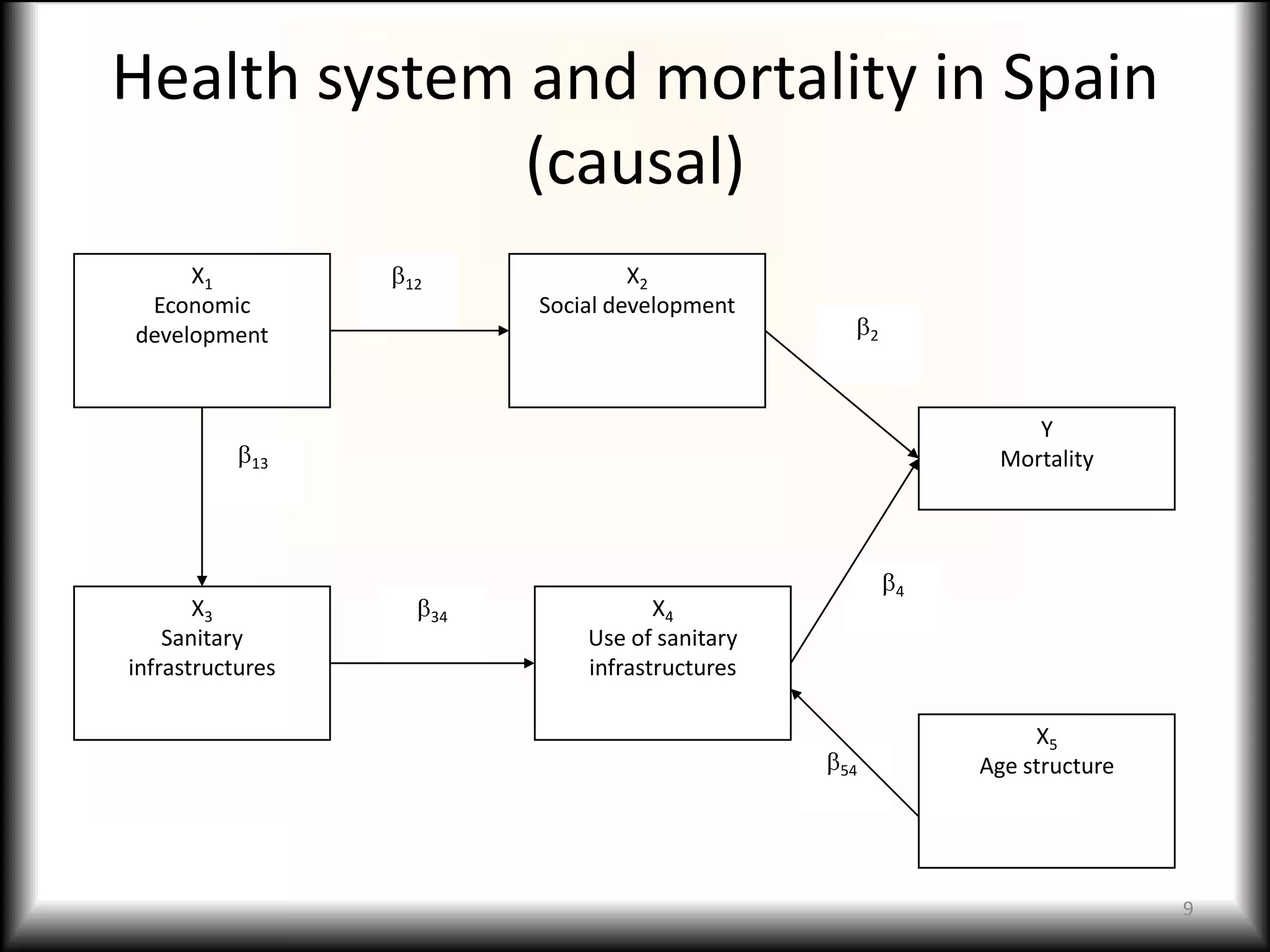
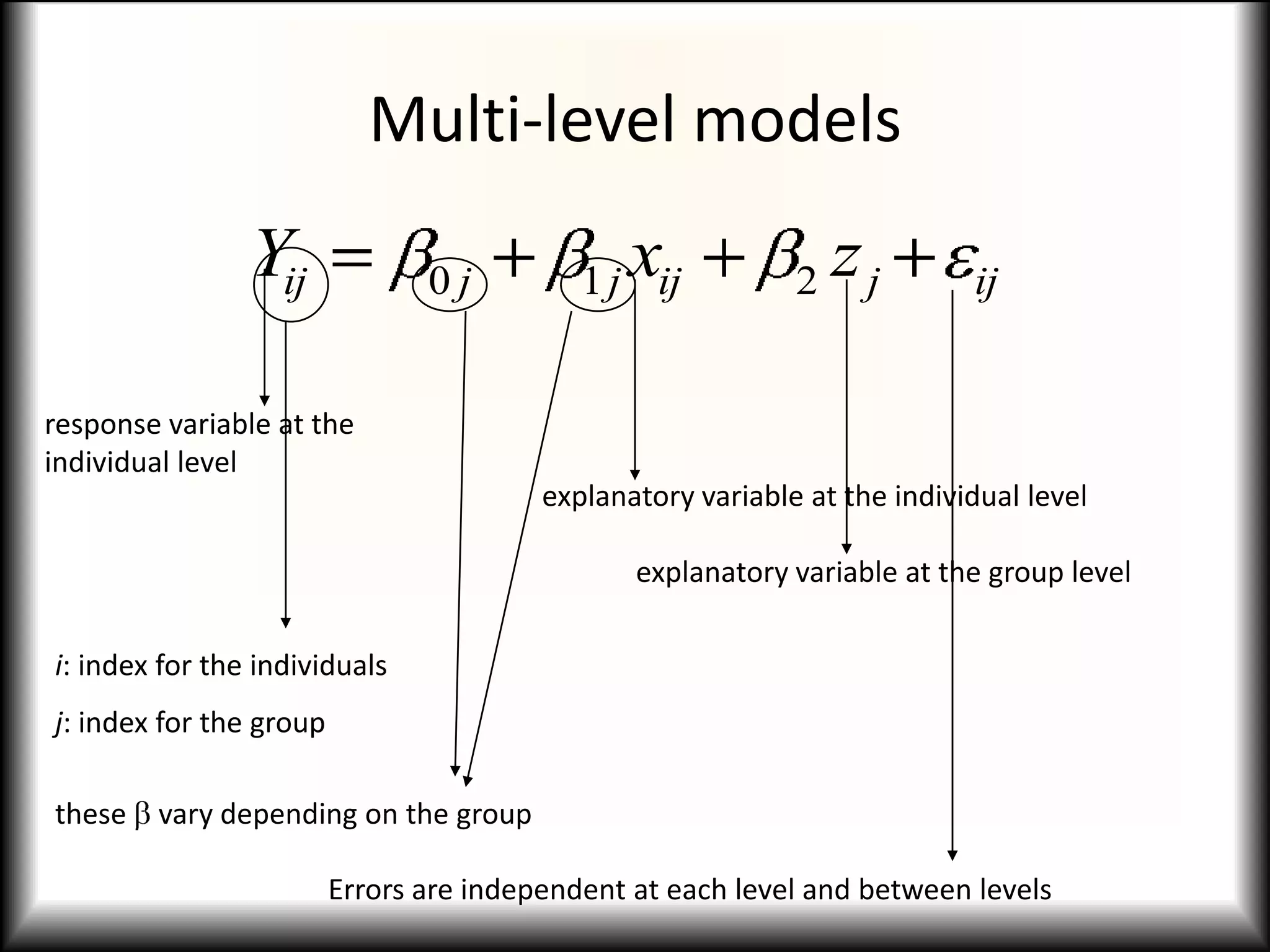
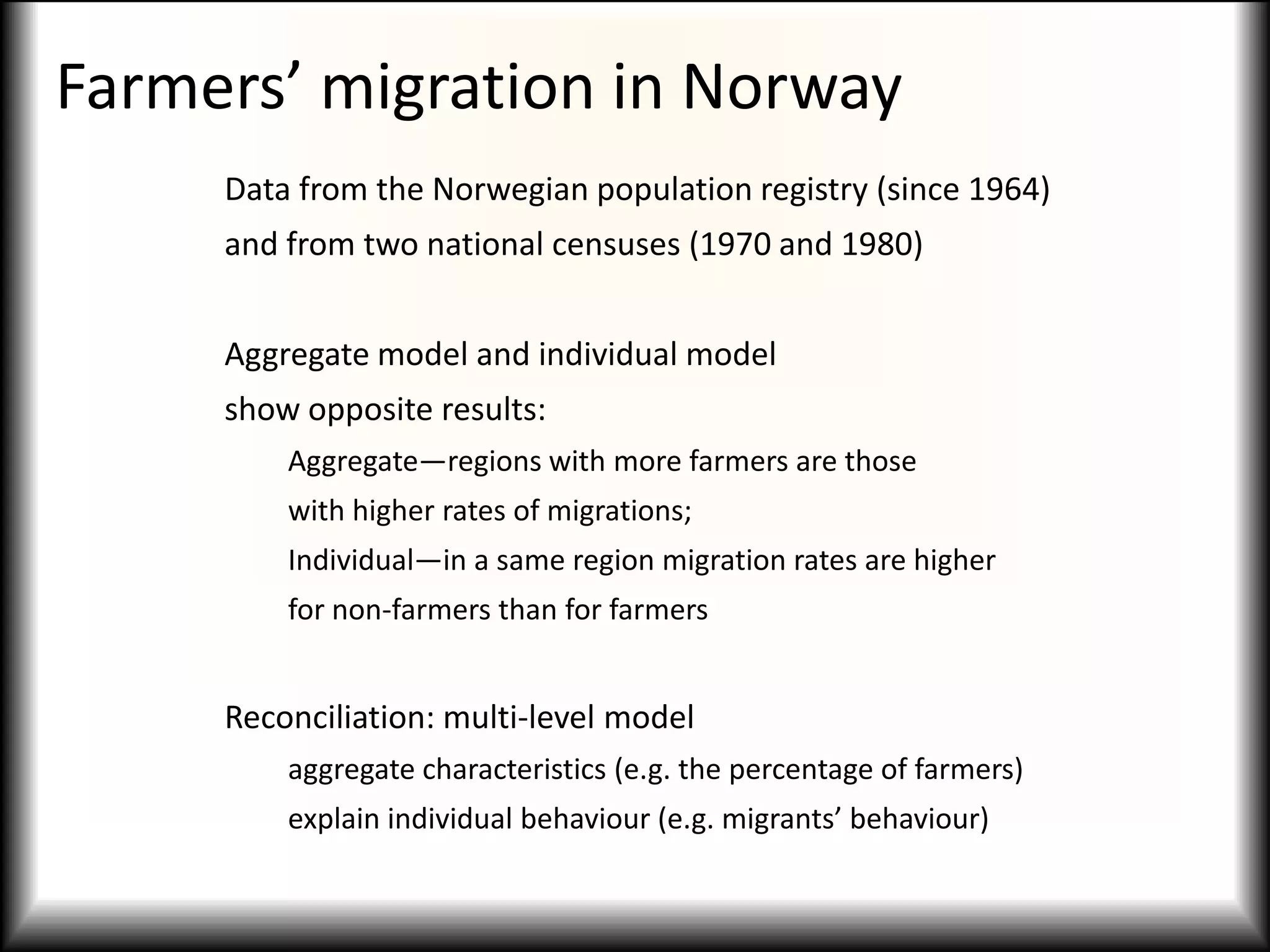
