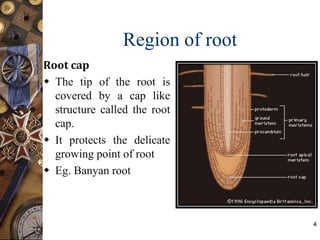
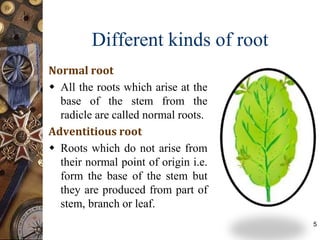
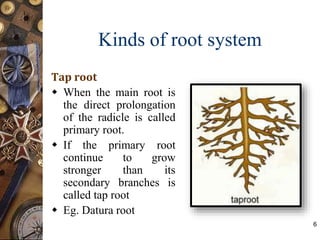
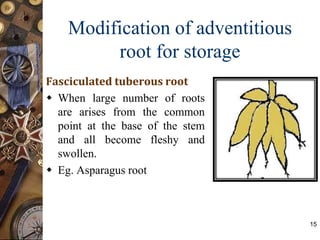
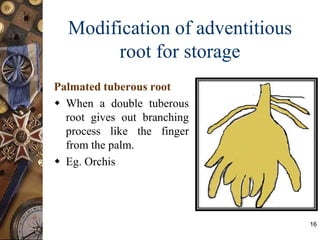
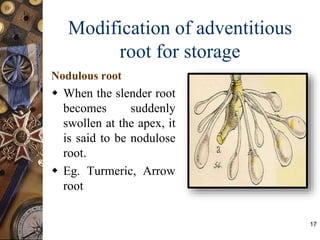
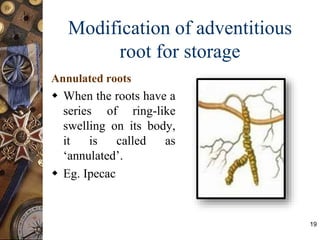
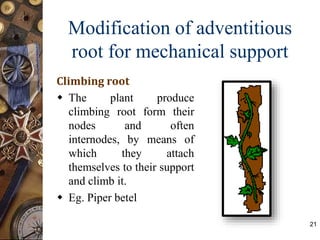
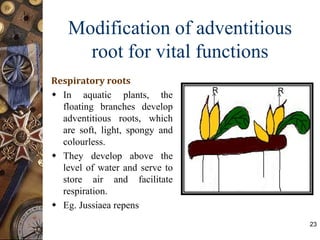
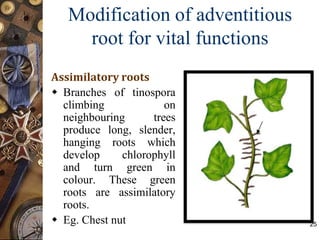
This document discusses the morphology and modifications of plant roots. It begins by defining morphology and describing the basic structure and functions of roots. It then discusses different root types including tap roots, fibrous roots, and adventitious roots. The document focuses on various modifications of roots for storage, respiration, mechanical support, and other vital functions. Examples are provided for different root modifications like tuberous roots, stilt roots, haustoria, and assimilatory roots. Key morphological features and functions of roots are summarized along with example questions asked in previous examinations.