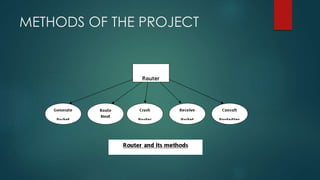
This document describes a routing simulator project. It discusses the existing systems for routing, their drawbacks, and a proposed new system. The proposed system would simulate a network topology with routers and links. It would display statistics for each router like efficiency and packet size. Failed or down links and routers would be highlighted. The routing would be controlled by a speed controller and statistics recalculated every 500 milliseconds. The goals are to select optimal routes, function with low overhead, and quickly adapt to network changes. The project uses Java tools like the Java Development Kit and compiler to develop the simulator.