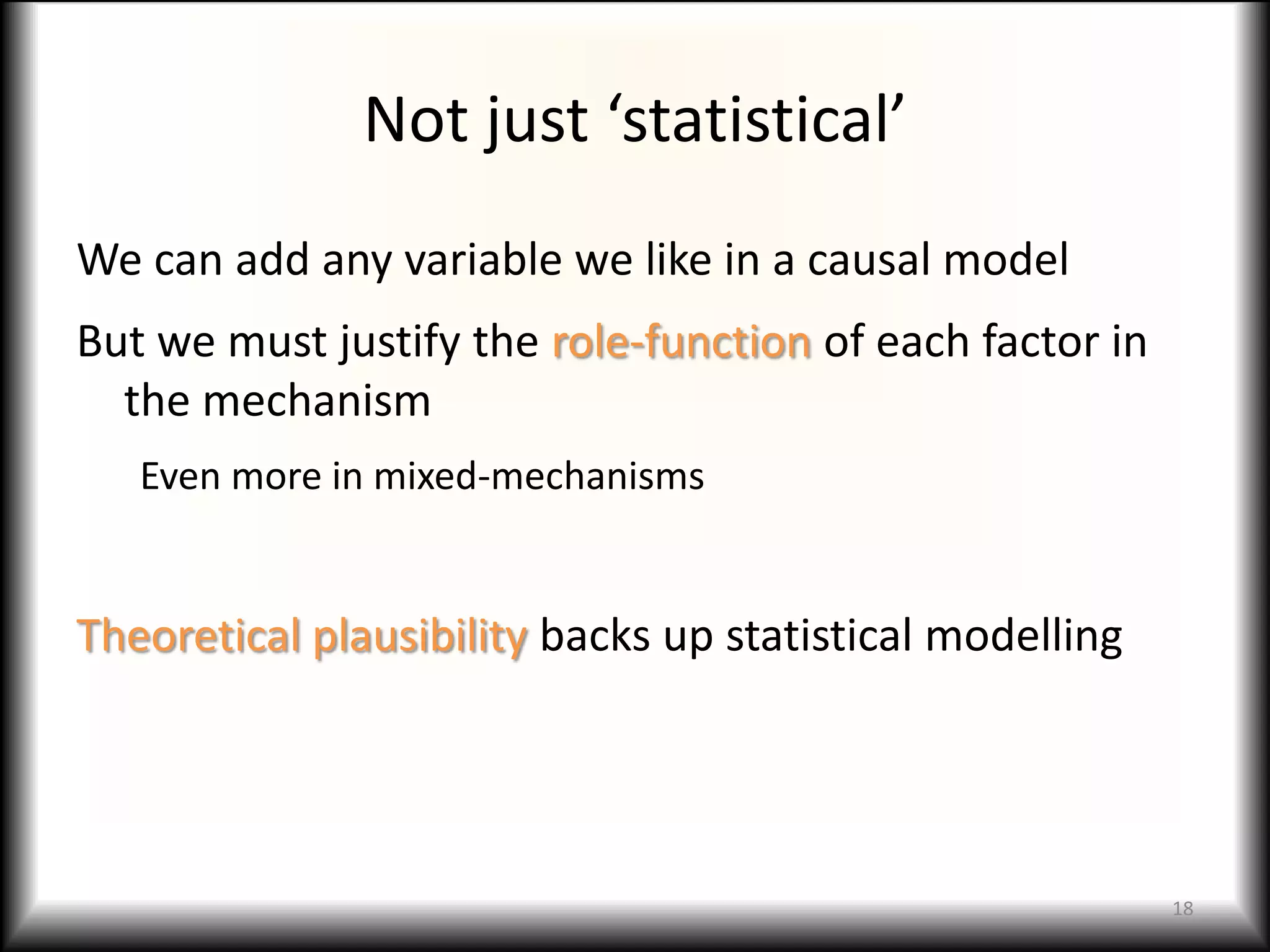
This document discusses causal models and their use in social science research. It covers