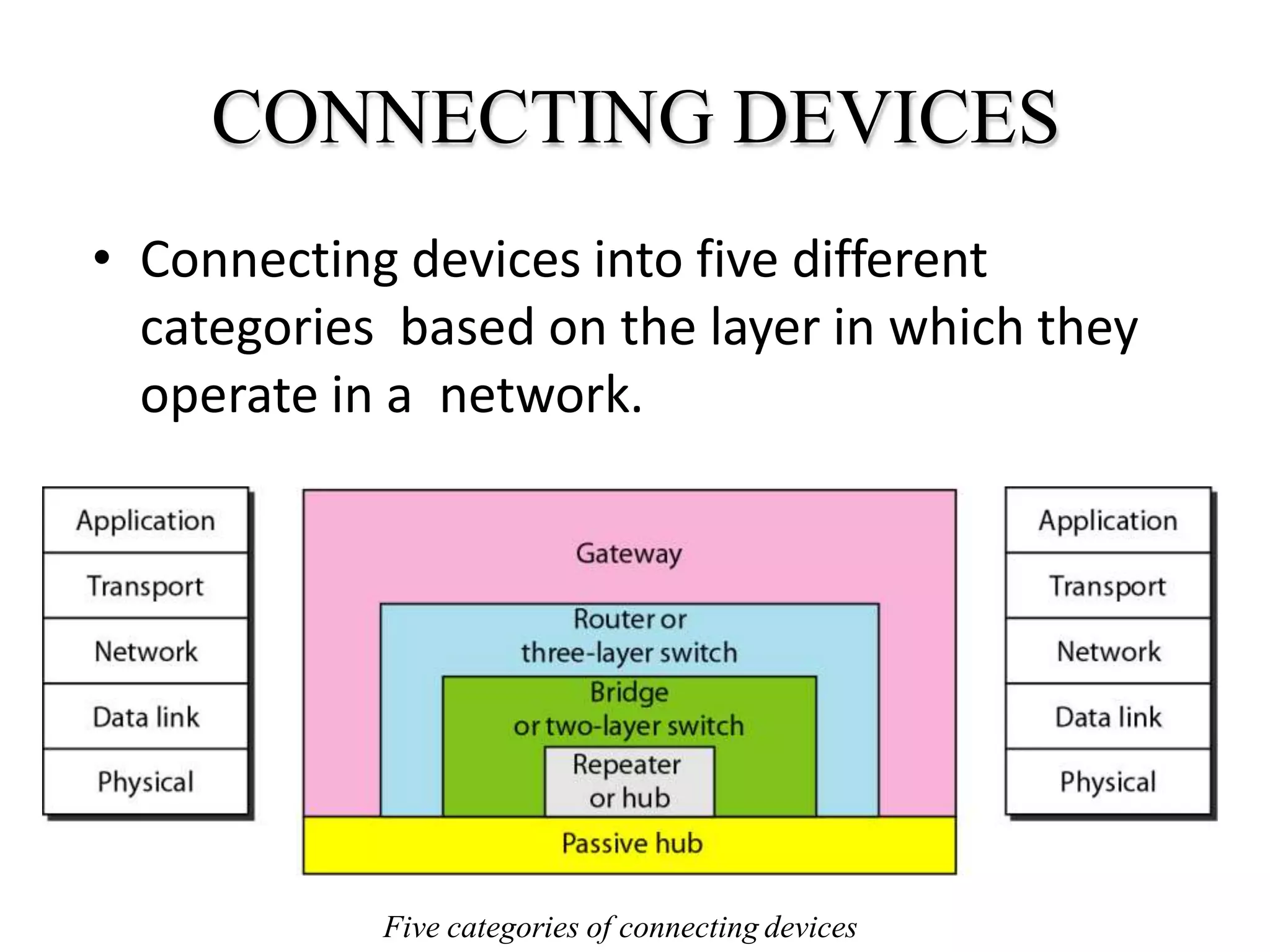
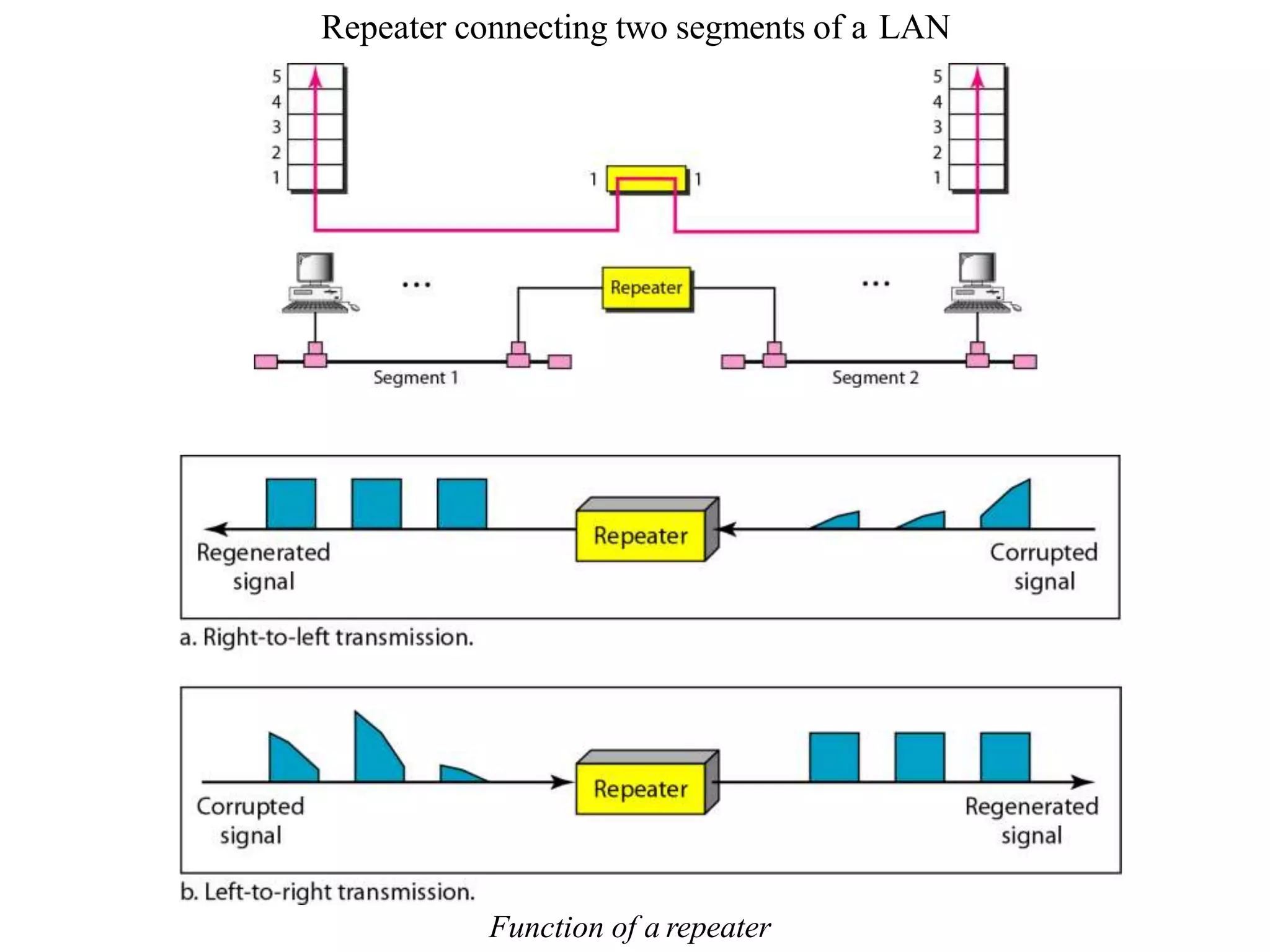
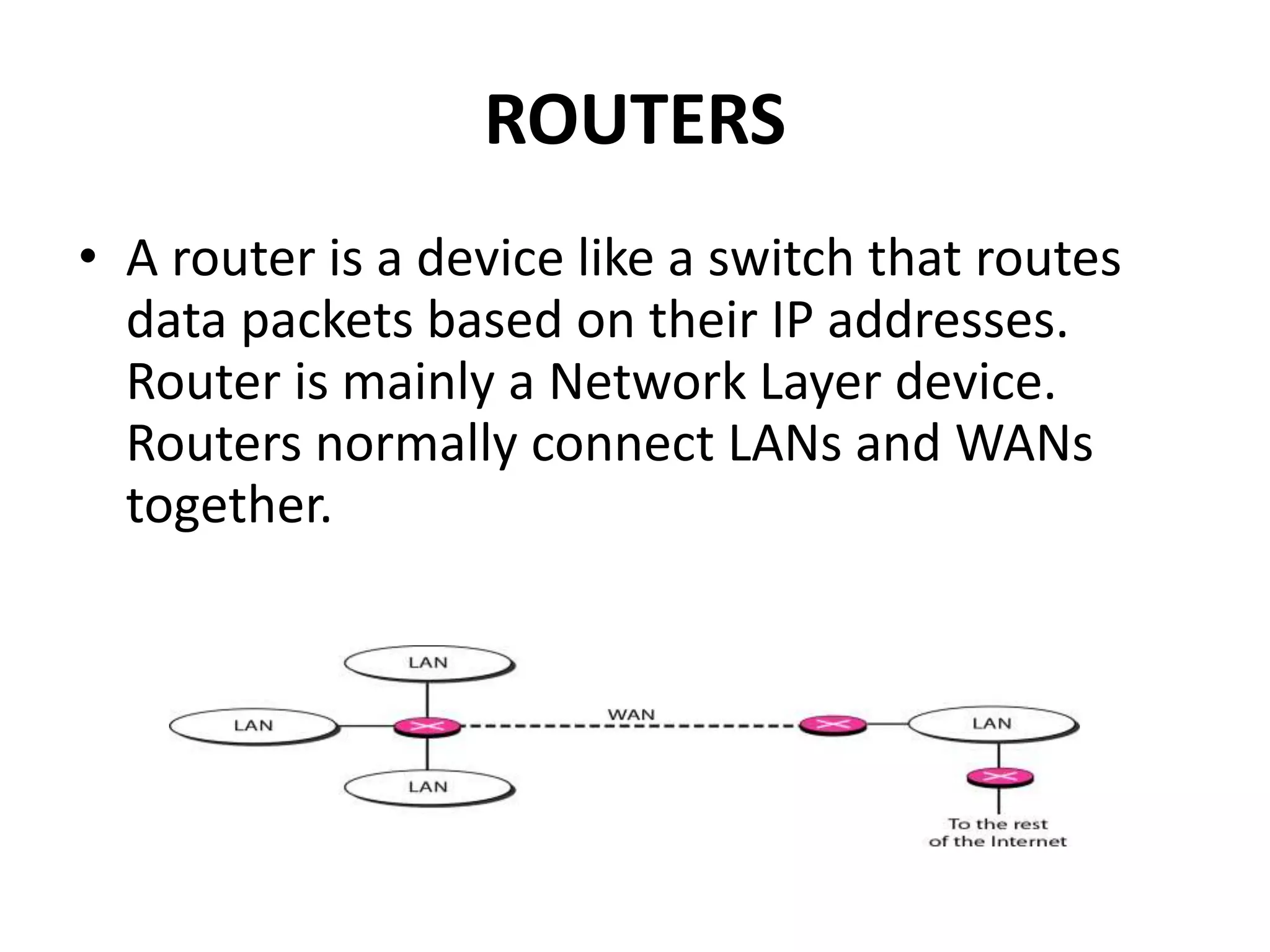
Network devices operate at different layers and perform different functions to connect hardware on a computer network. They include hubs, repeaters, bridges, routers, brouters, switches, and gateways. Hubs connect multiple devices but don't filter data. Repeaters regenerate weak signals to extend transmission distances without amplifying signals. Bridges filter traffic between local area networks by MAC address. Routers route packets between networks using IP addresses. Brouters combine bridging and routing. Switches efficiently forward packets to the correct port. Gateways connect networks that use different protocols.