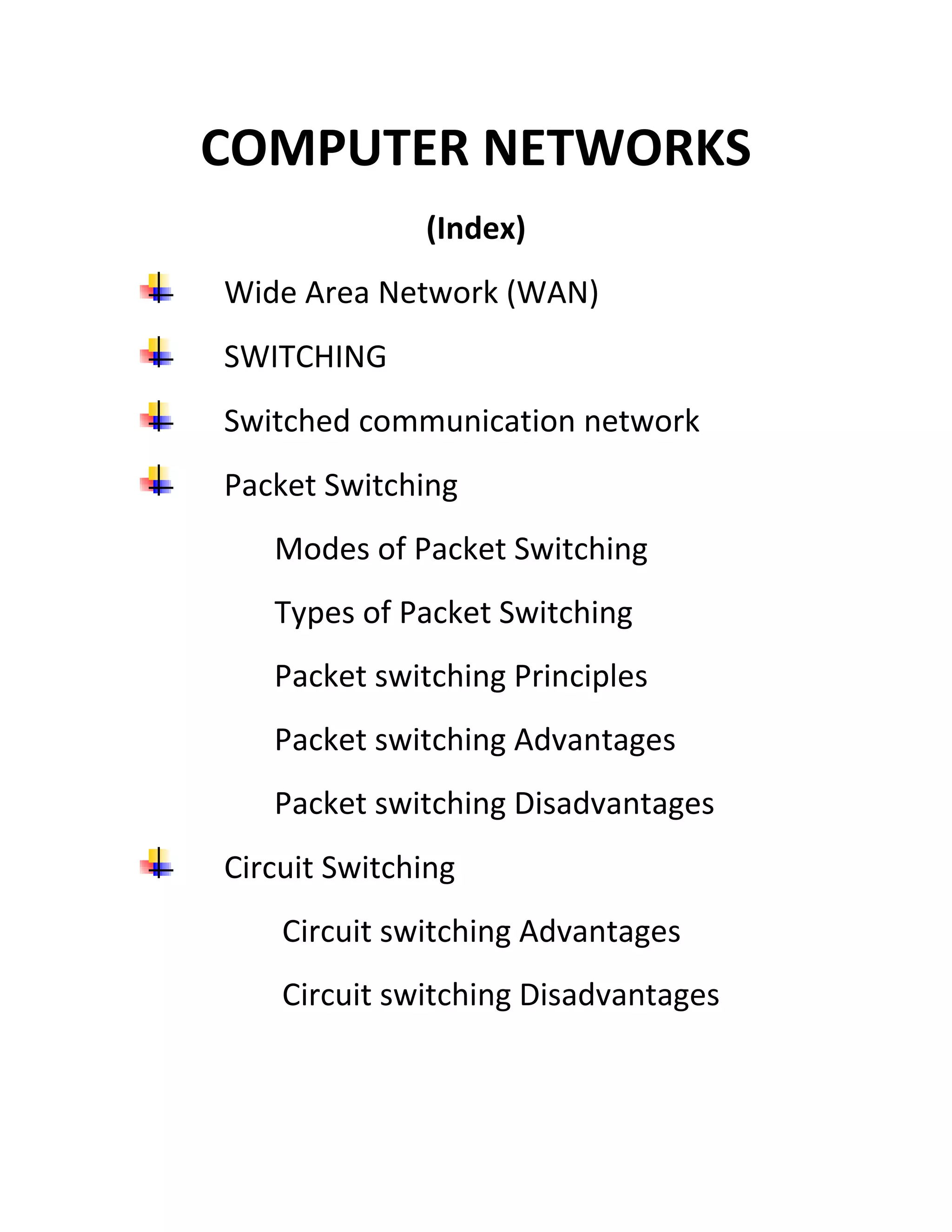
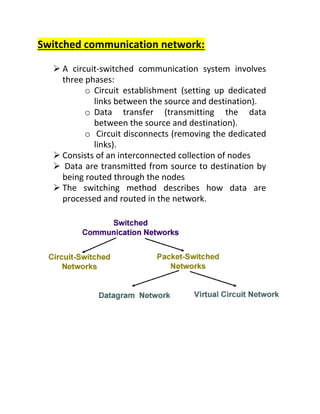
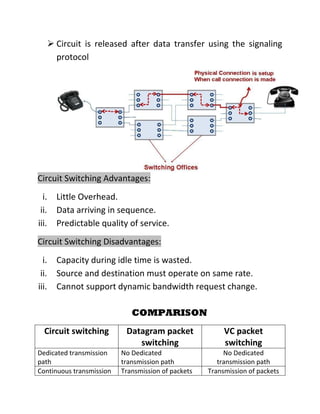
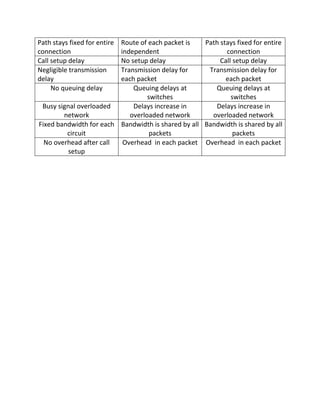
Wide area networks connect smaller networks over large geographical areas. Packet switching is the dominant switching method used, breaking data into packets that are routed independently to their destination. There are two main types of packet switching: connection-oriented uses virtual circuits to establish dedicated paths for packets to follow, while connectionless treats each packet independently without pre-establishing paths. Packet switching provides more efficient use of network bandwidth compared to circuit switching.