several key topics:
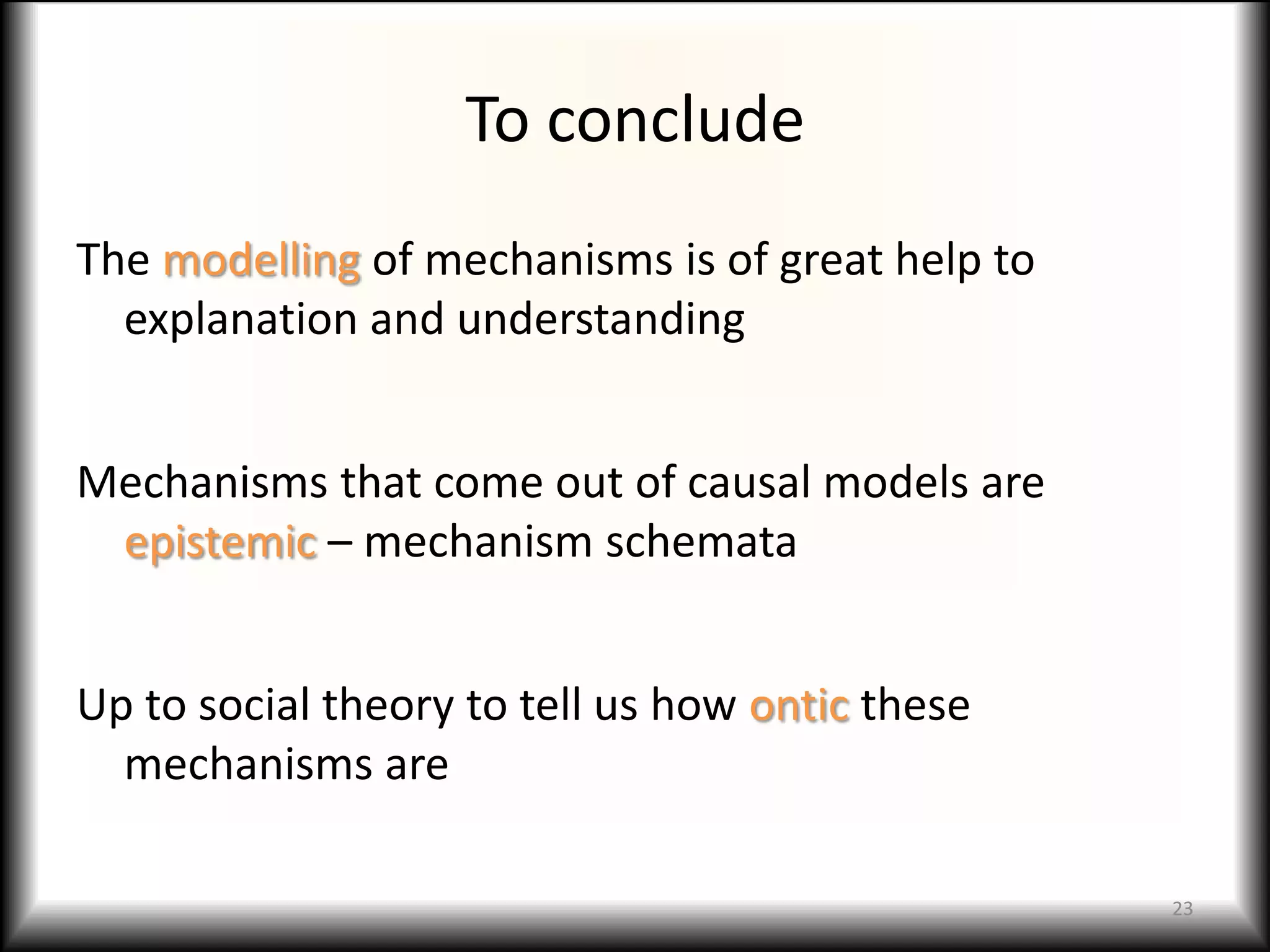
1) Causal models are used to explain social phenomena by modeling