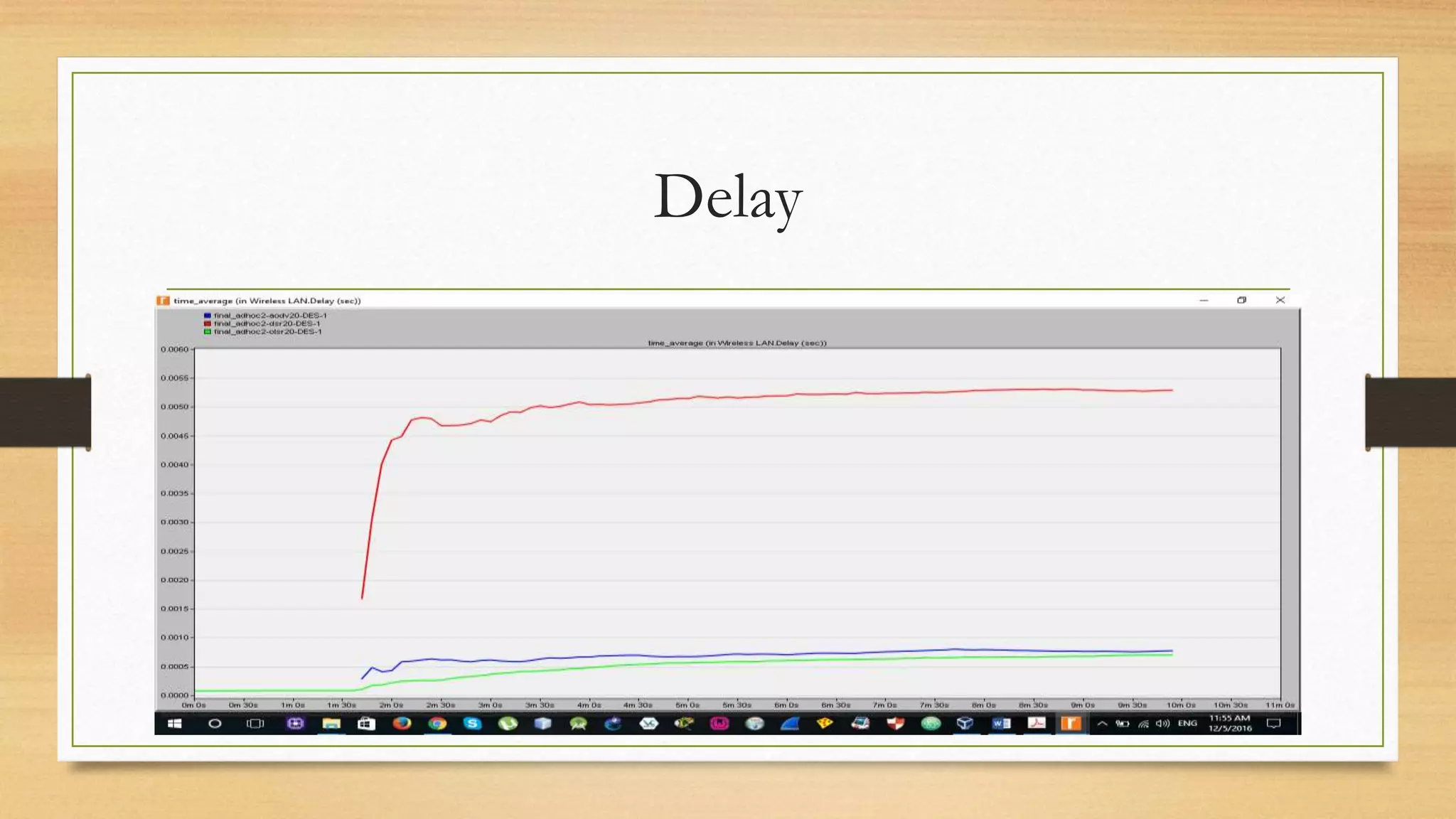
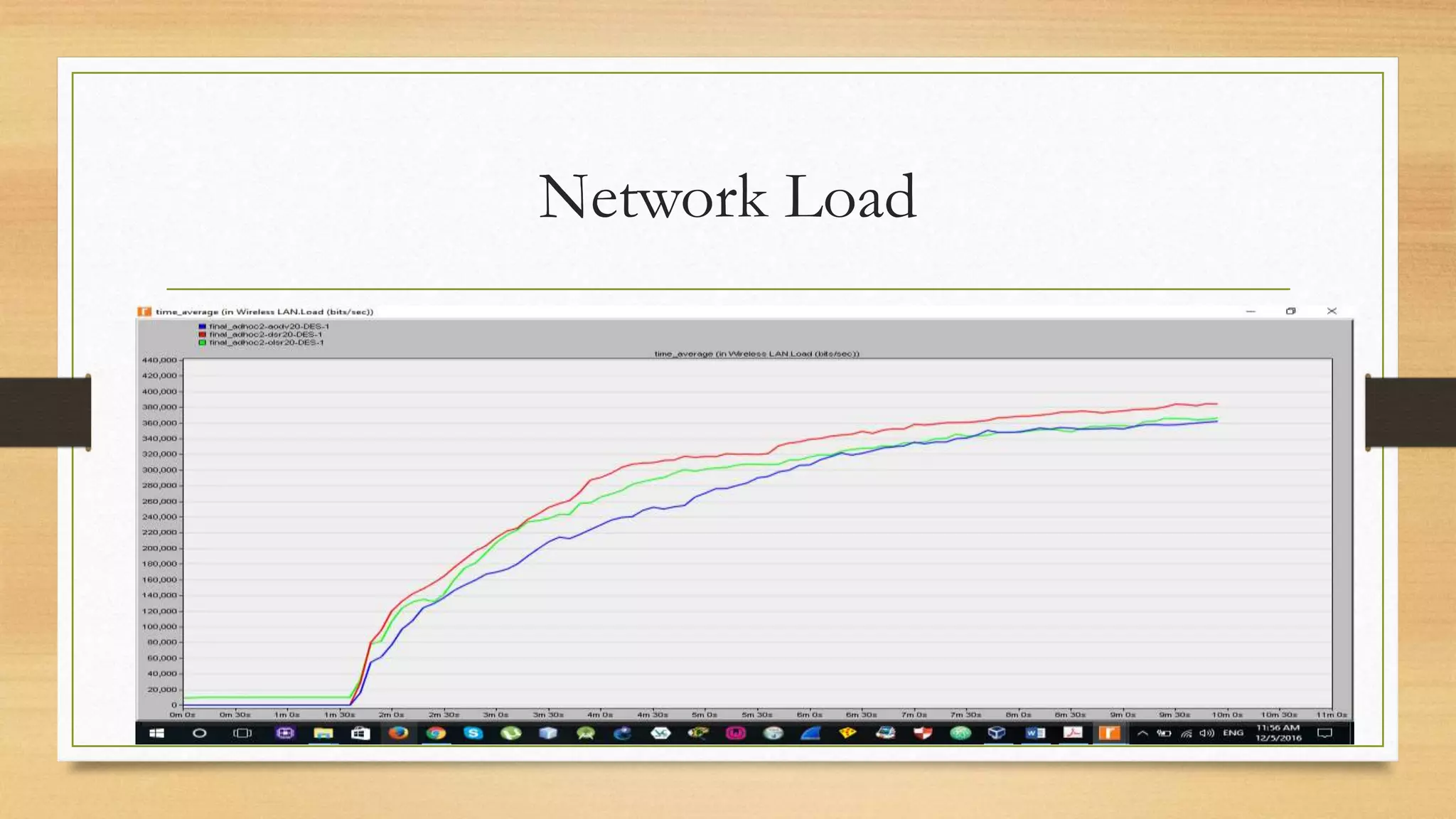
The document discusses Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (MANETs), characterized by decentralized, self-configuring mobile devices that communicate wirelessly with rapidly changing topologies. It explores different types of ad-hoc networks like VANETs and various routing protocols such as DSR, AODV, and OLSR, highlighting their advantages and challenges. The findings indicate that OLSR provides the lowest end-to-end delay and highest throughput compared to the other protocols analyzed.




![Ad-hoc Characteristics and challenges
Characteristics Challenges
Peer-to-peer Bandwidth [ capacity links]
Auto configured Dynamic Topologies [any node can join/leave at
any time]
Multi-hop Energy-constrained [Battery]
Zero-administration Limited Physical security [catch poisoning]
Dynamic Scalability [memory search time, processing]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/manet-171227110111/75/Manet-6-2048.jpg)