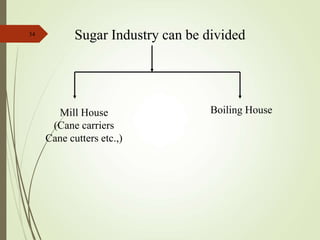
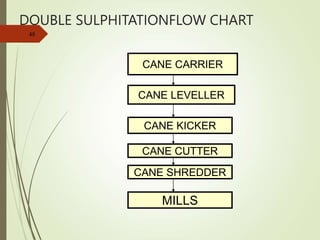
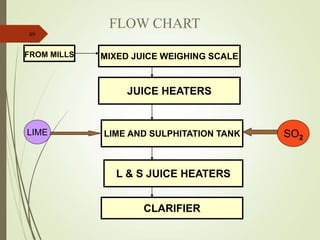
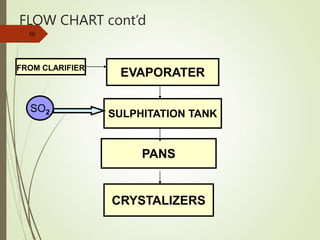
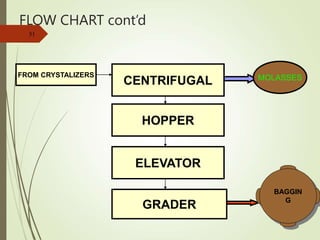
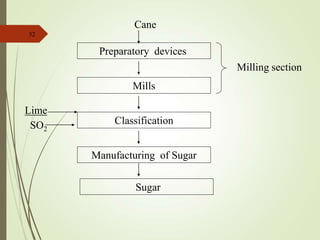
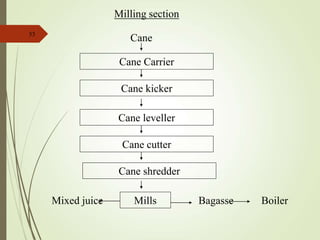
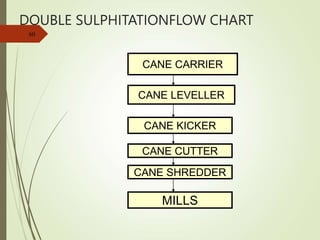
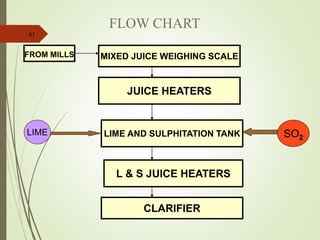
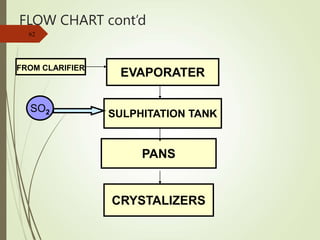
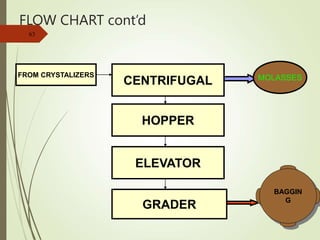
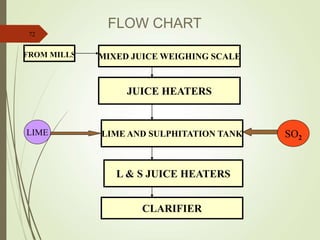
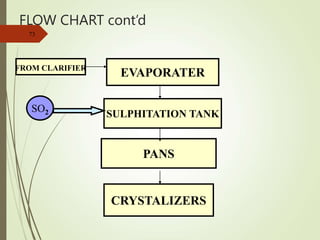
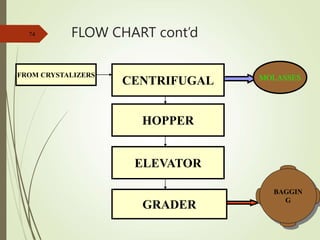
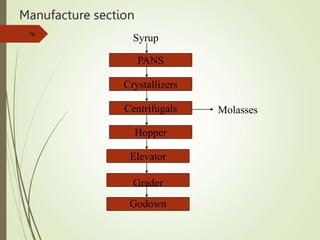
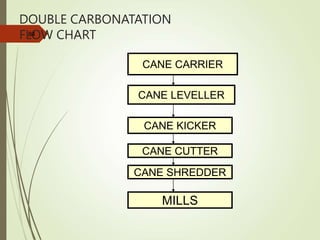
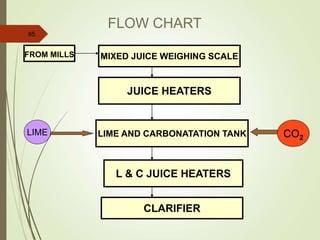
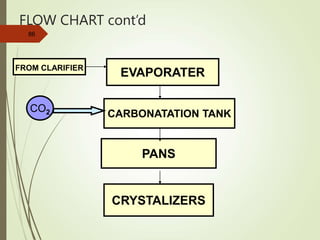
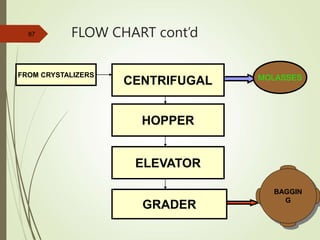
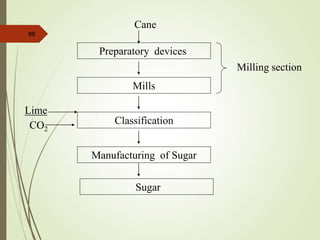
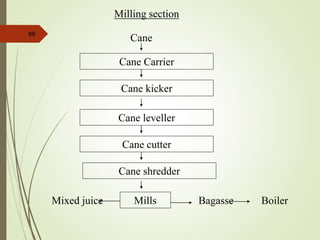