causal mechanisms. They involve defining variables, structuring relationships, and testing models.
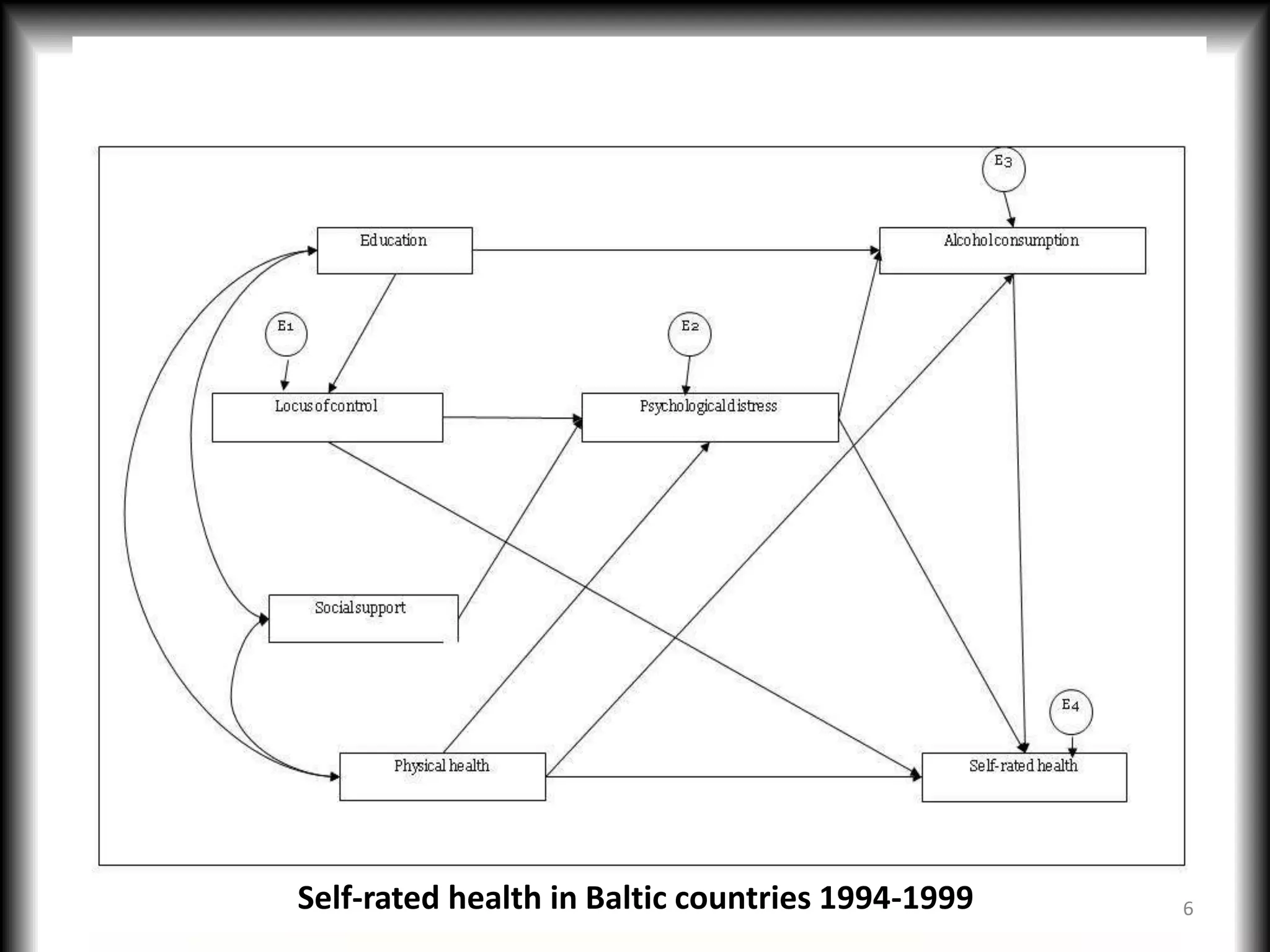
