities to determine the critical path and project duration. The document provides examples of network diagrams and describes key aspects of PERT/CPM like crashing activities to shorten the project duration.