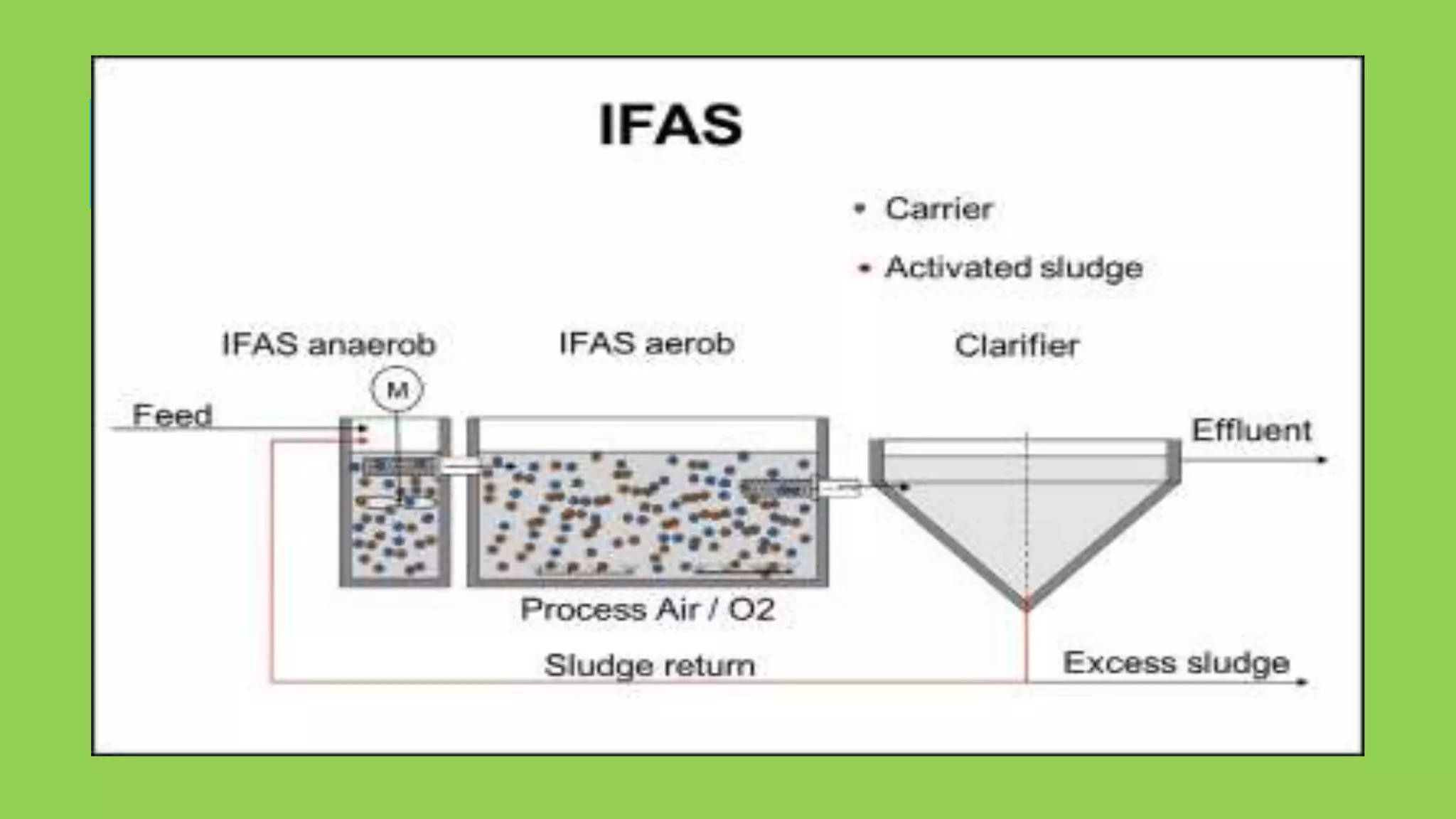
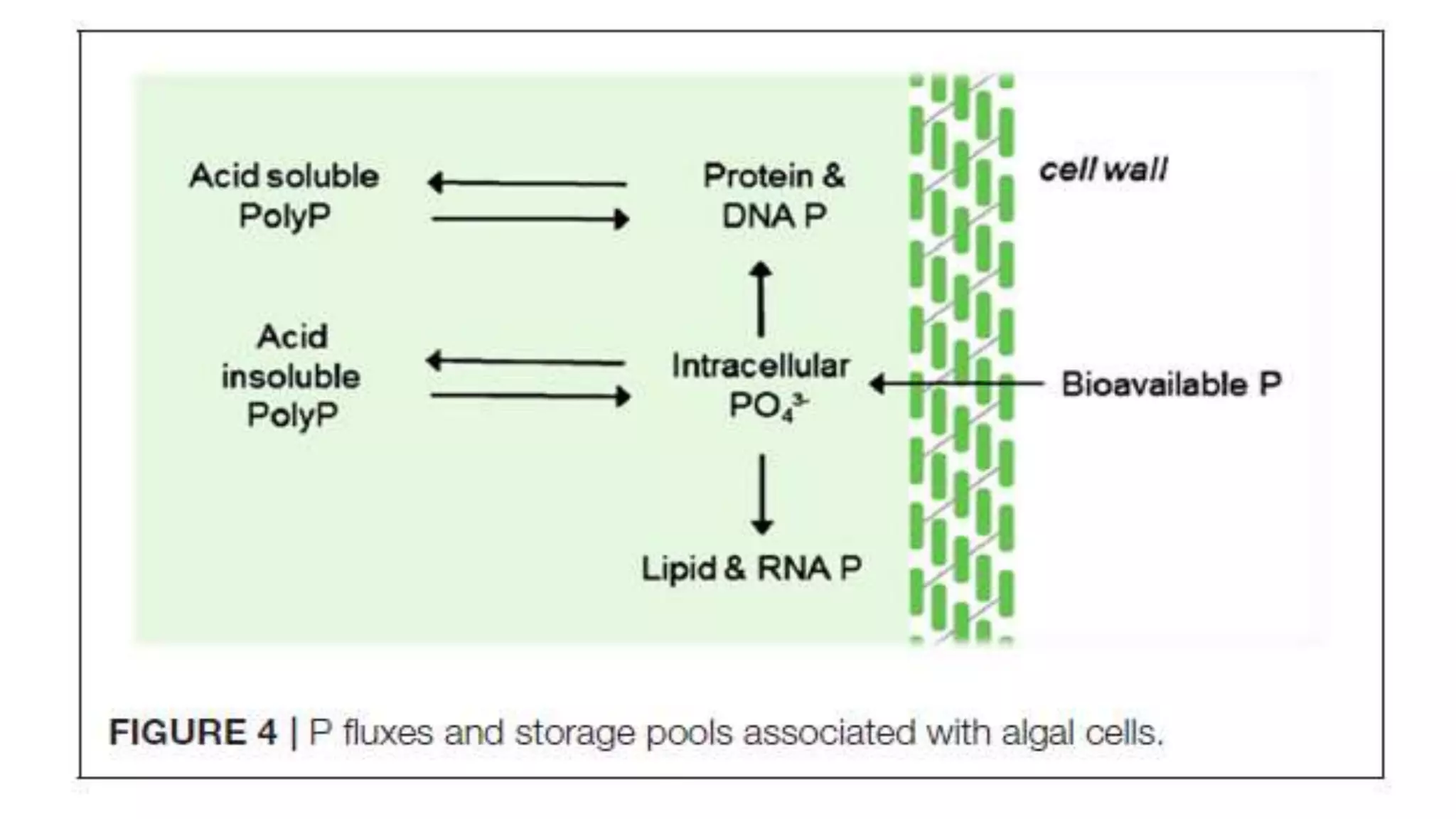
The document discusses biological phosphorus removal (BPR) in wastewater treatment, highlighting the environmental impacts of phosphorus and nitrogen in effluents. It emphasizes enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) processes as a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to chemical treatments, with specific microorganisms, particularly polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs), playing crucial roles in phosphorus uptake. Various treatment processes like integrated fixed film activated sludge and moving bed biofilm reactors are discussed, along with innovations using algal systems for effective phosphorus removal.