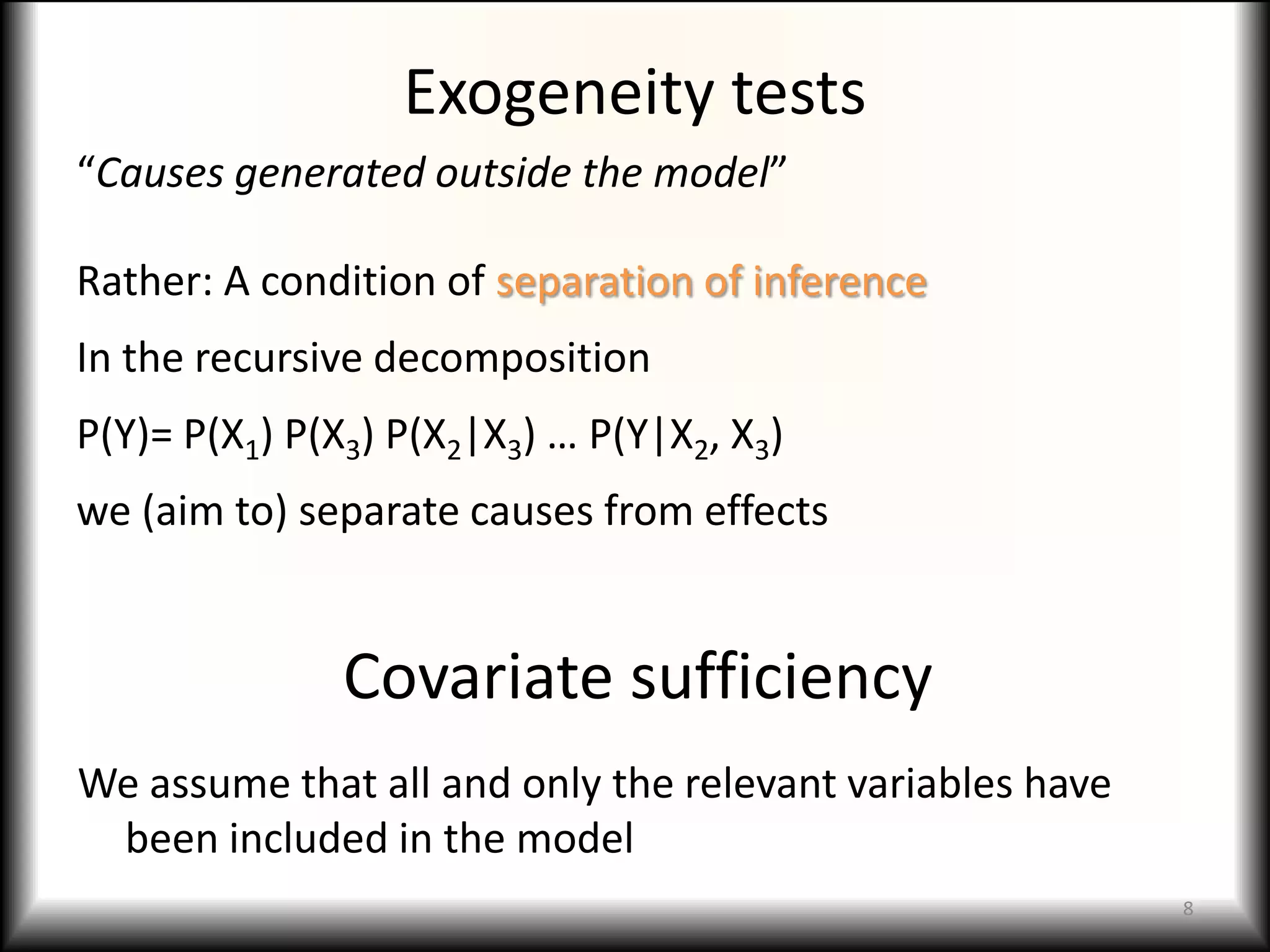
2) Causal models differ from systemic models in their treatment of exogeneity and covariate sufficiency. Multi-level models address social hierarchies by including individual and group level variables.
