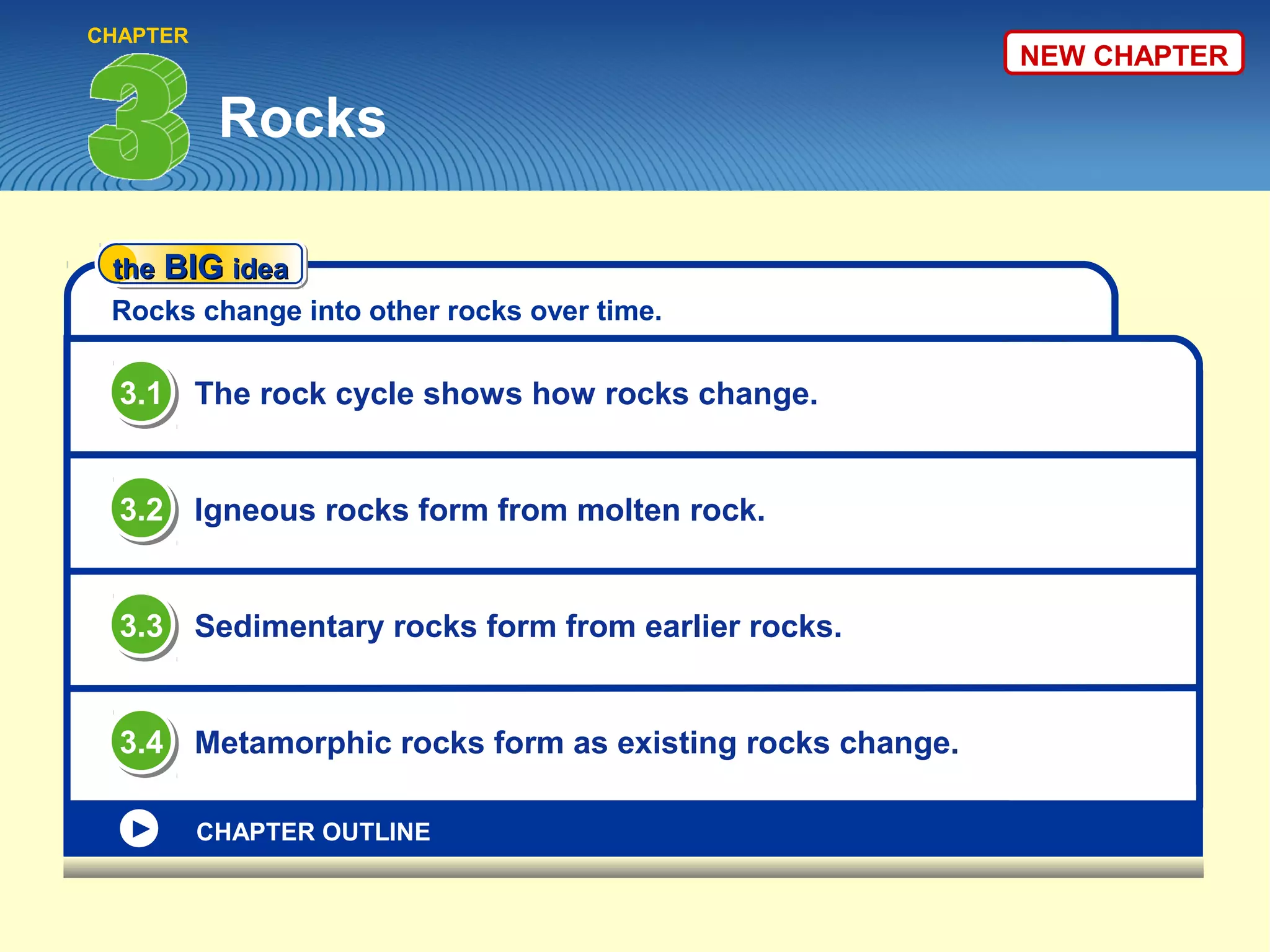
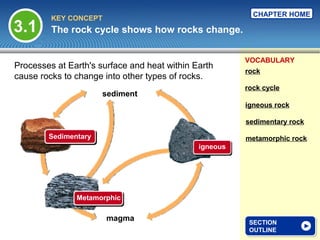
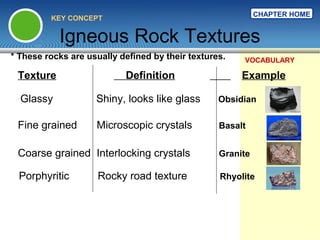
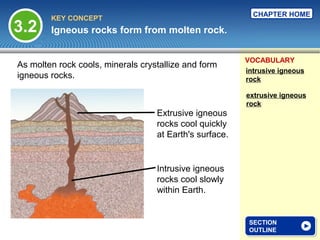
The document provides an overview of the rock cycle, detailing how different types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—are formed and transformed over time. It explains the processes involved in the transformation, including cooling of molten rock for igneous rocks, the sedimentation and cementation for sedimentary rocks, and the effects of heat and pressure for metamorphic rocks. Key concepts include the formation mechanisms, textures, and classifications of these rock types.