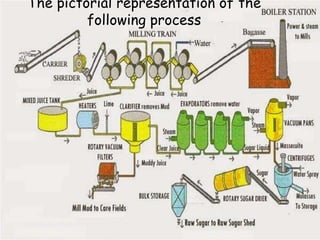
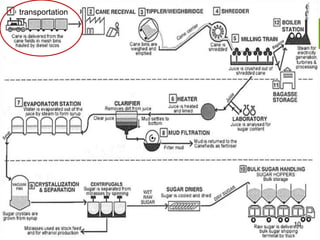
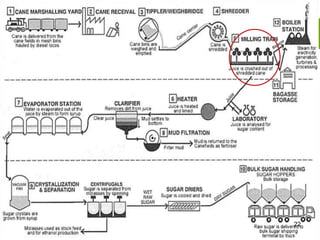
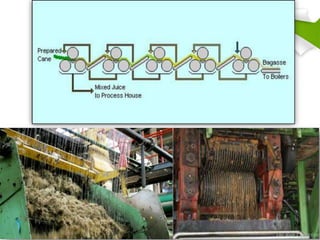
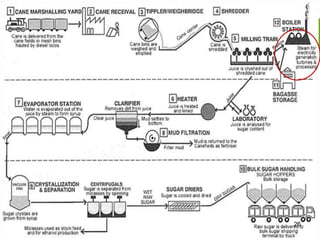
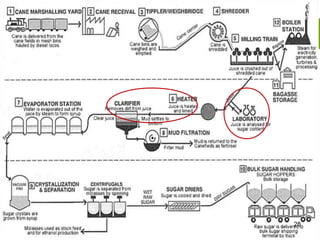
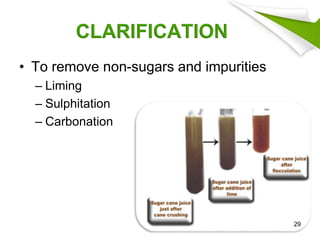
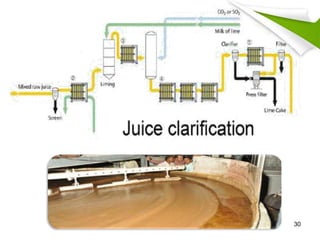
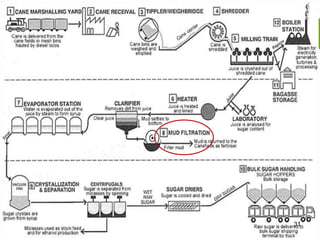
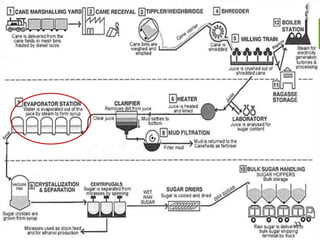
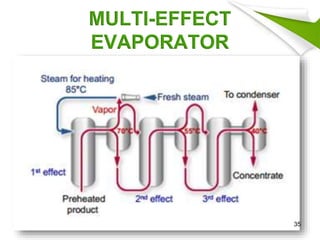
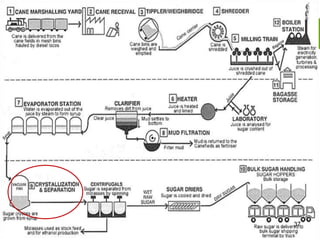
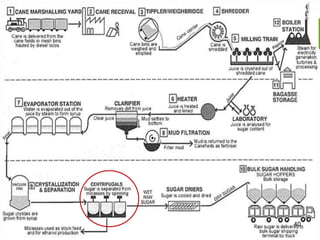
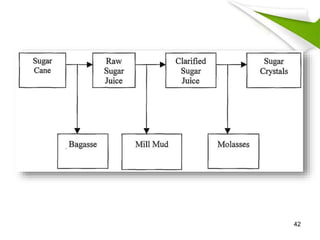
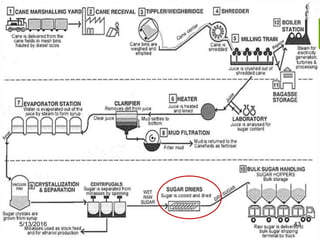
This document summarizes the process for harvesting and refining sugar from sugarcane. Sugarcane is first brought to a factory where it is cleaned, cut, and shredded. It is then crushed and passed through milling tandems to extract the juice. The leftover bagasse is used as fuel. The juice undergoes clarification, filtration, and evaporation to increase concentration. It is then crystallized and centrifuged to separate sugar crystals from molasses. The raw sugar is dried, packaged, and may undergo further refining. Factors like temperature, moisture, and light can affect sugar storage.