3) Mixed mechanism models recognize that multiple social, economic, and psychological factors can interact causally. Theoretical plausibility of relationships is important.
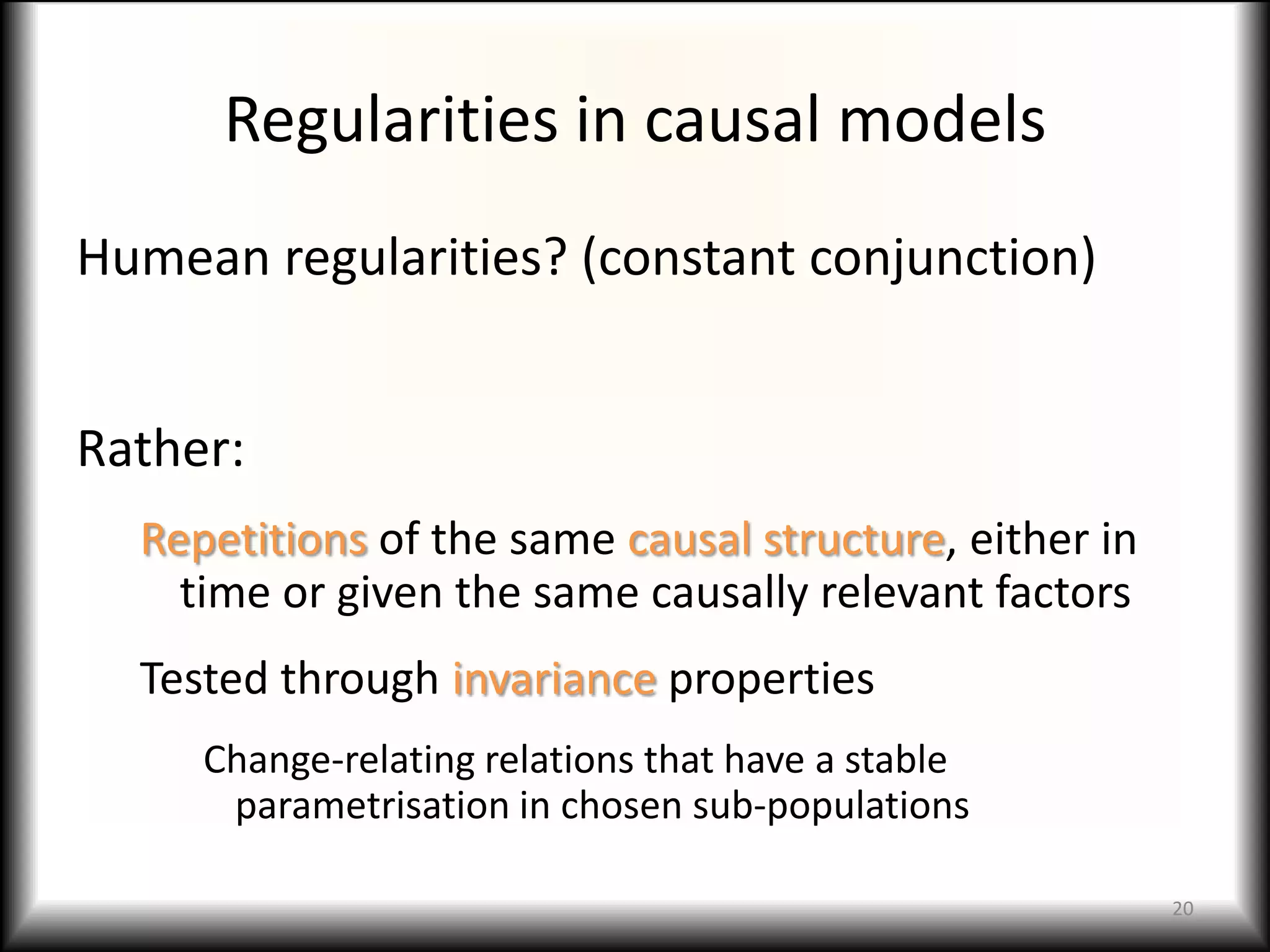
