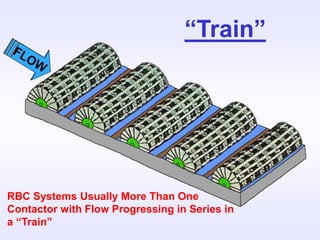
This document provides an overview of the rotating biological contactor (RBC) wastewater treatment process. RBC systems use disks mounted on a rotating shaft that are covered with microorganisms. As the disks rotate, wastewater flows over the surface where microorganisms consume organic matter. Key aspects of RBC systems discussed include components, media design, loadings, flow schemes, advantages like low energy use, and disadvantages like limited controls. Diagrams illustrate system configurations, load calculations, and process flow.