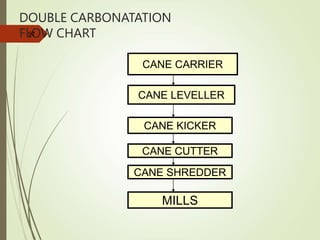
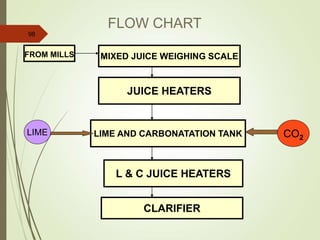
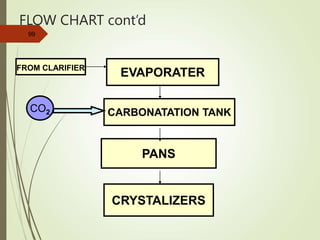
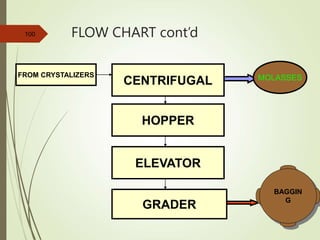
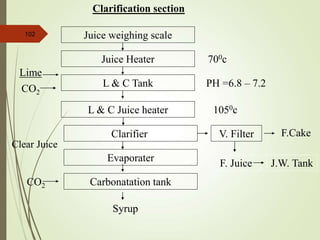
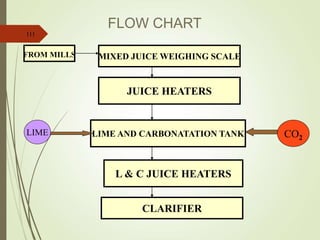
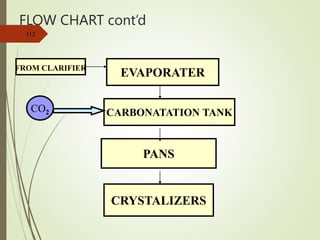
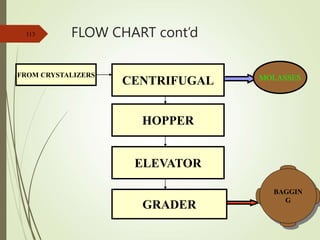
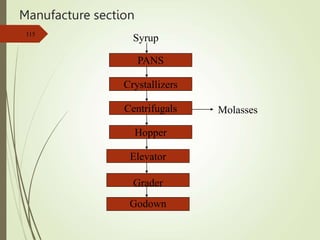
The document defines various terms used in the sugar industry and describes the processes involved. It discusses the mill house where cane is prepared and milled to extract mixed juice. It then describes the boiling house where the juice undergoes clarification, evaporation to produce syrup, sulphitation, boiling in pans to produce massecuite, and centrifuging to separate sugar crystals from molasses. A flow chart illustrates the double sulphitation process from cane preparation through sugar production and byproducts.