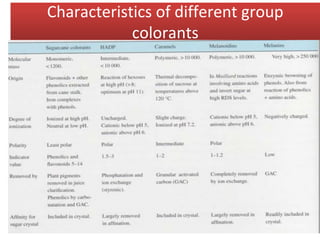
This document summarizes the key steps in sugar refining: affination removes adhering molasses film from raw sugar crystals using mechanical rubbing and dissolving in green syrup; carbonation and phosphatation remove impurities through precipitation and flocculation; sulfitation eliminates coloring matter; and decolorization processes like ion exchange, bone char, and activated carbon systems are used to remove color. The document provides details on equipment and process parameters used at each main stage of sugar refining.