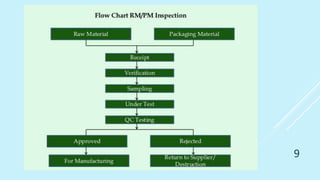
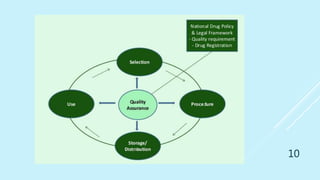
This presentation discusses quality assurance and validation. It defines quality assurance as the totality of arrangements made to ensure pharmaceutical products are fit for their intended use. Validation is establishing evidence that a process will consistently produce products meeting specifications. The presentation covers the need for and types of validation, including validation of analytical methods, equipment, processes, cleaning, and more. It emphasizes validation is important for consistency, reliability, and producing quality products. Documentation for validation includes validation master plans, protocols, reports and standard operating procedures.