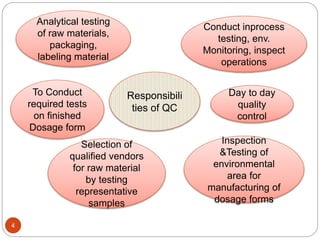
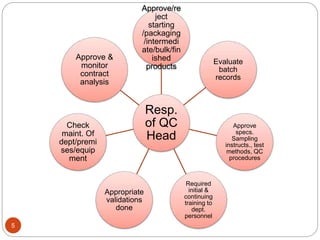
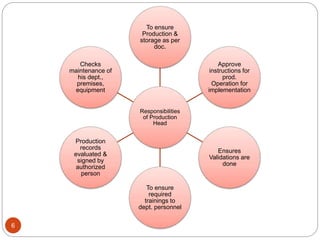
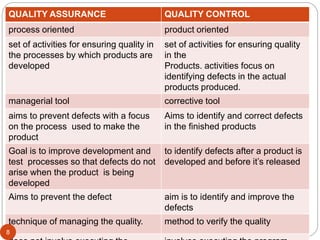
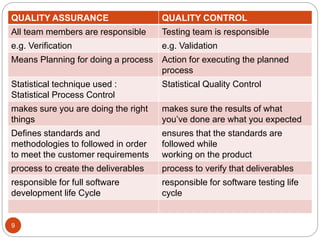
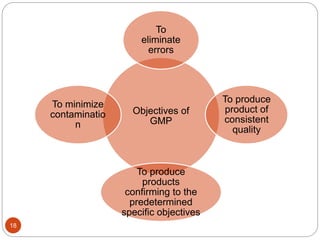
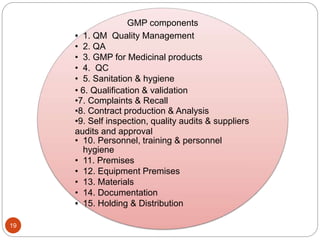
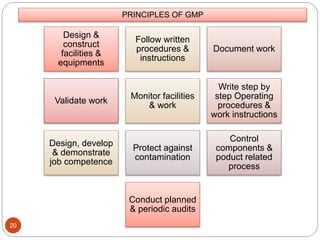
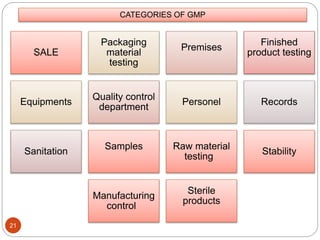
The document defines key concepts in quality assurance, quality control, and good manufacturing practices (GMP) for pharmaceuticals. It discusses that quality assurance is a process-oriented approach to ensuring quality, while quality control is a product-oriented approach focused on identifying defects. GMP involves all aspects of pharmaceutical production to minimize risks and ensure quality, safety, and efficacy. It outlines responsibilities for quality control, production, and procedures to verify that medicines meet specifications from raw materials to patient use.