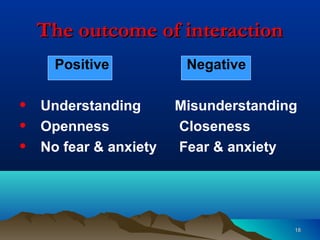
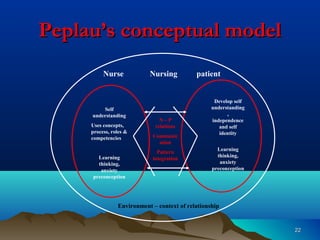
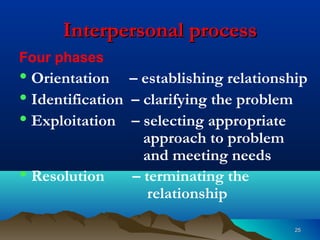
Hildegard Peplau developed the theory of interpersonal relations, which focuses on the nurse-patient relationship. The theory views nursing as an interpersonal process involving interaction between nurse and patient with a common goal. It outlines 4 phases of the nurse-patient relationship: orientation, identification, exploitation, and resolution. When implemented effectively, the theory aims to help patients learn and grow through improved communication and understanding between nurse and patient.