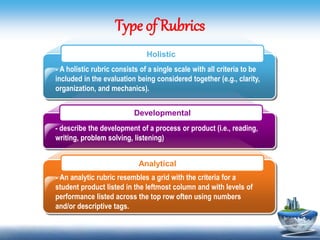
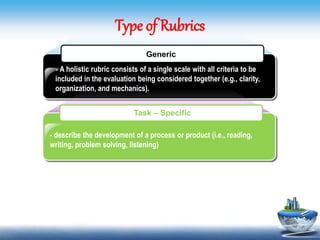
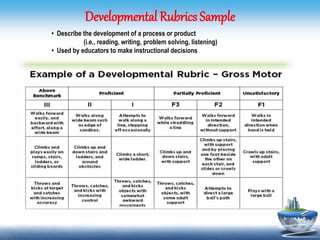
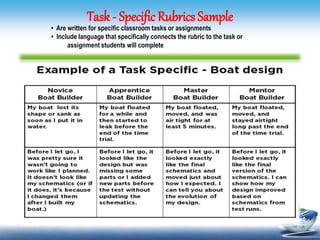
This document discusses different types of rubrics used to evaluate student work. It describes holistic rubrics, which evaluate multiple criteria together on a single scale, developmental rubrics, which assess the progress of a skill or process, and analytic rubrics, which evaluate each criterion separately. The document provides examples of generic rubrics that can be used for various tasks, and task-specific rubrics tailored to a particular assignment. It then shares samples of rubrics that evaluate knowledge, skills, understanding, and the transfer of understanding using rating scales.