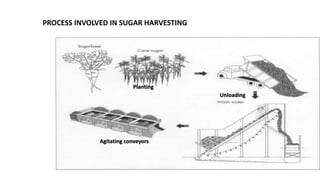
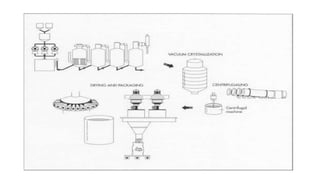
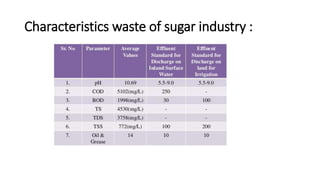
The sugar industry processes sugarcane and sugar beets to extract and refine sucrose into white table sugar. The manufacturing process involves planting, harvesting, preparation, juice extraction, purification, crystallization, centrifuging, drying and packaging. Byproducts include bagasse used as fuel in the factories and molasses used in cattle feed and products like rum. Wastewater from the industry is treated using aerobic or anaerobic methods to remove pollutants before discharge.