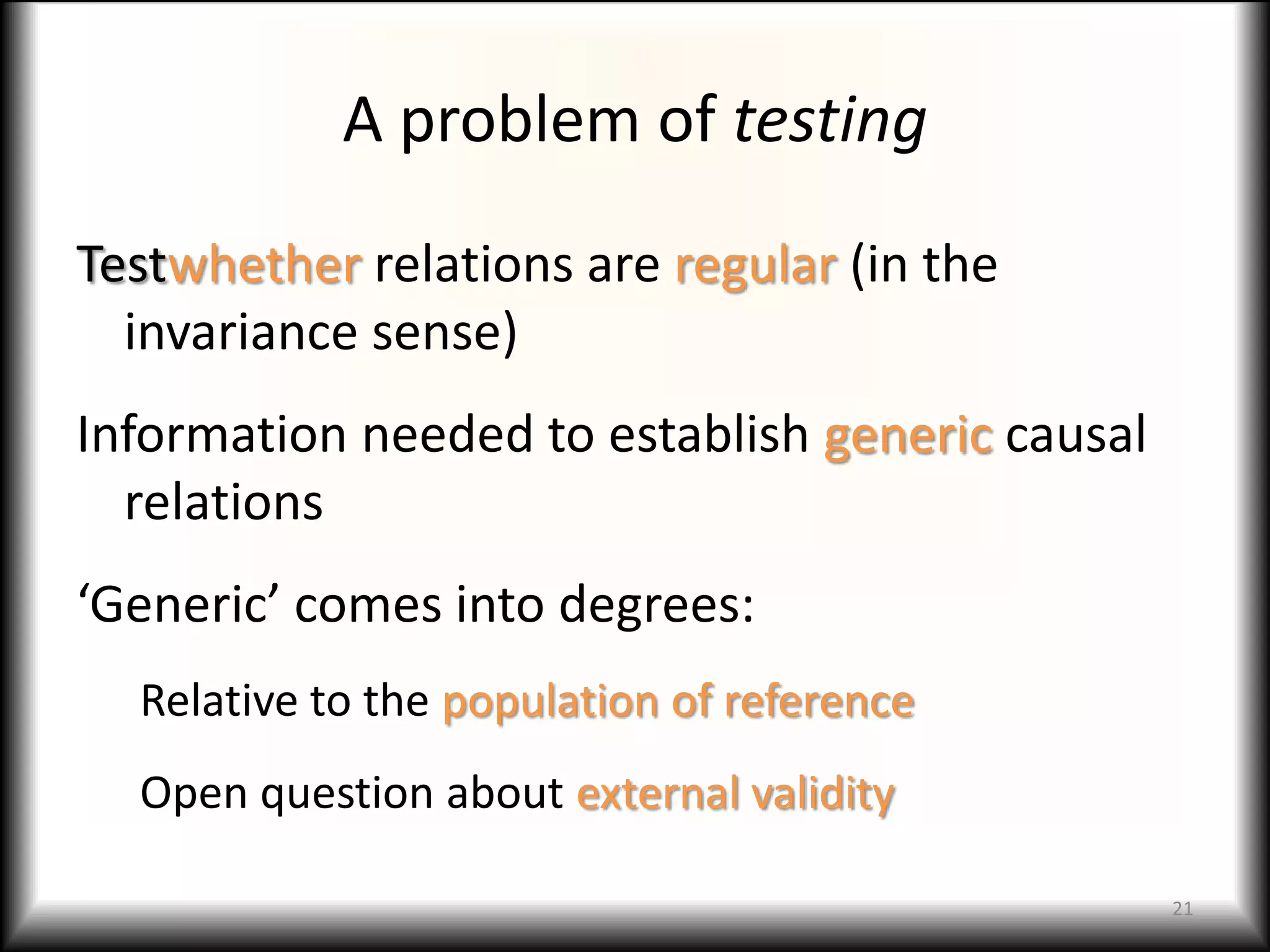
4) Causal relationships in social models may exhibit regularities across time or populations, though testing invariance poses challenges around reference